AP Biology Review Notes - Gooch
... Three trans membrane proteins that pump hydrogen out of the matrix. There are two carrier molecules that transport electrons between hydrogen pumps. There are thousands of electron transport chains in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Electrons are donated by the electron carriers (NADH and FADH2) t ...
... Three trans membrane proteins that pump hydrogen out of the matrix. There are two carrier molecules that transport electrons between hydrogen pumps. There are thousands of electron transport chains in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Electrons are donated by the electron carriers (NADH and FADH2) t ...
Chp5B - OoCities
... 2. Lipids. 3. Proteins. 4. Nucleic acids. Most polymerization reactions in living organisms are condensation reactions. Polymerization reactions -- Chemical reactions that link two or more small molecules to form larger molecules. Condensation reactions -- Monomers are covalently linked, resulting i ...
... 2. Lipids. 3. Proteins. 4. Nucleic acids. Most polymerization reactions in living organisms are condensation reactions. Polymerization reactions -- Chemical reactions that link two or more small molecules to form larger molecules. Condensation reactions -- Monomers are covalently linked, resulting i ...
Understanding Our Environment
... Stern - Introductory Plant Biology: 9th Ed. - All Rights Reserved - McGraw Hill Companies ...
... Stern - Introductory Plant Biology: 9th Ed. - All Rights Reserved - McGraw Hill Companies ...
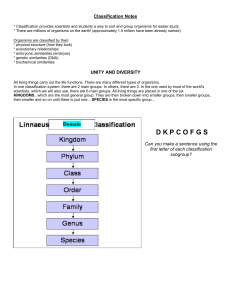
2013 Taxonomy Notes ppt
... All living things carry out the life functions. There are many different types of organisms. In one classification system, there are 2 main groups. In others, there are 3. In the one used by most of the world's scientists, which we will also use, there are 6 main groups. All living things are placed ...
... All living things carry out the life functions. There are many different types of organisms. In one classification system, there are 2 main groups. In others, there are 3. In the one used by most of the world's scientists, which we will also use, there are 6 main groups. All living things are placed ...
Document
... The water molecule “adds” to the doublebonded carbon atoms by placing an H- on one carbon and an –OH group on the other. H ...
... The water molecule “adds” to the doublebonded carbon atoms by placing an H- on one carbon and an –OH group on the other. H ...
Introduction to Plants
... Plants are classified the same way all other living organisms are classified and they all of have scientific names made of a scientific and common name (ex. Quercus alba is a White Oak tree) Historically botanists used the term _________________ while zoologist used the term _____________________, ...
... Plants are classified the same way all other living organisms are classified and they all of have scientific names made of a scientific and common name (ex. Quercus alba is a White Oak tree) Historically botanists used the term _________________ while zoologist used the term _____________________, ...
9 outline bio119 respiration
... – Stage 1-breakdown of large molecules (polysaccharides, lipids, proteins) into their component constituents with the release of little (if any) energy – Stage 2-degradation of the products of stage 1 aerobically or anaerobically to even simpler molecules with the production of some ATP, NADH, and/o ...
... – Stage 1-breakdown of large molecules (polysaccharides, lipids, proteins) into their component constituents with the release of little (if any) energy – Stage 2-degradation of the products of stage 1 aerobically or anaerobically to even simpler molecules with the production of some ATP, NADH, and/o ...
File - Ms. Kenyon`s Class
... work so organisms cannot get much energy! (this is why humans & other organisms need O2!) ...
... work so organisms cannot get much energy! (this is why humans & other organisms need O2!) ...
File
... Hydrogen ions _________________ through the inner membrane through an integral membrane _________________ called ATP Synthase. This complex protein acts as a tiny _________________, turned by the force of the _________________ ions diffusing through it, down their _________________ gradient from the ...
... Hydrogen ions _________________ through the inner membrane through an integral membrane _________________ called ATP Synthase. This complex protein acts as a tiny _________________, turned by the force of the _________________ ions diffusing through it, down their _________________ gradient from the ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ Unit 6, Part 2 Notes – Aerobic Cellular
... b. Cells manage their energy resources to do this work by energy coupling, using an exergonic reaction (one that releases energy) to drive an endergonic one (one that absorbs energy). c. Basically, enzymes catalyze the breakdown of high energy organic molecules to simpler, low energy products. Some ...
... b. Cells manage their energy resources to do this work by energy coupling, using an exergonic reaction (one that releases energy) to drive an endergonic one (one that absorbs energy). c. Basically, enzymes catalyze the breakdown of high energy organic molecules to simpler, low energy products. Some ...
Microscopy
... • 5 decline phase - deaths exceed multiplication • 6 exponential decline phase - maximal rate of decline, in a period of time half of total number of cell is lost ...
... • 5 decline phase - deaths exceed multiplication • 6 exponential decline phase - maximal rate of decline, in a period of time half of total number of cell is lost ...
KEY CONCEPT Life in an ecosystem requires a
... Primary consumers are herbivores that eat producers. Secondary consumers are carnivores that eat herbivores. Tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat secondary consumers. Omnivores, such as humans that eat both plants and animals, may be listed at different trophic levels in different food chains. ...
... Primary consumers are herbivores that eat producers. Secondary consumers are carnivores that eat herbivores. Tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat secondary consumers. Omnivores, such as humans that eat both plants and animals, may be listed at different trophic levels in different food chains. ...
Cellular Respiration www.AssignmentPoint.com Cellular respiration
... The potential of NADH and FADH2 is converted to more ATP through an electron transport chain with oxygen as the "terminal electron acceptor". Most of the ATP produced by aerobic cellular respiration is made by oxidative phosphorylation. This works by the energy released in the consumption of pyruvat ...
