Document
... Consuming whey before exercise supports fat burning and may help those who exercise to gain or maintain lean body mass, according to a study conducted in Paris, France.3 Scientists have long known that the composition of a before-workout meal helps determine what material the body burns as fuel duri ...
... Consuming whey before exercise supports fat burning and may help those who exercise to gain or maintain lean body mass, according to a study conducted in Paris, France.3 Scientists have long known that the composition of a before-workout meal helps determine what material the body burns as fuel duri ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION: AEROBIC HARVESTING OF ENERGY
... – a single molecule of glucose is enzymatically cut in half through a series of steps, – two molecules of pyruvate are produced, – two molecules of NAD+ are reduced to two molecules of NADH, and ...
... – a single molecule of glucose is enzymatically cut in half through a series of steps, – two molecules of pyruvate are produced, – two molecules of NAD+ are reduced to two molecules of NADH, and ...
Chapter 6 How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy
... respiration and removes CO2 Respiration, as it relates to breathing, and cellular respiration are not the same. – Respiration, in the breathing sense, refers to an exchange of gases. Usually an organism brings in oxygen from the environment and releases waste CO2. – Cellular respiration is the ...
... respiration and removes CO2 Respiration, as it relates to breathing, and cellular respiration are not the same. – Respiration, in the breathing sense, refers to an exchange of gases. Usually an organism brings in oxygen from the environment and releases waste CO2. – Cellular respiration is the ...
Inherited Propionyl
... 108 cells but her cells produced only 0.005 /Amoles "CO2/3 hr per 108 cells, although they oxidized methylmalonate-"C and succinate-1,4-"C normally. Thus, her fibroblasts expressed the same block in propionate oxidation as did her uncultured leukocytes (4). Propionate oxidation by her father's leuko ...
... 108 cells but her cells produced only 0.005 /Amoles "CO2/3 hr per 108 cells, although they oxidized methylmalonate-"C and succinate-1,4-"C normally. Thus, her fibroblasts expressed the same block in propionate oxidation as did her uncultured leukocytes (4). Propionate oxidation by her father's leuko ...
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... • Aerobic respiration consumes organic molecules and O2 and yields ATP • Anaerobic respiration is similar to aerobic respiration but consumes compounds other than O2 ...
... • Aerobic respiration consumes organic molecules and O2 and yields ATP • Anaerobic respiration is similar to aerobic respiration but consumes compounds other than O2 ...
Glycolysis
... 1) Inherited enzyme deficiencies of glycolysis - Pyruvate kinase deficiency; it genetic deficiency of this enzyme in the erythrocytes lead to hemolytic anemia (excess destruction of RBC) - The normal RBC lacks the mitochondria and it is completely depend on the glycolysis as source of energy. - The ...
... 1) Inherited enzyme deficiencies of glycolysis - Pyruvate kinase deficiency; it genetic deficiency of this enzyme in the erythrocytes lead to hemolytic anemia (excess destruction of RBC) - The normal RBC lacks the mitochondria and it is completely depend on the glycolysis as source of energy. - The ...
Autocatalytic Sets in E. coli Metabolism
... Groups of catalysts with common properties and common biosynthetic pathways, such as menaquinone/ubiquinone, NAD/NADP, or flavins, are grouped together into a “pool” of equivalent catalysts (see Table 1); vi) Bi-directional reactions are split up into two separate reactions, one forward and one reve ...
... Groups of catalysts with common properties and common biosynthetic pathways, such as menaquinone/ubiquinone, NAD/NADP, or flavins, are grouped together into a “pool” of equivalent catalysts (see Table 1); vi) Bi-directional reactions are split up into two separate reactions, one forward and one reve ...
Document
... The respiratory chain is capable of using the energy brought by NADH and FADH2 to pump proton in the inner mitochondrial space; the protons will go passing down the F1 and F0 ATPase system (ATP synthase system) to make ATP. Slide 3: The TCA cycle Pyruvate is decarboxylated and the acetyl group i ...
... The respiratory chain is capable of using the energy brought by NADH and FADH2 to pump proton in the inner mitochondrial space; the protons will go passing down the F1 and F0 ATPase system (ATP synthase system) to make ATP. Slide 3: The TCA cycle Pyruvate is decarboxylated and the acetyl group i ...
Metabolism & Enzymes
... Too much activation energy for life Activation energy amount of energy needed to destabilize the bonds of a molecule moves the reaction over an “energy hill” ...
... Too much activation energy for life Activation energy amount of energy needed to destabilize the bonds of a molecule moves the reaction over an “energy hill” ...
