Life Functions – Literacy Chart Vocabulary Term Book/internet
... Self-sustaining or self-nourishing organisms that have the ability to synthesize their own food from inorganic materials, e.g. carbon dioxide and nitrogen. ...
... Self-sustaining or self-nourishing organisms that have the ability to synthesize their own food from inorganic materials, e.g. carbon dioxide and nitrogen. ...
Respiratory System WS Answer the following questions. What are
... The dome-shaped muscle that helps move air in and out of the body is the ...
... The dome-shaped muscle that helps move air in and out of the body is the ...
Chapter 5 Lecture Notes
... 1. Light causes chlorophyll to give up electrons. Energy released from the transfer of electrons of chlorophyll through a system of carrier molecules via an electron transport chain is used to generate ATP and NADPH. 2. ATP and NADPH are then used to synthesize organic molecules from CO2 and H2O. (C ...
... 1. Light causes chlorophyll to give up electrons. Energy released from the transfer of electrons of chlorophyll through a system of carrier molecules via an electron transport chain is used to generate ATP and NADPH. 2. ATP and NADPH are then used to synthesize organic molecules from CO2 and H2O. (C ...
the Four Stages of Biochemical Energy Production
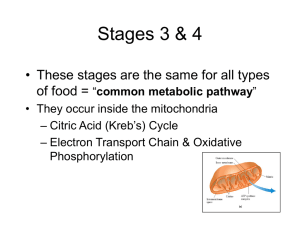
... Citric acid cycle – For every glucose, two acetyl groups enter the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) • Each two-carbon acetyl group combines with a fourcarbon compound • Two CO2 molecules are removed (why is this important?) • Energy captured as 1 ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2 form from each acetyl group ...
... Citric acid cycle – For every glucose, two acetyl groups enter the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) • Each two-carbon acetyl group combines with a fourcarbon compound • Two CO2 molecules are removed (why is this important?) • Energy captured as 1 ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2 form from each acetyl group ...
Interiorscaping - Metropolitan Community College
... Medium Light Plants Dracaena Ribbon Plant Swedish Ivy Arrowhead Vine ...
... Medium Light Plants Dracaena Ribbon Plant Swedish Ivy Arrowhead Vine ...
The Respiratory System - Alexmac
... – Emphysema - Some of the tiny alveoli collapse reducing the overall surface area for breathing to occur. – Chronic bronchitis - permanent swelling of tissues lining the airway leading to pathway narrowing and as a result coughing and breathlessness. ...
... – Emphysema - Some of the tiny alveoli collapse reducing the overall surface area for breathing to occur. – Chronic bronchitis - permanent swelling of tissues lining the airway leading to pathway narrowing and as a result coughing and breathlessness. ...
Metabolism: the chemical reactions of a cell
... In allosteric site, inhibitor is not reacted, but causes a shape change in the protein. The substrate no longer fits in the active site, so it is not chemically changed either. ghs.gresham.k12.or.us/.../ noncompetitive.htm ...
... In allosteric site, inhibitor is not reacted, but causes a shape change in the protein. The substrate no longer fits in the active site, so it is not chemically changed either. ghs.gresham.k12.or.us/.../ noncompetitive.htm ...
Ecology - Lamar County School District
... (the sun is this source for all life on earth) 2) there must be living organisms that can convert the energy into organic compounds (plants--Autotrophs--photosynthesis) 3) there must be a Recycling of materials between organisms and the environment. A balanced aquarium is an example of a very sm ...
... (the sun is this source for all life on earth) 2) there must be living organisms that can convert the energy into organic compounds (plants--Autotrophs--photosynthesis) 3) there must be a Recycling of materials between organisms and the environment. A balanced aquarium is an example of a very sm ...
A Process to Use Food
... Cellular Respiration is a gas exchange process by which plants release carbon dioxide and let oxygen into their cells. Water enters and leaves the cells in the leaves through the guard cells. When they absorb water they swell, opening the stoma (which lets in carbon dioxide and lets out water vapo ...
... Cellular Respiration is a gas exchange process by which plants release carbon dioxide and let oxygen into their cells. Water enters and leaves the cells in the leaves through the guard cells. When they absorb water they swell, opening the stoma (which lets in carbon dioxide and lets out water vapo ...
CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OF LIFE
... called monomers join together to form polymers. This is called polymerization. • The millions of carbon containing compounds are classified into four groups of organic compounds: carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. ...
... called monomers join together to form polymers. This is called polymerization. • The millions of carbon containing compounds are classified into four groups of organic compounds: carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. ...
56 kb - Mahopac Central School District
... f. life has progressed, from the simple to the complex, over geologic time 1) the ancestors of most modern species had simpler structures than those of their descendants B. The world presents living things with a constantly changing environment – to survive, organisms must be able to respond and adj ...
