Cells and Energy Cellular Respiration Chapter 2 Lesson 4 Part 1
... is a series of chemical reactions that convert the energy in food molecules into a usable form of energy called ATP the breaking down of an energy source by cells to obtain usable energy ...
... is a series of chemical reactions that convert the energy in food molecules into a usable form of energy called ATP the breaking down of an energy source by cells to obtain usable energy ...
The Respiratory System. Presented by Toni Davis and Niamh
... The nasal concha divide the nasal cavity into passageways and help increase the surface area of the mucous membrane. The mucous membrane with hairlike projections called cilia, lines the nasal cavity and moistens, filter and warms incoming air. Particles caught in mucous is carried away to the phary ...
... The nasal concha divide the nasal cavity into passageways and help increase the surface area of the mucous membrane. The mucous membrane with hairlike projections called cilia, lines the nasal cavity and moistens, filter and warms incoming air. Particles caught in mucous is carried away to the phary ...
L24_Krebs
... oxaloacetate prochiral • Citrate can leave the mitochondria or be oxidised – Depending on whether the cell is doing lipogenesis or needs energy ...
... oxaloacetate prochiral • Citrate can leave the mitochondria or be oxidised – Depending on whether the cell is doing lipogenesis or needs energy ...
Lecture 3 - Winthrop Chemistry, Physics, and Geology
... molecules come to be? •Initially, it is thought that only NH3, H2S, CO, CO2, CH4, N2, H2 and H2O were present on the early Earth •However, the planet was volcanically active (heat and pressure) and there was significant electrical activity in the atmosphere ...
... molecules come to be? •Initially, it is thought that only NH3, H2S, CO, CO2, CH4, N2, H2 and H2O were present on the early Earth •However, the planet was volcanically active (heat and pressure) and there was significant electrical activity in the atmosphere ...
The Theme of Oxidative Phosphorylation in Glycolysis and Cellular
... The main point of oxidative phosphorylation is the transfer of electrons from NADH and FADH2 to power ATP production. Similarly, the main purpose of playing arcade games is to win tickets for prizes (okay, and also maybe to have fun and earn high scores in the games). NADH is more often the electron ...
... The main point of oxidative phosphorylation is the transfer of electrons from NADH and FADH2 to power ATP production. Similarly, the main purpose of playing arcade games is to win tickets for prizes (okay, and also maybe to have fun and earn high scores in the games). NADH is more often the electron ...
2 395G Exam 3 11 Dec 2002 First calculate ∆E
... 4. a. Briefly summarize the mechanism by which light energy is converted to chemical energy in the light reactions of photosynthesis. (Just outline the fundamental processes involved.) Light absorption by PSI and PSII causes excitation of an electron to its singlet state. Electron is ejected and it ...
... 4. a. Briefly summarize the mechanism by which light energy is converted to chemical energy in the light reactions of photosynthesis. (Just outline the fundamental processes involved.) Light absorption by PSI and PSII causes excitation of an electron to its singlet state. Electron is ejected and it ...
The Biology Staff Handbook - St. Mary`s Independent School
... o A protease enzyme – called pepsin. This digests proteins into amino acids. o Hydrochloric acid – this kills bacteria in our food. It creates pH3. o Mucus – this protects the wall of our stomach from acid and pepsin. The wall of our stomach is muscular, and churns our food. The food remains in ou ...
... o A protease enzyme – called pepsin. This digests proteins into amino acids. o Hydrochloric acid – this kills bacteria in our food. It creates pH3. o Mucus – this protects the wall of our stomach from acid and pepsin. The wall of our stomach is muscular, and churns our food. The food remains in ou ...
Bacteria
... spore coat…very hard to kill…you have to autoclave to kill 2. Look at Slide # 5 of this presentation 3. Random mutations that occur ...
... spore coat…very hard to kill…you have to autoclave to kill 2. Look at Slide # 5 of this presentation 3. Random mutations that occur ...
Student Review Sheet Biology Semester A Examination
... Scientists believe that an increase in carbon dioxide, CO2, in the atmosphere is causing a gradual increase of the Earth’s temperature, a process known as global warming. They are concerned that one human activity, cutting down trees without replacing them, is contributing to global warming. Describ ...
... Scientists believe that an increase in carbon dioxide, CO2, in the atmosphere is causing a gradual increase of the Earth’s temperature, a process known as global warming. They are concerned that one human activity, cutting down trees without replacing them, is contributing to global warming. Describ ...
Powerpoint Notes
... organisms that rely on other sources of energy These organisms use energy stored in inorganic (bonds that do not contain carbon) chemical compounds A good example of these types of organisms are those found deep in the ocean near thermal vents The organisms use the chemical energy that is load ...
... organisms that rely on other sources of energy These organisms use energy stored in inorganic (bonds that do not contain carbon) chemical compounds A good example of these types of organisms are those found deep in the ocean near thermal vents The organisms use the chemical energy that is load ...
TRICARBOXYLIC ACID CYCLE
... • The tricarboxylic acid cycle (Krebs cycle, citric acid cycle) is a focal end point for the oxidation of carbohydrate, fat and amino acids via acetyl coenzyme A. • Pyruvate is converted to acetyl coenzyme A by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. • The reactions of the TCA cycle generate carbon diox ...
... • The tricarboxylic acid cycle (Krebs cycle, citric acid cycle) is a focal end point for the oxidation of carbohydrate, fat and amino acids via acetyl coenzyme A. • Pyruvate is converted to acetyl coenzyme A by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. • The reactions of the TCA cycle generate carbon diox ...
