Document
... Increased number of mitochondria per cell Increase in the concentration of Krebs cycle enzymes in the matrix ...
... Increased number of mitochondria per cell Increase in the concentration of Krebs cycle enzymes in the matrix ...
• Any living thing is an organism.
... Share your list with the person next to you. Between the two of you decide which five from your list are the most ...
... Share your list with the person next to you. Between the two of you decide which five from your list are the most ...
NEHRU ARTS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE, TM PALAYALAM
... 2. Discuss the influencing of salt concentration and nutrients on microbial growth 3. Describe the different phases of growth curve with illustrations ...
... 2. Discuss the influencing of salt concentration and nutrients on microbial growth 3. Describe the different phases of growth curve with illustrations ...
Energy Metabolism - 35-206-202
... • Occurs in cells with no mitochondria or cells that utilize it when there is no oxygen • Pyruvate is converted to lactate (instead of AcetylCoA) • Lactate is picked up the blood and delivered to the liver • Liver synthesizes compounds used in aerobic metabolism from lactate ...
... • Occurs in cells with no mitochondria or cells that utilize it when there is no oxygen • Pyruvate is converted to lactate (instead of AcetylCoA) • Lactate is picked up the blood and delivered to the liver • Liver synthesizes compounds used in aerobic metabolism from lactate ...
Macromoleucles Notes
... ____________________ _____________________ - usually bonded to oxygen, hydrogen, and other carbon atoms. Most of the matter in your body is _______________!! These are compounds that usually come from organisms Macromolecules Cells and their organelles are made up of smaller building blocks ...
... ____________________ _____________________ - usually bonded to oxygen, hydrogen, and other carbon atoms. Most of the matter in your body is _______________!! These are compounds that usually come from organisms Macromolecules Cells and their organelles are made up of smaller building blocks ...
PHOTOSYNTHESIS & RESPIRATION
... Whenever a bond holding a phosphate is broken, a large amount of usable cellular energy is released. ADENOSINE ...
... Whenever a bond holding a phosphate is broken, a large amount of usable cellular energy is released. ADENOSINE ...
Ecology = scientific study of interactions among organisms and
... At the core of every organism’s interaction with the environment is its need for energy to power life’s processes If an ecosystem is to be self-sustaining it must contain a constant supply of energy which is available to all the organisms within the ecosystem. Energy flows in one direction, from the ...
... At the core of every organism’s interaction with the environment is its need for energy to power life’s processes If an ecosystem is to be self-sustaining it must contain a constant supply of energy which is available to all the organisms within the ecosystem. Energy flows in one direction, from the ...
Second Sample Exam
... chloroplasts. You are testing the hypothesis that the pmf may also power bacteria movement via a flagellar motor. Your test subject is a motile strain of Streptococcus. These bacteria swim when glucose is available for oxidation, but they do not swim when glucose is absent. Explain how each of the f ...
... chloroplasts. You are testing the hypothesis that the pmf may also power bacteria movement via a flagellar motor. Your test subject is a motile strain of Streptococcus. These bacteria swim when glucose is available for oxidation, but they do not swim when glucose is absent. Explain how each of the f ...
9 and 10 notes with blanks
... Following glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, NADH and FADH2 account for most of the energy extracted from food These two electron carriers donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic ...
... Following glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, NADH and FADH2 account for most of the energy extracted from food These two electron carriers donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via oxidative phosphorylation In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic ...
Chapter 7- Microbial Nutrition, Ecology, and
... the flow of water across a membrane within a solution. Most bacteria live in hypotonic environments. Osmotic pressure increases as more and more water is taken up by the cell. The cell wall keeps the cell from bursting. In cells which lack a cell wall (ex. mycoplasmas) or in marine bacteria which re ...
... the flow of water across a membrane within a solution. Most bacteria live in hypotonic environments. Osmotic pressure increases as more and more water is taken up by the cell. The cell wall keeps the cell from bursting. In cells which lack a cell wall (ex. mycoplasmas) or in marine bacteria which re ...
respir532
... The pumping of H+ ions into the INTERMEMBRANE SPACE represents _______________________ potential energy that is harnessed to make ATP. As H+ ions escape through ion channels ATP SYNTHASE back into the matrix, ________________ spins and adds a phosphate to ADP to ATP form _______ ...
... The pumping of H+ ions into the INTERMEMBRANE SPACE represents _______________________ potential energy that is harnessed to make ATP. As H+ ions escape through ion channels ATP SYNTHASE back into the matrix, ________________ spins and adds a phosphate to ADP to ATP form _______ ...
