Kevin Ahern's Biochemistry (BB 450/550) at Oregon State University
... product of the reaction is G3P. The Delta G zero prime is close to zero, so this reaction is readily reversible. Everything after this step has two molecules of each. 10. Reaction 6 is the only oxidation in glycolysis. It is catalyzed by glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehyrogenase. The energy of the oxi ...
... product of the reaction is G3P. The Delta G zero prime is close to zero, so this reaction is readily reversible. Everything after this step has two molecules of each. 10. Reaction 6 is the only oxidation in glycolysis. It is catalyzed by glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehyrogenase. The energy of the oxi ...
Plant Notes- Kingdom Plantae
... • Primary producers in most ecosystems and provide the nutritional basis in terrestrial ecosystems • Release oxygen to atmosphere • Do you remember the equation for Photosynthesis? Write it below. 6 CO2 + 6 H2O ...
... • Primary producers in most ecosystems and provide the nutritional basis in terrestrial ecosystems • Release oxygen to atmosphere • Do you remember the equation for Photosynthesis? Write it below. 6 CO2 + 6 H2O ...
008 Chapter 08 Metabolism: Energy Enzymes and Regulation 1
... 59. In thermodynamic studies, energy changes are analyzed in a collection of matter called a __________. All other matter in the universe is called the __________. 60. Cells must efficiently transfer energy from their energy-trapping systems to the systems actually carrying out work and also use var ...
... 59. In thermodynamic studies, energy changes are analyzed in a collection of matter called a __________. All other matter in the universe is called the __________. 60. Cells must efficiently transfer energy from their energy-trapping systems to the systems actually carrying out work and also use var ...
APES Fall Final Outline
... In order to be considered a “sustainable” practice, it must preserve the condition of the resource/environment today, tomorrow, and do it in such a way that it is healthy to the environment. 2. Human population growth began arithmetically in a linear fashion. Now, and for the past 4,000 years, the h ...
... In order to be considered a “sustainable” practice, it must preserve the condition of the resource/environment today, tomorrow, and do it in such a way that it is healthy to the environment. 2. Human population growth began arithmetically in a linear fashion. Now, and for the past 4,000 years, the h ...
Study Guide - LAURELELEM
... 13. What is the function of the chloroplasts? _____A green structure where the energy from sunlight is used to produce food for the plant___________________________________ 14. What is chlorophyll? _____A green chemical in plant cells that allows plants to use the Sun’s energy to make food. Chloroph ...
... 13. What is the function of the chloroplasts? _____A green structure where the energy from sunlight is used to produce food for the plant___________________________________ 14. What is chlorophyll? _____A green chemical in plant cells that allows plants to use the Sun’s energy to make food. Chloroph ...
The Mechanics of Breathing
... Your VO2 Max can be increased through training, as this causes adaptations within the cardiovascular, respiratory and muscular systems which make the processes of gas exchange, Oxygen transport and aerobic metabolism more efficient. There are a number of ways of testing your VO2 max. The most accur ...
... Your VO2 Max can be increased through training, as this causes adaptations within the cardiovascular, respiratory and muscular systems which make the processes of gas exchange, Oxygen transport and aerobic metabolism more efficient. There are a number of ways of testing your VO2 max. The most accur ...
Chapter 3: Energy for Cells
... Electron Transport Chain takes place on the cristae of the mitochondria. (Remember the light reactions in photosynthesis? They are also an ETC, and where do they happen? What does that tell you about ETCs?) ...
... Electron Transport Chain takes place on the cristae of the mitochondria. (Remember the light reactions in photosynthesis? They are also an ETC, and where do they happen? What does that tell you about ETCs?) ...
EOC Study Guide
... and umbilical cord form. It is a time of rapid growth. After 8 weeks the embryo is called a fetus. The baby’s brain, spinal cord and other organs begin to form and the heart begins to beat. Bones and muscles start to form. Muscles can contract and hands can make a fist. Fingers and toes begin to tak ...