... The potential of NADH and FADH2 is converted to more ATP through an electron transport chain with oxygen as the "terminal electron acceptor". Most of the ATP produced by aerobic cellular respiration is made by oxidative phosphorylation. This works by the energy released in the consumption of pyruvat ...
• The biosphere is that part of the Earth that contains all of its liv
... whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. ...
... whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. ...
Observe Them in Their Native Habitat: Atomic Force
... stromal lamellae; the small amount of space between the stacked grana limits which protein complexes can fit in that region. Photosystem I (PSI) and ATP synthase, both of which have large domains that protrude into the stroma (outside the thylakoid), are found in the nonappressed stromal lamellae. P ...
... stromal lamellae; the small amount of space between the stacked grana limits which protein complexes can fit in that region. Photosystem I (PSI) and ATP synthase, both of which have large domains that protrude into the stroma (outside the thylakoid), are found in the nonappressed stromal lamellae. P ...
The Living World - Mr D`Antoni`s Wonderful World of Science
... A biogeochemical cycle is a set of processes by which an element passes from one environment to the next and eventually returns to its original environment, in an infinite loop of recycling There are two cycles we will be dealing with ◦ Carbon cycle ◦ Nitrogen cycle ...
... A biogeochemical cycle is a set of processes by which an element passes from one environment to the next and eventually returns to its original environment, in an infinite loop of recycling There are two cycles we will be dealing with ◦ Carbon cycle ◦ Nitrogen cycle ...
1) Check off which of the following things that soil does: __X __ Acts
... __X__Humans use soil as a holding facility for solid waste _X___A filter for wastewater _X___Foundation for our cities and towns 2) How long does it take to form a 2 inch layer of topsoil? 500 years 3) The 5 factors of soil formation are Climate, Organisms, Parent material, Topography and Time. 4) W ...
... __X__Humans use soil as a holding facility for solid waste _X___A filter for wastewater _X___Foundation for our cities and towns 2) How long does it take to form a 2 inch layer of topsoil? 500 years 3) The 5 factors of soil formation are Climate, Organisms, Parent material, Topography and Time. 4) W ...
B2 Knowledge Powerpoint
... Anaerobic respiration = respiration without oxygen Glucose is broken down to supply energy to the muscles Releases less energy then aerobic and produces Lactic Acid Amount of blood pumped around the body depends on the stroke volume and the heart rate. Exercise = increase in heart rate and stroke vo ...
... Anaerobic respiration = respiration without oxygen Glucose is broken down to supply energy to the muscles Releases less energy then aerobic and produces Lactic Acid Amount of blood pumped around the body depends on the stroke volume and the heart rate. Exercise = increase in heart rate and stroke vo ...
B2 Knowledge Powerpoint
... Anaerobic respiration = respiration without oxygen Glucose is broken down to supply energy to the muscles Releases less energy then aerobic and produces Lactic Acid Amount of blood pumped around the body depends on the stroke volume and the heart rate. Exercise = increase in heart rate and stroke vo ...
... Anaerobic respiration = respiration without oxygen Glucose is broken down to supply energy to the muscles Releases less energy then aerobic and produces Lactic Acid Amount of blood pumped around the body depends on the stroke volume and the heart rate. Exercise = increase in heart rate and stroke vo ...
NOTES FOR THE MIGHTY PLANTOFE
... A leaf is a plant organ, that is photosynthetic, contains chloroplasts, and is usually thin so light can penetrate. The big three aspects of light and plants. Quality (how good) Quantity (how much) Duration (how long) Photosynthesis: Plants make sugar from sunlight. Light energy is turned into ...
... A leaf is a plant organ, that is photosynthetic, contains chloroplasts, and is usually thin so light can penetrate. The big three aspects of light and plants. Quality (how good) Quantity (how much) Duration (how long) Photosynthesis: Plants make sugar from sunlight. Light energy is turned into ...
Plant Evolution
... What is a plant? Kingdom Plantae includes over 350,000 species of Eukaryotic, multicellular, land dwelling, photosynthesizing organisms. A. What do plants have in common? Chloroplasts (contain chlorophyll-pigment that traps light energy), undergo photosynthesis (CO2 + H2O C6H12O6 + O2), & a cell wal ...
... What is a plant? Kingdom Plantae includes over 350,000 species of Eukaryotic, multicellular, land dwelling, photosynthesizing organisms. A. What do plants have in common? Chloroplasts (contain chlorophyll-pigment that traps light energy), undergo photosynthesis (CO2 + H2O C6H12O6 + O2), & a cell wal ...
Unit Title:
... ENRG1. Identify the reactants, products, and basic purposes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Explain the interrelated nature of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in the cells of photosynthetic organisms. (2.4) ENRG2. Explain the important role that ATP serves in metabolism. (2.5) EN ...
... ENRG1. Identify the reactants, products, and basic purposes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Explain the interrelated nature of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in the cells of photosynthetic organisms. (2.4) ENRG2. Explain the important role that ATP serves in metabolism. (2.5) EN ...
New York State Intermediate Science Review
... The habitat must supply the needs of organisms, such as food, water, temperature, oxygen, and minerals. If the population's needs are not met, it will move to a better habitat, or the population will not survive. An organism's niche is their role in the ecosystem. If a habitat describes where an ...
... The habitat must supply the needs of organisms, such as food, water, temperature, oxygen, and minerals. If the population's needs are not met, it will move to a better habitat, or the population will not survive. An organism's niche is their role in the ecosystem. If a habitat describes where an ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.