Honors Biology - LangdonBiology.org
... is passed from producer to primary consumer, from primary consumer to secondary consumer, etc. 7. Define ecological succession. Know the role of pioneer organisms, and what a climax community is. 8. Be able to discuss the following cycles of material in the environment: (You do not need to memorize ...
... is passed from producer to primary consumer, from primary consumer to secondary consumer, etc. 7. Define ecological succession. Know the role of pioneer organisms, and what a climax community is. 8. Be able to discuss the following cycles of material in the environment: (You do not need to memorize ...
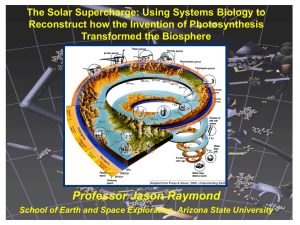
Professor Jason Raymond - School of Earth and Space Exploration
... Aerobic respiration is essential for ATP production in complex life… but none of this existed before oxygen ...
... Aerobic respiration is essential for ATP production in complex life… but none of this existed before oxygen ...
Middle East Jeopardy
... Name the 3 of the many forms in which nitrogen exists during the nitrogen cycle Ammonia, Nitrate, Nitrogen Gas, protein/amino acids ...
... Name the 3 of the many forms in which nitrogen exists during the nitrogen cycle Ammonia, Nitrate, Nitrogen Gas, protein/amino acids ...
Cellular Respiration – Chapter 7 – Lesson 2 – Aerobic Cellular
... Recall that by the end of Stage 1, glycolysis, the cell had formed 2 ATPs, 2NADHs and 2 pyruvate molecules—all in the cytoplasm Stage 2 begins when the two pyruvate molecules formed in glycolysis are transported through the two mitochondrial membranes into the matrix ...
... Recall that by the end of Stage 1, glycolysis, the cell had formed 2 ATPs, 2NADHs and 2 pyruvate molecules—all in the cytoplasm Stage 2 begins when the two pyruvate molecules formed in glycolysis are transported through the two mitochondrial membranes into the matrix ...
Study Guide
... Find all assignments, lectures, and handouts listed above and revisit them. Review Enzymes Quiz – go through all questions without looking at original answers. Connect all of the above terms/concepts together. a. One way to do this would be to pick three terms and form a sentence that uses all three ...
... Find all assignments, lectures, and handouts listed above and revisit them. Review Enzymes Quiz – go through all questions without looking at original answers. Connect all of the above terms/concepts together. a. One way to do this would be to pick three terms and form a sentence that uses all three ...
Chapter 9
... Decomposition involves respiration: the release of the energy fixed by photosynthesis, CO2 and H2O. Decomposition involves several processes: fragmentation, ingestion, egestion, and concentration. All heterotrophs are decomposers to some extent, but the concept of decomposers is reserved for those o ...
... Decomposition involves respiration: the release of the energy fixed by photosynthesis, CO2 and H2O. Decomposition involves several processes: fragmentation, ingestion, egestion, and concentration. All heterotrophs are decomposers to some extent, but the concept of decomposers is reserved for those o ...
Glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to
... phase of glycolysis requires energy, while the second phase completes the conversion to pyruvate and produces ATP and NADH for the cell to use for energy. Overall, the process of glycolysis produces a net gain of two pyruvate molecules, two ATP molecules, and two NADH molecules for the cell to use f ...
... phase of glycolysis requires energy, while the second phase completes the conversion to pyruvate and produces ATP and NADH for the cell to use for energy. Overall, the process of glycolysis produces a net gain of two pyruvate molecules, two ATP molecules, and two NADH molecules for the cell to use f ...
Biological Molecules - Princeton High School
... nutritional value, digested more quickly, converted to fat more quickly) Whole grain bread is a complex carbohydrate (high in fiber, vitamins and minerals, provide more energy, digested slowly) ...
... nutritional value, digested more quickly, converted to fat more quickly) Whole grain bread is a complex carbohydrate (high in fiber, vitamins and minerals, provide more energy, digested slowly) ...
Energy and Nutrients
... Heterotrophs must eat other organisms to obtain nutrients. Fats and carbohydrates provide immediate energy or are stored in the animal’s body. Proteins are broken down into amino acids, which are used to build the animal’s proteins. ...
... Heterotrophs must eat other organisms to obtain nutrients. Fats and carbohydrates provide immediate energy or are stored in the animal’s body. Proteins are broken down into amino acids, which are used to build the animal’s proteins. ...
