Arrangement of the Electrons Chapter 4
... electron was observed from the diffraction pattern created by a stream of electrons. Schrodinger (1926)-Developed an equation that correctly accounts for the wave property of the electron and all spectra of ...
... electron was observed from the diffraction pattern created by a stream of electrons. Schrodinger (1926)-Developed an equation that correctly accounts for the wave property of the electron and all spectra of ...
Introductory Microbiology Chap. 5 Chapter Outlines/Notes I
... Note: Cells use only two kinds of energy: 1) light energy: trapped and used by plants, algae, and some bacteria for photosynthesis and 2) chemical energy: the energy held in the bonds of various chemicals. Cells do not use thermal or electrical energy because they don't have thermal or electrical co ...
... Note: Cells use only two kinds of energy: 1) light energy: trapped and used by plants, algae, and some bacteria for photosynthesis and 2) chemical energy: the energy held in the bonds of various chemicals. Cells do not use thermal or electrical energy because they don't have thermal or electrical co ...
O 2
... only used in cell that produces it only short term energy storage carbohydrates & fats are long term energy storage Whoa! Pass me the glucose & oxygen! ...
... only used in cell that produces it only short term energy storage carbohydrates & fats are long term energy storage Whoa! Pass me the glucose & oxygen! ...
Quiz 7 Name: 1. After ATP fuels the Na+/K+ pump at the cell
... C) NADH has more energy than NAD+. D) NADH can transfer electrons into the mitochondrial electron transport chain. 8. Cellular respiration harvests the most chemical energy from which of the following? A) glycolysis B) fermentation C) generating carbon dioxide and oxygen in the mitochondrial electro ...
... C) NADH has more energy than NAD+. D) NADH can transfer electrons into the mitochondrial electron transport chain. 8. Cellular respiration harvests the most chemical energy from which of the following? A) glycolysis B) fermentation C) generating carbon dioxide and oxygen in the mitochondrial electro ...
Plant Test Name________________
... 2. Plants that live for only one year - _____________________________ 3. The process through which plants make food - _____________________________ 4. To make more of the same kind of living thing - ____________________________ 5. Trees that lose their leaves in winter - ____________________________ ...
... 2. Plants that live for only one year - _____________________________ 3. The process through which plants make food - _____________________________ 4. To make more of the same kind of living thing - ____________________________ 5. Trees that lose their leaves in winter - ____________________________ ...
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... Electrons carried to the inner membrane by NADH and FADH are dropped off at the beginning As the electrons are passed along, their energy is used to pump H+ ions out of the matrix and into the intermembrane space creating a Conc. Gradient The only way back into the matrix for H+ ions is through a pr ...
... Electrons carried to the inner membrane by NADH and FADH are dropped off at the beginning As the electrons are passed along, their energy is used to pump H+ ions out of the matrix and into the intermembrane space creating a Conc. Gradient The only way back into the matrix for H+ ions is through a pr ...
SR 47(2) 29-33
... of the plants there is about three times as much chlorophyll as carotenoids. Again anthocyanin is responsible for the red, pink and purple colours in leaves that are so attractive. Chlorophyll is not a very stable compound; bright sunlight causes it to degenerate. This is known as solarisation. To m ...
... of the plants there is about three times as much chlorophyll as carotenoids. Again anthocyanin is responsible for the red, pink and purple colours in leaves that are so attractive. Chlorophyll is not a very stable compound; bright sunlight causes it to degenerate. This is known as solarisation. To m ...
File
... An organism that gets energy from recycling nutrients by breaking down decaying material. An organism that makes its own food by the process of photosynthesis. A chemical process by which plants use sunlight to create their own food. An organism that gets its energy by eating other organisms. Areas ...
... An organism that gets energy from recycling nutrients by breaking down decaying material. An organism that makes its own food by the process of photosynthesis. A chemical process by which plants use sunlight to create their own food. An organism that gets its energy by eating other organisms. Areas ...
Biochemistry 2
... Enantiomers- isomers that are mirror images of each other Functional group- Chemical groups that affect molecular function by being directly involved in chemical reactions Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)- consisting of an organic molecule called adenosine attached to a string of three phosphates that w ...
