Metabolic Flux Analysis on the Production of Poly(3 - Wiley-VCH
... recovery processes (Lee, 1996a,b; Choi et al., 1998; Choi and Lee, 1999a,b). Process design and economic analysis of SCL-PHA production by various bacteria have been reported, which provided the guidelines for designing an efficient means of PHA production (Choi and Lee, 1997, 1999c, 2000; Lee and C ...
... recovery processes (Lee, 1996a,b; Choi et al., 1998; Choi and Lee, 1999a,b). Process design and economic analysis of SCL-PHA production by various bacteria have been reported, which provided the guidelines for designing an efficient means of PHA production (Choi and Lee, 1997, 1999c, 2000; Lee and C ...
THE STUDY OF INTERMEDIARY METABOLISM OF
... isotopes is increased, this cannot constitute a material foreign to the body, as the living cell is accustomed to molecules containing “heavy atoms .” In work with deuterium, however, care must be taken not to raise its concentration too much. It has been shown by several workers (18) that high conc ...
... isotopes is increased, this cannot constitute a material foreign to the body, as the living cell is accustomed to molecules containing “heavy atoms .” In work with deuterium, however, care must be taken not to raise its concentration too much. It has been shown by several workers (18) that high conc ...
Past Exam Questions - Intermediate School Biology
... 42. Name a compound to which pyruvic acid may be converted, in the absence of oxygen. Lactic acid or ethanol + CO2 43. In aerobic respiration, the product of the first stage moves to the mitochondrion. Outline subsequent events in the total breakdown of this product. (Begins with) acetyl co-enzyme A ...
... 42. Name a compound to which pyruvic acid may be converted, in the absence of oxygen. Lactic acid or ethanol + CO2 43. In aerobic respiration, the product of the first stage moves to the mitochondrion. Outline subsequent events in the total breakdown of this product. (Begins with) acetyl co-enzyme A ...
AMINO ACIDS METABOLISM ** Dr. Mohammed Abdullateef **
... 4. Urea: nitrogen compound composed of 2 amino groups (−NH2) joined by acarbonyl (−C=O) functional group; is the main nitrogen-containing ...
... 4. Urea: nitrogen compound composed of 2 amino groups (−NH2) joined by acarbonyl (−C=O) functional group; is the main nitrogen-containing ...
Chapter 9: Pathways that Harvest Chemical
... Three metabolic processes harvest the energy in the chemical bonds of glucose: glycolysis, cellular respiration, and fermentation (Figure 9.1). All three processes involve pathways made up of many distinct chemical reactions. ...
... Three metabolic processes harvest the energy in the chemical bonds of glucose: glycolysis, cellular respiration, and fermentation (Figure 9.1). All three processes involve pathways made up of many distinct chemical reactions. ...
Ecological speciation model
... Heterofermentative organisms use a pathway with a greater number of redox reactions than Streptococcus. Make very oxidized and very reduced compounds. More NAD(P)H to be reoxidized constrains ATP synthesis, high energy intermediate used as an electron acceptor. Vitamins: essential portions of cofact ...
... Heterofermentative organisms use a pathway with a greater number of redox reactions than Streptococcus. Make very oxidized and very reduced compounds. More NAD(P)H to be reoxidized constrains ATP synthesis, high energy intermediate used as an electron acceptor. Vitamins: essential portions of cofact ...
Table of Available Analyses - NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyde
... This term is a misnomer as the assays look for specific drugs or groups of drugs only. The commonly abused substances screened for at present are amphetamines (but not ecstasy), opiates, benzodiazepines and methadone. Where clinical suspicion is raised, specific requests for ecstasy, barbiturates, b ...
... This term is a misnomer as the assays look for specific drugs or groups of drugs only. The commonly abused substances screened for at present are amphetamines (but not ecstasy), opiates, benzodiazepines and methadone. Where clinical suspicion is raised, specific requests for ecstasy, barbiturates, b ...
Role of Krebs Cycle in the Mechanism of Stability Internal Medium
... of DNA replication. Then it occurs M phase of cellular cycle of Mitosis in cell division that transfers the new cells into Go phase of normal cellular cycle. Thus, nuclei DNA (nDNA) of formed new cells are not subjected to ruining capability of ROS/H2O2/free radicals in normal development cellular c ...
... of DNA replication. Then it occurs M phase of cellular cycle of Mitosis in cell division that transfers the new cells into Go phase of normal cellular cycle. Thus, nuclei DNA (nDNA) of formed new cells are not subjected to ruining capability of ROS/H2O2/free radicals in normal development cellular c ...
Hydrostatic pressure effects on deswelling of de
... pressures greater than 15 mm. Hg there is an influence of pressure on the deswelling rate. Between 5 and 15 mm. Hg there is no significant difference in deswelling rate, thus a curve is shown with a pressure-independent component between 5 and 15 mm. Hg and a linear relationship indicated from 15 to ...
... pressures greater than 15 mm. Hg there is an influence of pressure on the deswelling rate. Between 5 and 15 mm. Hg there is no significant difference in deswelling rate, thus a curve is shown with a pressure-independent component between 5 and 15 mm. Hg and a linear relationship indicated from 15 to ...
Chapter 6 Slides
... respiration and removes CO2 Respiration, as it relates to breathing, and cellular respiration are not the same. – Respiration, in the breathing sense, refers to an exchange of gases. Usually an organism brings in oxygen from the environment and releases waste CO2. – Cellular respiration is the aer ...
