7-cellular-respiration
... from either the breakdown of starch or glycogen. Other sugars can be used as these can produce glucose or other intermediates. Proteins form amino acids when broken down. Deamination in the liver produces molecules that can be used either in glycolysis or the citric acid cycle as respiratory sub ...
... from either the breakdown of starch or glycogen. Other sugars can be used as these can produce glucose or other intermediates. Proteins form amino acids when broken down. Deamination in the liver produces molecules that can be used either in glycolysis or the citric acid cycle as respiratory sub ...
Ch. 5 Enzyme Review
... a. its substrate may not fit properly in the active site b. it will be missing one of its polypeptides c. the helical coil will be stretched out d. the product of the reaction will be a different molecule e. its substrate will bond covalently with the wrong part of the molecule 10. Why does heating ...
... a. its substrate may not fit properly in the active site b. it will be missing one of its polypeptides c. the helical coil will be stretched out d. the product of the reaction will be a different molecule e. its substrate will bond covalently with the wrong part of the molecule 10. Why does heating ...
Atomic Structure (Bohr or Planetary Model)
... • Nucleotide derivative bound to 3 phosphate groups – second and third phosphate groups are attached by high energy covalent bonds • phosphate groups are negatively charged and naturally repel each other • Enzymes that hydrolyze the high energy bond of ATP produces releases chemical energy – ATP → A ...
... • Nucleotide derivative bound to 3 phosphate groups – second and third phosphate groups are attached by high energy covalent bonds • phosphate groups are negatively charged and naturally repel each other • Enzymes that hydrolyze the high energy bond of ATP produces releases chemical energy – ATP → A ...
Study Guide Cellular Respiration
... 2. Respiration and Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis uses CO2 and H2O molecules to form C6H12O6 (glucose) and O2. Respiration is just the opposite, it uses O2 to breakdown glucose into CO2 and H2O. It results in chemical cycling in biosphere. 3. Respiration and Breathing: Respiration takes place in cel ...
... 2. Respiration and Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis uses CO2 and H2O molecules to form C6H12O6 (glucose) and O2. Respiration is just the opposite, it uses O2 to breakdown glucose into CO2 and H2O. It results in chemical cycling in biosphere. 3. Respiration and Breathing: Respiration takes place in cel ...
Chapter 25
... • The food we eat is our only source of energy for performing biological work. • There are three major metabolic destinations for the principle nutrients. They will be used for energy for active processes, synthesized into structural or functional molecules, or synthesized as fat or glycogen for lat ...
... • The food we eat is our only source of energy for performing biological work. • There are three major metabolic destinations for the principle nutrients. They will be used for energy for active processes, synthesized into structural or functional molecules, or synthesized as fat or glycogen for lat ...
Are you ready for S279?
... Protons and neutrons each have approximately the same mass, whereas the mass of an electron is negligible. The atom of any element is characterised by the number of protons in its nucleus – called the atomic number, Z. Carbon for example has six protons, whereas nitrogen has seven and oxygen has eig ...
... Protons and neutrons each have approximately the same mass, whereas the mass of an electron is negligible. The atom of any element is characterised by the number of protons in its nucleus – called the atomic number, Z. Carbon for example has six protons, whereas nitrogen has seven and oxygen has eig ...
chapter 14
... Pyruvic acid is the end product of glycolysis. What are the three metabolic fates of pyruvic acid under aerobic and anaerobic conditions? Write in the space provided in the diagram. ...
... Pyruvic acid is the end product of glycolysis. What are the three metabolic fates of pyruvic acid under aerobic and anaerobic conditions? Write in the space provided in the diagram. ...
An Overview of Organic Reactions
... The energy is mostly determined by the type of bond, independent of the molecule § The C-H bond in methane requires a net energy input of 106 kcal/mol to be broken at 25 ºC. § Table 6.3 lists energies for many bond types Changes in bonds can be used to calculate net changes in heat ...
... The energy is mostly determined by the type of bond, independent of the molecule § The C-H bond in methane requires a net energy input of 106 kcal/mol to be broken at 25 ºC. § Table 6.3 lists energies for many bond types Changes in bonds can be used to calculate net changes in heat ...
Cellular respiration
... ADP = adenosine diphosphate H2O + ATP ADP + P + energy • This is the energy used by the body to carry out the functions of life ...
... ADP = adenosine diphosphate H2O + ATP ADP + P + energy • This is the energy used by the body to carry out the functions of life ...
File
... Acids, Bases, and pH • Our body uses buffers to resist changes in pH – Slight pH disturbances can disrupt physiological functions and alter drug actions – pH of blood ranges from 7.35 to 7.45 – Deviations from this range cause tremors, paralysis, or even death ...
... Acids, Bases, and pH • Our body uses buffers to resist changes in pH – Slight pH disturbances can disrupt physiological functions and alter drug actions – pH of blood ranges from 7.35 to 7.45 – Deviations from this range cause tremors, paralysis, or even death ...
are an example of a nonvascular plant. Flowers an
... atmosphere that most living organisms need. The food (sugar) created through the process of photosynthesis is used to provide energy needed by the plants to perform life functions. ...
... atmosphere that most living organisms need. The food (sugar) created through the process of photosynthesis is used to provide energy needed by the plants to perform life functions. ...
