a local ecosystem
... Photosynthesis is carried out by plants. It is the process by which the plant converts some of the suns light energy, trapped by the chloroplasts, reacts with carbon dioxide and water to produce glucose and oxygen. These products (oxygen + glucose) are either converted into other carbohydrates or a ...
... Photosynthesis is carried out by plants. It is the process by which the plant converts some of the suns light energy, trapped by the chloroplasts, reacts with carbon dioxide and water to produce glucose and oxygen. These products (oxygen + glucose) are either converted into other carbohydrates or a ...
Notes III
... • In the tissue capillaries, gradients of partial pressure favor the diffusion of oxygen out of the blood and carbon dioxide into the blood. • Cellular respiration removes oxygen from and adds carbon dioxide to the interstitial fluid by diffusion, and from the mitochondria in nearby cells. • After ...
... • In the tissue capillaries, gradients of partial pressure favor the diffusion of oxygen out of the blood and carbon dioxide into the blood. • Cellular respiration removes oxygen from and adds carbon dioxide to the interstitial fluid by diffusion, and from the mitochondria in nearby cells. • After ...
Ecology Section
... think, etc.) or the energy may be lost as heat. The dark arrows represent the movement of this energy. Note that all energy comes from the sun, and that the ultimate fate of all energy in ecosystems is to be lost as heat. Energy does not recycle!! Be careful of which way the arrows point. They point ...
... think, etc.) or the energy may be lost as heat. The dark arrows represent the movement of this energy. Note that all energy comes from the sun, and that the ultimate fate of all energy in ecosystems is to be lost as heat. Energy does not recycle!! Be careful of which way the arrows point. They point ...
Biology 233
... phosphorylation – addition of phosphate groups to a molecule substrate level phosphorylation – energy from breaking a chemical bond is used to phosphorylate ADP (eg. ADP + creatine phosphate -----> ATP + creatine) oxidative phosphorylation – energy from oxidation of organic molecules in mitochondria ...
... phosphorylation – addition of phosphate groups to a molecule substrate level phosphorylation – energy from breaking a chemical bond is used to phosphorylate ADP (eg. ADP + creatine phosphate -----> ATP + creatine) oxidative phosphorylation – energy from oxidation of organic molecules in mitochondria ...
respiration review
... Reduction is the addition of electrons (hydrogen) to a substance. In respiration, oxygen is reduced to form ...
... Reduction is the addition of electrons (hydrogen) to a substance. In respiration, oxygen is reduced to form ...
Science - Sacred Heart RC Primary School
... I can compare how things move on different surfaces. Notice that some forces need contact between two objects but magnetic forces can act at a distance. I can see that some forces need contact between two objects but magnetic forces can act at a distance. Compare and group together a variety of ever ...
... I can compare how things move on different surfaces. Notice that some forces need contact between two objects but magnetic forces can act at a distance. I can see that some forces need contact between two objects but magnetic forces can act at a distance. Compare and group together a variety of ever ...
Standard B-5 - Wando High School
... Organisms play a major role in recycling carbon from one form to another in the following processes: ○ Photosynthesis: Photosynthetic organisms take in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and convert it to simple sugars. ○ Respiration: Organisms break down glucose and carbon is released into the at ...
... Organisms play a major role in recycling carbon from one form to another in the following processes: ○ Photosynthesis: Photosynthetic organisms take in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and convert it to simple sugars. ○ Respiration: Organisms break down glucose and carbon is released into the at ...
Biology 20 Ch 3 Practice Test
... methane, ammonia, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and nitrogen. There was no atmospheric oxygen because it was chemically combined in Earth’s crust in compounds such as iron oxide. Scientists speculate that without life on earth, the composition of the atmosphere would be about 98% carbon dioxide. What bi ...
... methane, ammonia, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and nitrogen. There was no atmospheric oxygen because it was chemically combined in Earth’s crust in compounds such as iron oxide. Scientists speculate that without life on earth, the composition of the atmosphere would be about 98% carbon dioxide. What bi ...
8.3 - Patterns in Nature
... USES: Needed for growth and repair, make up a major part of the body’s structure. Vital to the structure and function of cells. Are essential for metabolism (all chemical reactions in cells) as enzymes are made up of proteins. Made up of long chains of amino acids, joined together by peptide bon ...
... USES: Needed for growth and repair, make up a major part of the body’s structure. Vital to the structure and function of cells. Are essential for metabolism (all chemical reactions in cells) as enzymes are made up of proteins. Made up of long chains of amino acids, joined together by peptide bon ...
Biochemistry Practice Questions
... Scientists study DNA to understand heredity, disease, and the evolutionary history of organisms. During these studies, DNA must rst be separated into two complementary strands. Next, the appropriate nucleotides are attached to the nucleotides in each original strand to produce two new complete DNA s ...
... Scientists study DNA to understand heredity, disease, and the evolutionary history of organisms. During these studies, DNA must rst be separated into two complementary strands. Next, the appropriate nucleotides are attached to the nucleotides in each original strand to produce two new complete DNA s ...
Cell Energy - Brookwood High School
... NADPH • NADP+ - carrier molecule that accepts and holds 2 high-energy electrons along with a hydrogen ion (H+) – results in the production of NADPH – this conversion to NADPH allows some energy of light to be trapped in a chemical form – chemical energy can then be used by cell for chemical reaction ...