... f. life has progressed, from the simple to the complex, over geologic time 1) the ancestors of most modern species had simpler structures than those of their descendants B. The world presents living things with a constantly changing environment – to survive, organisms must be able to respond and adj ...
How energy
... • 10 protons will translocate per electron pair passed from NADH to O2. • 3 protons consumed per ATP synthesized. • (1 ATP/4 H+)/(10 H+/electron pair) = 2.5 ATP/electron pair. • No energy will lost or waste! ...
... • 10 protons will translocate per electron pair passed from NADH to O2. • 3 protons consumed per ATP synthesized. • (1 ATP/4 H+)/(10 H+/electron pair) = 2.5 ATP/electron pair. • No energy will lost or waste! ...
TRANSPORT PROCESSES TAKS QUESTIONS SPRING 2003 – 10
... F Photosynthesis produces twice as many ATP molecules as cellular respiration does. G Water is released during photosynthesis and consumed during cellular respiration. H Photosynthesis occurs during the day, and cellular respiration occurs at night. J* Oxygen is produced during photosynthesis and us ...
... F Photosynthesis produces twice as many ATP molecules as cellular respiration does. G Water is released during photosynthesis and consumed during cellular respiration. H Photosynthesis occurs during the day, and cellular respiration occurs at night. J* Oxygen is produced during photosynthesis and us ...
Ecological Principles 2
... lst level carnivore - feeds on herbivores 2nd level carnivore - feeds on 1st level carnivores Decomposers the 'final' consumer group use energy available in dead plants and animals transform organic material into inorganic material Food chains are more often called food webs because no o ...
... lst level carnivore - feeds on herbivores 2nd level carnivore - feeds on 1st level carnivores Decomposers the 'final' consumer group use energy available in dead plants and animals transform organic material into inorganic material Food chains are more often called food webs because no o ...
NAME: : :______ Honors Biology Reading Guide – Chapter 6
... Honors Biology Reading Guide – Chapter 6 Metabolism: energy and Enzymes 6.1 Life and the Flow of Energy 1. How do cells and living thing use energy? ...
... Honors Biology Reading Guide – Chapter 6 Metabolism: energy and Enzymes 6.1 Life and the Flow of Energy 1. How do cells and living thing use energy? ...
EOC Practice
... noticed a steady decline in the presence of field mice and an increase in the number of snakes. Which of these is the MOST LIKELY explanation about why the population size of each animal changed? a) The snakes introduced to the region dominated the habitat, forcing the mice to find another place to ...
... noticed a steady decline in the presence of field mice and an increase in the number of snakes. Which of these is the MOST LIKELY explanation about why the population size of each animal changed? a) The snakes introduced to the region dominated the habitat, forcing the mice to find another place to ...
chem notes unit 2 bk
... -Some are used to form bones and muscles. -Some transport substances into or out of cells, or help to fight disease. -Proteins have 4 levels of organization: 1. Sequence of amino acid in a protein chain. 2. Amino acids within a chain can be twisted or folded. 3. Amino acid is folded. 4. Each chain h ...
... -Some are used to form bones and muscles. -Some transport substances into or out of cells, or help to fight disease. -Proteins have 4 levels of organization: 1. Sequence of amino acid in a protein chain. 2. Amino acids within a chain can be twisted or folded. 3. Amino acid is folded. 4. Each chain h ...
Created by G. Baker www.thesciencequeen.net
... 1. What do all plants have in common? _______________________________________ Click on Photosynthesis in the right hand menu. 2. Plants mostly absorb ________________ and ______________ wavelengths. 3. Within this cell organelle is the chlorophyll that captures the light from the Sun. ______________ ...
... 1. What do all plants have in common? _______________________________________ Click on Photosynthesis in the right hand menu. 2. Plants mostly absorb ________________ and ______________ wavelengths. 3. Within this cell organelle is the chlorophyll that captures the light from the Sun. ______________ ...
Chapter 3 Flash Cards
... The process by which plants and some other organisms use light energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into oxygen and highenergy carbohydrates such as sugars and starches. ...
... The process by which plants and some other organisms use light energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into oxygen and highenergy carbohydrates such as sugars and starches. ...
Glossary of terms
... Atmospheric layer at 15-30km altitude, in which ozone (O3) is at its most concentrated. This layer limits the amount of solar radiation reaching the Earth’s surface. Damage to the ozone layer increases the rate of global warming. ...
... Atmospheric layer at 15-30km altitude, in which ozone (O3) is at its most concentrated. This layer limits the amount of solar radiation reaching the Earth’s surface. Damage to the ozone layer increases the rate of global warming. ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.