MEMBRANE-BOUND ELECTRON TRANSFER AND ATP
... respiratory chain proteins Many proteins encoded by cell nuclear DNA Cells depend on organelle for oxidative phosphorylation , mitochondrion depend on cell for their very existence Suggested that all extant mitochondria are derived from ...
... respiratory chain proteins Many proteins encoded by cell nuclear DNA Cells depend on organelle for oxidative phosphorylation , mitochondrion depend on cell for their very existence Suggested that all extant mitochondria are derived from ...
Bioenergetics
... Could be a Q&A treasure hunt – images around the room, eg: Which product is high in protein? Which product contains caffeine? Discuss uses of glucose and produce a Mind map or poster. ...
... Could be a Q&A treasure hunt – images around the room, eg: Which product is high in protein? Which product contains caffeine? Discuss uses of glucose and produce a Mind map or poster. ...
leaf primordia
... • Cuticle – Waxy substance that prevents water loss from the leaf, thicker in dry, arid regions. • Sunken stomata – increase the thickness of the boundary layer. • Reduced leaf areas – reduce the size of the leaf, which in turn reduces the amt. of water lost to transpiration. • Leaf abscission – pla ...
... • Cuticle – Waxy substance that prevents water loss from the leaf, thicker in dry, arid regions. • Sunken stomata – increase the thickness of the boundary layer. • Reduced leaf areas – reduce the size of the leaf, which in turn reduces the amt. of water lost to transpiration. • Leaf abscission – pla ...
Which factors regulate seagrass growth and distribution?
... By Tina M. Greve and Thomas Binzer (FBL) ...
... By Tina M. Greve and Thomas Binzer (FBL) ...
BIO 101 Worksheet Metabolism and Cellular Respiration
... Glycolysis True or false. If false, indicate why 1. _______Glycolysis takes place in the cristae of mitochondria 2. _______ An end product of glycolysis is pyruvate 3. _______ A 6 carbon sugar is oxidized in glycolysis 4. _______ CO2 is a waste product of glycolysis 5. _______ sugar + NAD+ pyruvat ...
... Glycolysis True or false. If false, indicate why 1. _______Glycolysis takes place in the cristae of mitochondria 2. _______ An end product of glycolysis is pyruvate 3. _______ A 6 carbon sugar is oxidized in glycolysis 4. _______ CO2 is a waste product of glycolysis 5. _______ sugar + NAD+ pyruvat ...
click here. - FIU Faculty Websites
... transmission of any image over a network; • preparation of any derivative work, including the extraction, in whole or in part, of any images; • any rental, lease, or lending of the program. ...
... transmission of any image over a network; • preparation of any derivative work, including the extraction, in whole or in part, of any images; • any rental, lease, or lending of the program. ...
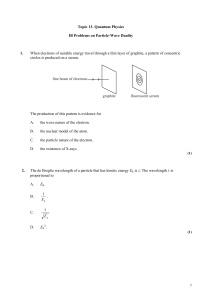
Wave-particle_duality
... After the collision, the de Broglie wavelengths of the α-particle and the carbon nucleus are λf and λc respectively. Which of the following is a true statement related to the de Broglie wavelengths? ...
... After the collision, the de Broglie wavelengths of the α-particle and the carbon nucleus are λf and λc respectively. Which of the following is a true statement related to the de Broglie wavelengths? ...
Plants and fungi evolved together as life moved onto land over 400
... •Plants and green algae have a number of homologous features, such as identical photosynthetic pigments, food storage molecules, cell walls, and mechanisms of cell division. ...
... •Plants and green algae have a number of homologous features, such as identical photosynthetic pigments, food storage molecules, cell walls, and mechanisms of cell division. ...
Science 1206 - Nova Central
... • As the food is passed through the food web, most of the energy is lost. – Pyramid of energy - about 10% of the energy stored in one trophic level (such as producers) is actually transferred to the next trophic level (for example the herbivores). – Which means that 90% of the energy is lost. – Eve ...
... • As the food is passed through the food web, most of the energy is lost. – Pyramid of energy - about 10% of the energy stored in one trophic level (such as producers) is actually transferred to the next trophic level (for example the herbivores). – Which means that 90% of the energy is lost. – Eve ...
Chapter vocabulary graphic organizer
... germinate: begins to grow (pg. 20) seedling: a new, small plant that grows from a seed fossil: remains or mark of a living thing from long ago extinct: no longer lives on Earth ...
... germinate: begins to grow (pg. 20) seedling: a new, small plant that grows from a seed fossil: remains or mark of a living thing from long ago extinct: no longer lives on Earth ...
Metabolism of Glucose C6H12O6+6O2 1 unit of Glucose 38 ATP
... In exercise, first you burn off muscle glycogen, then liver glycogen, then lipid. If you only exercise In Diabetes, the cells cannot use glucose for energy. Only lipids. It depends on lipids, but the the Fatty Acids produce much more acetyl-CoA that kreb cycle cannot handle. This results in an accu ...
... In exercise, first you burn off muscle glycogen, then liver glycogen, then lipid. If you only exercise In Diabetes, the cells cannot use glucose for energy. Only lipids. It depends on lipids, but the the Fatty Acids produce much more acetyl-CoA that kreb cycle cannot handle. This results in an accu ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.