... NADPH • NADP+ - carrier molecule that accepts and holds 2 high-energy electrons along with a hydrogen ion (H+) – results in the production of NADPH – this conversion to NADPH allows some energy of light to be trapped in a chemical form – chemical energy can then be used by cell for chemical reaction ...
adjusting the conditions inside when the outside conditions change
... 10. Where does this process occur in eukaryotic cells? ___________________ 11. Where does this process occur in prokaryotic cells? ___________________ 12. If oxygen is not present, either ____________________ or ______________ and ________ are made. Pg. 105 13. The main fuel for respiration is _____ ...
... 10. Where does this process occur in eukaryotic cells? ___________________ 11. Where does this process occur in prokaryotic cells? ___________________ 12. If oxygen is not present, either ____________________ or ______________ and ________ are made. Pg. 105 13. The main fuel for respiration is _____ ...
www.theallpapers.com
... There are forty questions on this paper. Answer all questions. For each question there are four possible answers A, B, C and D. Choose the one you consider correct and record your choice in soft pencil on the separate Answer Sheet. Read the instructions on the Answer Sheet very carefully. Each corre ...
... There are forty questions on this paper. Answer all questions. For each question there are four possible answers A, B, C and D. Choose the one you consider correct and record your choice in soft pencil on the separate Answer Sheet. Read the instructions on the Answer Sheet very carefully. Each corre ...
Biology EOC Study Guide: Part 1, Ecology
... o The pyramid of numbers may be inverted if, for instance, thousands of insects feed off of one tree. The pyramid of biomass usually does not get inverted. How do plants and animals cycle carbon and nitrogen within an ecosystem? - The Carbon Cycle: carbon dioxide is exchanged between the atmosphere ...
... o The pyramid of numbers may be inverted if, for instance, thousands of insects feed off of one tree. The pyramid of biomass usually does not get inverted. How do plants and animals cycle carbon and nitrogen within an ecosystem? - The Carbon Cycle: carbon dioxide is exchanged between the atmosphere ...
Unit 1 Ecology Label the parts of the food chain below. Below the
... The reason they have such a negative impact on the ecosystems into which they are introduced is that they often have nothing limiting their growth (no predators/ disease/ etc) and because of this, their populations increase rapidly. Through sheer numbers, they outcompete native species for resources ...
... The reason they have such a negative impact on the ecosystems into which they are introduced is that they often have nothing limiting their growth (no predators/ disease/ etc) and because of this, their populations increase rapidly. Through sheer numbers, they outcompete native species for resources ...
Ch.8 - Wikispaces
... • The structure of the leaf is ideal for carrying out photosynthesis • The cells that contain the most chloroplasts are located near the leaf’s upper surface, where they get the most light • Carbon dioxide enters the leaf through open stomata, water which is absorbed by the plant’s roots travel up t ...
... • The structure of the leaf is ideal for carrying out photosynthesis • The cells that contain the most chloroplasts are located near the leaf’s upper surface, where they get the most light • Carbon dioxide enters the leaf through open stomata, water which is absorbed by the plant’s roots travel up t ...
I. Metabolism
... Oxidative phosphorylation cannot occur substrate-level phosphorylation (energy provided by degrading the original substrate) is an alternative route, but the efficiency of energy production is typically 8% of aerobic metabolism. ...
... Oxidative phosphorylation cannot occur substrate-level phosphorylation (energy provided by degrading the original substrate) is an alternative route, but the efficiency of energy production is typically 8% of aerobic metabolism. ...
Pentose Phosphate Pathway - Lectures For UG-5
... • This portion of the pathway is particularly important in the liver, lactating mammary glands, and adipose, which are active in the biosynthesis of fatty acids, in the adrenal cortex, which is active in the NADPH-dependent synthesis of steroids, and in erythro-cytes, which require NADPH to keep glu ...
... • This portion of the pathway is particularly important in the liver, lactating mammary glands, and adipose, which are active in the biosynthesis of fatty acids, in the adrenal cortex, which is active in the NADPH-dependent synthesis of steroids, and in erythro-cytes, which require NADPH to keep glu ...
kines fo realz - CCVI
... without sacrificing the output, the body must tap into its anaerobic metabolism. This where the body goes into a mix of aerobic and anaerobic energy production. While not hugely detrimental, oxygen deficits can grow to a level that the anaerobic energy system cannot cover. This can cause performance ...
... without sacrificing the output, the body must tap into its anaerobic metabolism. This where the body goes into a mix of aerobic and anaerobic energy production. While not hugely detrimental, oxygen deficits can grow to a level that the anaerobic energy system cannot cover. This can cause performance ...
Electron Transport Chain
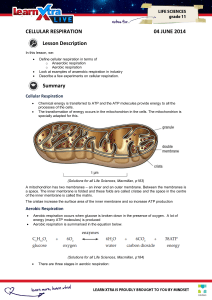
... • Cellular respiration includes both aerobic and anaerobic respiration but is often used to refer to aerobic respiration • Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose: ...
... • Cellular respiration includes both aerobic and anaerobic respiration but is often used to refer to aerobic respiration • Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose: ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.