... Enantiomers- isomers that are mirror images of each other Functional group- Chemical groups that affect molecular function by being directly involved in chemical reactions Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)- consisting of an organic molecule called adenosine attached to a string of three phosphates that w ...
words - Learning With Pride
... An organism that gets energy from recycling nutrients by breaking down decaying material. An organism that makes its own food by the process of photosynthesis. A chemical process by which plants use sunlight to create their own food. An organism that gets its energy by eating other organisms. Areas ...
... An organism that gets energy from recycling nutrients by breaking down decaying material. An organism that makes its own food by the process of photosynthesis. A chemical process by which plants use sunlight to create their own food. An organism that gets its energy by eating other organisms. Areas ...
Carbon Macromolecules
... • Unsaturated fats come primarily from plant foods like nuts and seeds • Are liquid at room temperature. Ex. include vegetable oils such as olive, peanut, safflower, sunflower, soybean and corn. ...
... • Unsaturated fats come primarily from plant foods like nuts and seeds • Are liquid at room temperature. Ex. include vegetable oils such as olive, peanut, safflower, sunflower, soybean and corn. ...
Biology 231
... quaternary structure – some proteins are composed of more than 1 polypeptide chain held together like tertiary structures enzymes – 100s of protein catalysts (end in –ase) function depends on structure very specific – only catalyze specific reactions substrate – reactant molecule(s) enzyme acts on ...
... quaternary structure – some proteins are composed of more than 1 polypeptide chain held together like tertiary structures enzymes – 100s of protein catalysts (end in –ase) function depends on structure very specific – only catalyze specific reactions substrate – reactant molecule(s) enzyme acts on ...
File
... – A phosphate is removed from each triose bisphosphate--. Back to 2 triose phosphates – Hydrogen is removed from each triose phosphate by NAD 2 reduced NAD molecules – Reduced NAD travels to mitochondria to be used in oxidative phosphorylation ...
... – A phosphate is removed from each triose bisphosphate--. Back to 2 triose phosphates – Hydrogen is removed from each triose phosphate by NAD 2 reduced NAD molecules – Reduced NAD travels to mitochondria to be used in oxidative phosphorylation ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... The breakdown products, CO2 and H20, are lowenergy molecules • Facts 1 & 2 mean this is an ______________ process—a chemical reaction that releases energy • As noted in previous slide…. A) Glucose is oxidized (losses electron) B) O2 is reduced (gains electron) The slower this reaction (cellular re ...
... The breakdown products, CO2 and H20, are lowenergy molecules • Facts 1 & 2 mean this is an ______________ process—a chemical reaction that releases energy • As noted in previous slide…. A) Glucose is oxidized (losses electron) B) O2 is reduced (gains electron) The slower this reaction (cellular re ...
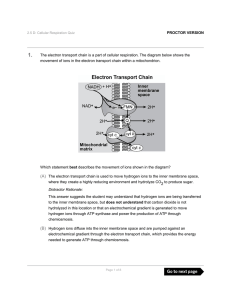
The electron transport chain is a part of cellular respiration. The
... (A) The electron transport chain is used to move hydrogen ions to the inner membrane space, where they create a highly reducing environment and hydrolyze CO2 to produce sugar. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that hydrogen ions are being transferred to the inner ...
... (A) The electron transport chain is used to move hydrogen ions to the inner membrane space, where they create a highly reducing environment and hydrolyze CO2 to produce sugar. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that hydrogen ions are being transferred to the inner ...
Krebs Cycle - WordPress.com
... Cellular respiration is an example of a metabolic pathway It is a complex energy release process, controlled by enzymes, that breaks down the complex molecules one step at a time, releasing energy in small controlled amounts All of the reactions involved in cellular respiration can be grouped int ...
... Cellular respiration is an example of a metabolic pathway It is a complex energy release process, controlled by enzymes, that breaks down the complex molecules one step at a time, releasing energy in small controlled amounts All of the reactions involved in cellular respiration can be grouped int ...
Pusillus Poseidon`s Guide to Protozoa
... of algae. Recently, the classification system has been overhauled and has become immensely complicated. (Information about DNA is now the primary consideration for classification, rather than how a creature looks or acts.) If you research these creatures on Wikipedia, you will see this new system be ...
... of algae. Recently, the classification system has been overhauled and has become immensely complicated. (Information about DNA is now the primary consideration for classification, rather than how a creature looks or acts.) If you research these creatures on Wikipedia, you will see this new system be ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.