... and umbilical cord form. It is a time of rapid growth. After 8 weeks the embryo is called a fetus. The baby’s brain, spinal cord and other organs begin to form and the heart begins to beat. Bones and muscles start to form. Muscles can contract and hands can make a fist. Fingers and toes begin to tak ...
Physiology of Respiration - International Fire Training Centre
... on subsequent very deep exhalation, this may be increased by a further 1½ litres. The total amount thus exhaled, i.e. about 4½ litres on average, is known as the vital capacity and varies with different people. This variation in lung capacity is the reason for the varying demands on breathing appara ...
... on subsequent very deep exhalation, this may be increased by a further 1½ litres. The total amount thus exhaled, i.e. about 4½ litres on average, is known as the vital capacity and varies with different people. This variation in lung capacity is the reason for the varying demands on breathing appara ...
Ecology Standards
... __ Explanation of the role of green plants as producers __ Mention of herbivores in a way that indicated an understanding of their role __ An indication that carnivores obtained C from herbivores __ Discussion of the role of decomposers in returning C to the atmosphere as CO2 __ Mention of CO2 produ ...
... __ Explanation of the role of green plants as producers __ Mention of herbivores in a way that indicated an understanding of their role __ An indication that carnivores obtained C from herbivores __ Discussion of the role of decomposers in returning C to the atmosphere as CO2 __ Mention of CO2 produ ...
Multiple Choice Questions
... 10. Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are two major processes of carbon cycling in living organisms. Which statement correctly describes one similarity between photosynthesis and cellular respiration? A. Both occur in animal and plant cells. B. Both include reactions that transform energy. C. ...
... 10. Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are two major processes of carbon cycling in living organisms. Which statement correctly describes one similarity between photosynthesis and cellular respiration? A. Both occur in animal and plant cells. B. Both include reactions that transform energy. C. ...
Willingham, College Biology: Microbes 1 In This Chapter o
... chemotrophs. A chemotroph obtains energy by oxidizing, or stripping electrons from, a molecule, usually a reduced compound (one that has some extra electrons hanging around). And every lithotroph requires a carbon source, which can help define them, too. Like plants, lithoautotrophs use CO2 , while ...
... chemotrophs. A chemotroph obtains energy by oxidizing, or stripping electrons from, a molecule, usually a reduced compound (one that has some extra electrons hanging around). And every lithotroph requires a carbon source, which can help define them, too. Like plants, lithoautotrophs use CO2 , while ...
200KB - NZQA
... (a) Water is required by the miro seed for the seed to swell, break its testa / seed coat. (b) Water is required to activate the enzymes in the testa of the seed. Oxygen is required by the cells, which breaks down the starch in the testa to produce glucose required for respiration. This provides the ...
... (a) Water is required by the miro seed for the seed to swell, break its testa / seed coat. (b) Water is required to activate the enzymes in the testa of the seed. Oxygen is required by the cells, which breaks down the starch in the testa to produce glucose required for respiration. This provides the ...
Cell Respiration DiagramSkit WS NEW
... For the following, fill in the blanks. Most of the terms are from the above bank, and a few are not. 1. The purpose of cell respiration is to __________________________________________, which takes place in the _____________________________ of the cell. There are _____ major steps. 2. The first step ...
... For the following, fill in the blanks. Most of the terms are from the above bank, and a few are not. 1. The purpose of cell respiration is to __________________________________________, which takes place in the _____________________________ of the cell. There are _____ major steps. 2. The first step ...
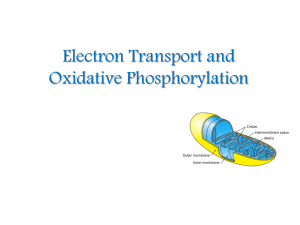
Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation
... When these electrons are used to reduce molecular oxygen to water, a large amount of free energy is liberated, which can be used to generate ATP. Oxidative phosphorylation is the process in which ATP is formed as a result of the transfer of electrons from NADH or FADH2 to O2 by a series of elect ...