Aerobic vs. Anaerobic respiration
... • When exercise too much or too quickly muscles use lactic acid fermentation. • Build up of acid causes muscles to burn. • Occurs in animals ...
... • When exercise too much or too quickly muscles use lactic acid fermentation. • Build up of acid causes muscles to burn. • Occurs in animals ...
Ch 3 Notes - The Biosphere (2012
... • Unlike the one-way flow of energy, matter is recycled in the biosphere. • Where does your body get the materials, such as Carbon, it needs to function? __________ • Elements , chemical compounds and other forms of matter are passed from one organism to another through biogeochemical cycles. Bio - ...
... • Unlike the one-way flow of energy, matter is recycled in the biosphere. • Where does your body get the materials, such as Carbon, it needs to function? __________ • Elements , chemical compounds and other forms of matter are passed from one organism to another through biogeochemical cycles. Bio - ...
Ecosystem - angelteach
... C6H12O6 + 6 O2 --> 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy Anaerobic Respiration- (a.k.a. fermentation) a ...
... C6H12O6 + 6 O2 --> 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy Anaerobic Respiration- (a.k.a. fermentation) a ...
Metabolism
... • ATP synthase is the enzyme that makes ATP by chemiosmosis. • It allows protons to pass through the membrane using the kinetic energy to phosphorylate ADP making ATP. • The generation of ATP by chemiosmosis occurs in chloroplasts and mitochondria as well as in some bacteria. ...
... • ATP synthase is the enzyme that makes ATP by chemiosmosis. • It allows protons to pass through the membrane using the kinetic energy to phosphorylate ADP making ATP. • The generation of ATP by chemiosmosis occurs in chloroplasts and mitochondria as well as in some bacteria. ...
Microbial metabolism
Microbial metabolism is the means by which a microbe obtains the energy and nutrients (e.g. carbon) it needs to live and reproduce. Microbes use many different types of metabolic strategies and species can often be differentiated from each other based on metabolic characteristics. The specific metabolic properties of a microbe are the major factors in determining that microbe’s ecological niche, and often allow for that microbe to be useful in industrial processes or responsible for biogeochemical cycles.== Types of microbial metabolism ==All microbial metabolisms can be arranged according to three principles:1. How the organism obtains carbon for synthesising cell mass: autotrophic – carbon is obtained from carbon dioxide (CO2) heterotrophic – carbon is obtained from organic compounds mixotrophic – carbon is obtained from both organic compounds and by fixing carbon dioxide2. How the organism obtains reducing equivalents used either in energy conservation or in biosynthetic reactions: lithotrophic – reducing equivalents are obtained from inorganic compounds organotrophic – reducing equivalents are obtained from organic compounds3. How the organism obtains energy for living and growing: chemotrophic – energy is obtained from external chemical compounds phototrophic – energy is obtained from lightIn practice, these terms are almost freely combined. Typical examples are as follows: chemolithoautotrophs obtain energy from the oxidation of inorganic compounds and carbon from the fixation of carbon dioxide. Examples: Nitrifying bacteria, Sulfur-oxidizing bacteria, Iron-oxidizing bacteria, Knallgas-bacteria photolithoautotrophs obtain energy from light and carbon from the fixation of carbon dioxide, using reducing equivalents from inorganic compounds. Examples: Cyanobacteria (water (H2O) as reducing equivalent donor), Chlorobiaceae, Chromatiaceae (hydrogen sulfide (H2S) as reducing equivalent donor), Chloroflexus (hydrogen (H2) as reducing equivalent donor) chemolithoheterotrophs obtain energy from the oxidation of inorganic compounds, but cannot fix carbon dioxide (CO2). Examples: some Thiobacilus, some Beggiatoa, some Nitrobacter spp., Wolinella (with H2 as reducing equivalent donor), some Knallgas-bacteria, some sulfate-reducing bacteria chemoorganoheterotrophs obtain energy, carbon, and reducing equivalents for biosynthetic reactions from organic compounds. Examples: most bacteria, e. g. Escherichia coli, Bacillus spp., Actinobacteria photoorganoheterotrophs obtain energy from light, carbon and reducing equivalents for biosynthetic reactions from organic compounds. Some species are strictly heterotrophic, many others can also fix carbon dioxide and are mixotrophic. Examples: Rhodobacter, Rhodopseudomonas, Rhodospirillum, Rhodomicrobium, Rhodocyclus, Heliobacterium, Chloroflexus (alternatively to photolithoautotrophy with hydrogen)