Batteries convert chemically stored energy to electrical energy, and
... Photosynthesis uses the energy of sunlight to produce sugars and other organic molecules. These molecules in turn serve as food for other organisms. Many of these organisms carry out respiration, a process that uses O2 to form CO2 from the same carbon atoms that had been taken up as CO2 and converte ...
... Photosynthesis uses the energy of sunlight to produce sugars and other organic molecules. These molecules in turn serve as food for other organisms. Many of these organisms carry out respiration, a process that uses O2 to form CO2 from the same carbon atoms that had been taken up as CO2 and converte ...
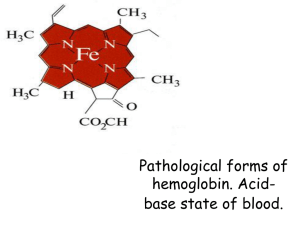
Pathological forms of hemoglobin. Acid
... iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein in the red blood cells of vertebrates,and the tissues of some invertebrates. In mammals, the protein makes up about 97% of the red blood cell's dry content, and around 35% of the total content (including water). Hemoglobin transports oxygen from the lu ...
... iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein in the red blood cells of vertebrates,and the tissues of some invertebrates. In mammals, the protein makes up about 97% of the red blood cell's dry content, and around 35% of the total content (including water). Hemoglobin transports oxygen from the lu ...
ecology - Westlake FFA
... 3. Secondary Consumer: (always a carnivore) - feeds upon other consumers (frogs, sparrows, snakes, and foxes above) (The hawk is a secondary or 3rd level consumer depending on the availability of food.) Omnivores may be primary or secondary consumers. ...
... 3. Secondary Consumer: (always a carnivore) - feeds upon other consumers (frogs, sparrows, snakes, and foxes above) (The hawk is a secondary or 3rd level consumer depending on the availability of food.) Omnivores may be primary or secondary consumers. ...
Topic 16 Some non-metals and their compounds notes
... Carbon dioxide is causing the global temperature of the Earth to rise. This rise in temperature affects the climate all over the planet in ways which are hard to predict. Some areas may become wetter or dryer, other areas may become hotter. The main (predictable) directions of wind and ocean current ...
... Carbon dioxide is causing the global temperature of the Earth to rise. This rise in temperature affects the climate all over the planet in ways which are hard to predict. Some areas may become wetter or dryer, other areas may become hotter. The main (predictable) directions of wind and ocean current ...
2009-2010 BIOLOGY C
... -ATP is useful as a basic energy source for all cells. -In the process of photosynthesis, plants convert sunlight into chemical energy Vocab adenosine triphosphate autotroph (ATP) (228) heterotroph (228) photosynthesis (228) 8.2 Photosynthesis: An Overview -Photosynthetic organisms capture energy fr ...
... -ATP is useful as a basic energy source for all cells. -In the process of photosynthesis, plants convert sunlight into chemical energy Vocab adenosine triphosphate autotroph (ATP) (228) heterotroph (228) photosynthesis (228) 8.2 Photosynthesis: An Overview -Photosynthetic organisms capture energy fr ...
how plants convert solar energy into chemical energy
... to cold and moisture loss. Some, like pine and fir trees, have long thin needles. Others, like holly, have broad leaves with tough, waxy surfaces. On very cold, dry days, these leaves sometimes curl up to reduce their exposed surface. Evergreens may continue to photosynthesize during the winter as l ...
... to cold and moisture loss. Some, like pine and fir trees, have long thin needles. Others, like holly, have broad leaves with tough, waxy surfaces. On very cold, dry days, these leaves sometimes curl up to reduce their exposed surface. Evergreens may continue to photosynthesize during the winter as l ...
2013年1月12日托福写作真题回忆
... appearance from most of the family. At least superficially, plants of the genus Pereskia resemble other trees and shrubs growing around them. They have persistent leaves, and when older, bark-covered stems. Their areoles identify them as cacti, and in spite of their appearance, they, too, have many ...
... appearance from most of the family. At least superficially, plants of the genus Pereskia resemble other trees and shrubs growing around them. They have persistent leaves, and when older, bark-covered stems. Their areoles identify them as cacti, and in spite of their appearance, they, too, have many ...
Plants Woo Woo! Notes for 4-15
... Problems of Land Plants (Algae rely on water): • Need lots of water for photosynthesis • Need sunlight for P.S. • Need to transport water to all parts of the plant. • Need to transport photosynthesis products to all parts of the plant. • Sperm needs to swim in water to egg. ...
... Problems of Land Plants (Algae rely on water): • Need lots of water for photosynthesis • Need sunlight for P.S. • Need to transport water to all parts of the plant. • Need to transport photosynthesis products to all parts of the plant. • Sperm needs to swim in water to egg. ...
Plant Kingdom
... b) They use pollen and seeds to reproduce. How do you use seed plants? (pg. 262) a) eat seed plants—rice, peas, squash b) wear clothes made from seed plants—cotton and flax c) live in homes built from seed plants—oak, pine, maple d) seed plants produce oxygen What are the two types of vascular tissu ...
... b) They use pollen and seeds to reproduce. How do you use seed plants? (pg. 262) a) eat seed plants—rice, peas, squash b) wear clothes made from seed plants—cotton and flax c) live in homes built from seed plants—oak, pine, maple d) seed plants produce oxygen What are the two types of vascular tissu ...
Breathing versus Respiration
... How are Breathing and Cell Respiration Connected? • In order for cell respiration to occur, oxygen must move into cells, while carbon dioxide must move out of cells. • The exchange is made in the lungs during breathing ...
... How are Breathing and Cell Respiration Connected? • In order for cell respiration to occur, oxygen must move into cells, while carbon dioxide must move out of cells. • The exchange is made in the lungs during breathing ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.