... When these electrons are used to reduce molecular oxygen to water, a large amount of free energy is liberated, which can be used to generate ATP. Oxidative phosphorylation is the process in which ATP is formed as a result of the transfer of electrons from NADH or FADH2 to O2 by a series of elect ...
121KB - NZQA
... (a) Water is required by the miro seed for the seed to swell, break its testa / seed coat. (b) Water is required to activate the enzymes in the testa of the seed. Oxygen is required by the cells, which breaks down the starch in the testa to produce glucose required for respiration. This provides the ...
... (a) Water is required by the miro seed for the seed to swell, break its testa / seed coat. (b) Water is required to activate the enzymes in the testa of the seed. Oxygen is required by the cells, which breaks down the starch in the testa to produce glucose required for respiration. This provides the ...
Respiration Notes (chapter 8)
... -occurs on the cristae of the inner mitochondrial membrane. -produces 32-34 ATP using Chemiosmosis - e- of NADH & FADH2 (produced in steps 1&2). -the ETC consists of: 1.NADH dehydrogenase or reductase protein 2.Cytochromes (proteins) 3.at the end of the chain is oxygen -the energy derived from the E ...
... -occurs on the cristae of the inner mitochondrial membrane. -produces 32-34 ATP using Chemiosmosis - e- of NADH & FADH2 (produced in steps 1&2). -the ETC consists of: 1.NADH dehydrogenase or reductase protein 2.Cytochromes (proteins) 3.at the end of the chain is oxygen -the energy derived from the E ...
Chapter 2: Principles of Ecology
... Trophic levels and food chains Trophic level: A feeding level in an ecosystem Food chain: lineup of organisms that shows who eats who o Shows how matter and energy move through an ecosystem ...
... Trophic levels and food chains Trophic level: A feeding level in an ecosystem Food chain: lineup of organisms that shows who eats who o Shows how matter and energy move through an ecosystem ...
Principles of Ecology
... A network of connected food chains More realistic than a food chain because most organisms feed on more than one species for food ...
... A network of connected food chains More realistic than a food chain because most organisms feed on more than one species for food ...
Water Properties
... • What part of the body is responisible for homeostasis? • Any of the organ systems work to maintain homeostasis. Also, cell membrane and your metabolism. ...
... • What part of the body is responisible for homeostasis? • Any of the organ systems work to maintain homeostasis. Also, cell membrane and your metabolism. ...
Chapter 21 - Cloudfront.net
... • All bronchioles end in alveoli. • Most of lung tissue is alveoli! (300 million of them!) • Capillaries surround each alveoli allowing the blood to exchange gas with the environment. ...
... • All bronchioles end in alveoli. • Most of lung tissue is alveoli! (300 million of them!) • Capillaries surround each alveoli allowing the blood to exchange gas with the environment. ...
Name - TeacherWeb
... c. Gas exchange is more efficient in wet areas. d. Without moisture, rhizoids cannot anchor the plants. _____ 10. Xylem tissue is important because it a. can conduct water over long distances. b. allows water to diff use from the roots. c. carries carbohydrates to all parts of the plant. d. carries ...
... c. Gas exchange is more efficient in wet areas. d. Without moisture, rhizoids cannot anchor the plants. _____ 10. Xylem tissue is important because it a. can conduct water over long distances. b. allows water to diff use from the roots. c. carries carbohydrates to all parts of the plant. d. carries ...
Chapter 2
... What is Matter? • Atoms, ions and molecules • Anything that has mass and takes up space. • Two forms: – Element – distinctive building blocks of matter that make up every material substance – Compound – two or more different elements held together by chemical bonds ...
... What is Matter? • Atoms, ions and molecules • Anything that has mass and takes up space. • Two forms: – Element – distinctive building blocks of matter that make up every material substance – Compound – two or more different elements held together by chemical bonds ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.