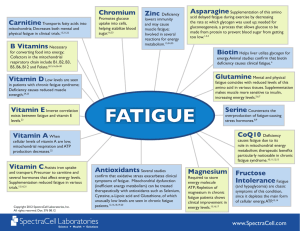
fatigue - Spectracell
... Moorkens G, Manuel Y et al. Magnesium deficit in a sample of the Belgium population presenting with chronic fatigue. Magnes Res 1997;10:329-337. Maes M, Mihaylova I et al. Not in the mind of neurasthenic lazybones but in the cell nucleus: patients with chronic fatigue syndrome have increased product ...
... Moorkens G, Manuel Y et al. Magnesium deficit in a sample of the Belgium population presenting with chronic fatigue. Magnes Res 1997;10:329-337. Maes M, Mihaylova I et al. Not in the mind of neurasthenic lazybones but in the cell nucleus: patients with chronic fatigue syndrome have increased product ...
Chapter 6 How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy
... of organic molecules, generating many NADH and FADH2 molecules With the help of CoA, the acetyl (two-carbon) compound enters the citric acid cycle – At this point, the acetyl group associates with a fourcarbon molecule forming a six-carbon molecule – The six-carbon molecule then passes through a s ...
... of organic molecules, generating many NADH and FADH2 molecules With the help of CoA, the acetyl (two-carbon) compound enters the citric acid cycle – At this point, the acetyl group associates with a fourcarbon molecule forming a six-carbon molecule – The six-carbon molecule then passes through a s ...
AP Biology - TeacherWeb
... Some chemical reactions release energy ___________________ digesting polymers hydrolysis = catabolism ...
... Some chemical reactions release energy ___________________ digesting polymers hydrolysis = catabolism ...
09_Lecture_Presentation
... Cellular respiration includes both aerobic and anaerobic respiration but is often used to refer to aerobic respiration Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy ...
... Cellular respiration includes both aerobic and anaerobic respiration but is often used to refer to aerobic respiration Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy ...
Cellular respiration
... Catabolic Pathways and Production of ATP • The breakdown of organic molecules is exergonic (releasing energy) ...
... Catabolic Pathways and Production of ATP • The breakdown of organic molecules is exergonic (releasing energy) ...
Ketone Bodies Mimic the Life Span Extending
... The toxicity of ROS/RNS is ameliorated by the NADPH system (Fig. 2), the redox potential of which is made more negative by the metabolism of ketone bodies (19,38,39). The redox potential of the free cytosolic [NADP1]/[NADPH] system is about 20.42 V, about the same redox potential as hydrogen and is ...
... The toxicity of ROS/RNS is ameliorated by the NADPH system (Fig. 2), the redox potential of which is made more negative by the metabolism of ketone bodies (19,38,39). The redox potential of the free cytosolic [NADP1]/[NADPH] system is about 20.42 V, about the same redox potential as hydrogen and is ...
Regulation of intermediary metabolism by protein acetylation
... suggest renaming them as lysine-acetyltransferases (KATs) to reflect their broad function in regulating a great number of nonhistone proteins [54], including many metabolic enzymes discussed herein. Intermediary metabolism: often referred to simply as metabolism, includes all steps between extracell ...
... suggest renaming them as lysine-acetyltransferases (KATs) to reflect their broad function in regulating a great number of nonhistone proteins [54], including many metabolic enzymes discussed herein. Intermediary metabolism: often referred to simply as metabolism, includes all steps between extracell ...
Lesson 4.2 Link Reaction and Krebs Cycle
... removed from pyruvate in the form of CO2. The remaining 2-carbon molecule combines with coenzyme A to produce Acetyl Coenzyme A (acetyl CoA). Another oxidation reaction occurs when NAD+ collects more hydrogen ions. This forms reduced NAD (NADH + H+) No ATP is produced in this reaction. ...
... removed from pyruvate in the form of CO2. The remaining 2-carbon molecule combines with coenzyme A to produce Acetyl Coenzyme A (acetyl CoA). Another oxidation reaction occurs when NAD+ collects more hydrogen ions. This forms reduced NAD (NADH + H+) No ATP is produced in this reaction. ...
Volume 201 - 1995 - Part 12 of 67
... Using proximate analyses as a basis for an hypothesis, one can estimate oxygen uptake rate of larval spot and menhaden reaching levels of about 5-10 n m o l ind“ 1I T 1 at 19 ± 1°C. These are not unrealistic values for fish larvae at this temperature. During development and before tissue autolysis b ...
... Using proximate analyses as a basis for an hypothesis, one can estimate oxygen uptake rate of larval spot and menhaden reaching levels of about 5-10 n m o l ind“ 1I T 1 at 19 ± 1°C. These are not unrealistic values for fish larvae at this temperature. During development and before tissue autolysis b ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.