... respiration and removes CO2 Respiration, as it relates to breathing, and cellular respiration are not the same. – Respiration, in the breathing sense, refers to an exchange of gases. Usually an organism brings in oxygen from the environment and releases waste CO2. – Cellular respiration is the aer ...
File
... In plasma-niacin found in nicotinic amide bloodand nicotinic acid 1/3 of nicotinic acid (plasma) bound to plasma proteins bloodnicotinamide and acidcell membrane by simple diffusion Nicotinic acid transport kidney tubules and red blood cells require carrier ...
... In plasma-niacin found in nicotinic amide bloodand nicotinic acid 1/3 of nicotinic acid (plasma) bound to plasma proteins bloodnicotinamide and acidcell membrane by simple diffusion Nicotinic acid transport kidney tubules and red blood cells require carrier ...
biochem ch 23 [2-9
... Phytanic acid oxidized via α-oxidation pathway; fatty acid shortened so methyl groups appear on αcarbon and can no longer interfere with oxidation of β-carbon; peroxisomal β-oxidation then goes When medium-chain length reached, fatty acid transferred to mitochondrion as carnitine derivative and β- ...
... Phytanic acid oxidized via α-oxidation pathway; fatty acid shortened so methyl groups appear on αcarbon and can no longer interfere with oxidation of β-carbon; peroxisomal β-oxidation then goes When medium-chain length reached, fatty acid transferred to mitochondrion as carnitine derivative and β- ...
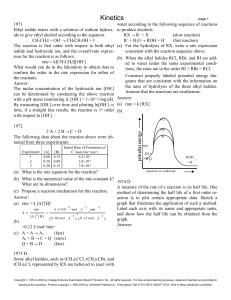
Kinetics
... (a) According to the data shown, what is the rate law (a) Explain how this statement can be true. for the reaction above? (b) 2 XY X2 + Y2 (b) On the basis of the rate law determined in part (a), 1. For the hypothetical reaction above, give a calculate the specific rate constant. Specify the rate ...
... (a) According to the data shown, what is the rate law (a) Explain how this statement can be true. for the reaction above? (b) 2 XY X2 + Y2 (b) On the basis of the rate law determined in part (a), 1. For the hypothetical reaction above, give a calculate the specific rate constant. Specify the rate ...
Lab Module 7 - philipdarrenjones.com
... a. The number of drops of NaOH should be equal to the amount of carbonic acid produced and therefore the amount of CO2 you blew into the water. b. Record the number of drops of NaOH in the table below. 7. Now perform vigorous exercise (do not perform this part if your health does not permit it) such ...
... a. The number of drops of NaOH should be equal to the amount of carbonic acid produced and therefore the amount of CO2 you blew into the water. b. Record the number of drops of NaOH in the table below. 7. Now perform vigorous exercise (do not perform this part if your health does not permit it) such ...
Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis
... Glycolysis • Generation of ATP (with or without oxygen) • The role of glycolysis in different tissues ...
... Glycolysis • Generation of ATP (with or without oxygen) • The role of glycolysis in different tissues ...
Chapter 6
... respiration and removes CO2 Respiration, as it relates to breathing, and cellular respiration are not the same. – Respiration, in the breathing sense, refers to an exchange of gases. Usually an organism brings in oxygen from the environment and releases waste CO2. – Cellular respiration is the aer ...
... respiration and removes CO2 Respiration, as it relates to breathing, and cellular respiration are not the same. – Respiration, in the breathing sense, refers to an exchange of gases. Usually an organism brings in oxygen from the environment and releases waste CO2. – Cellular respiration is the aer ...
Fatty Acid Catabolism
... primary energy source. Glucose is used to recharge cellular ATP and NADPH levels. The ATP and NADPH are used as the energy source and reducing equivalents for biosynthetic reactions. Glucose not immediately needed for energy is stored as glycogen or used as a precursor for the hetero-oligosaccharide ...
... primary energy source. Glucose is used to recharge cellular ATP and NADPH levels. The ATP and NADPH are used as the energy source and reducing equivalents for biosynthetic reactions. Glucose not immediately needed for energy is stored as glycogen or used as a precursor for the hetero-oligosaccharide ...
5. TCA Cycle
... Looking back at glycolysis Glucose + 2Pi + 2 ADP + 2 NAD+ -> 2 pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2H+ + 2H2O ...
... Looking back at glycolysis Glucose + 2Pi + 2 ADP + 2 NAD+ -> 2 pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2H+ + 2H2O ...
The rate of glycolysis quantitatively mediates specific
... these proposals however is not without difficulties. For example, estimates have found that over 90 % of the carbon from glucose is secreted as lactate and alanine, leaving little room for biosynthesis [10]. Also, the rapid ATP produced by glycolysis can also be obtained by other mechanisms such as ...
... these proposals however is not without difficulties. For example, estimates have found that over 90 % of the carbon from glucose is secreted as lactate and alanine, leaving little room for biosynthesis [10]. Also, the rapid ATP produced by glycolysis can also be obtained by other mechanisms such as ...
Energy „flow” in the organism
... Proteins of animal origin – high BV (they contain all of the essential amino acids, with a nearly optimal composition) meat (75%), milk, diary products (lactalbumin, lactoglobulin, casein; ~85%), egg (ovalbumin; 94%), whey protein (~100%!) Proteins of plant origin: usually lower BV ...
... Proteins of animal origin – high BV (they contain all of the essential amino acids, with a nearly optimal composition) meat (75%), milk, diary products (lactalbumin, lactoglobulin, casein; ~85%), egg (ovalbumin; 94%), whey protein (~100%!) Proteins of plant origin: usually lower BV ...
U4L22 exercise - University of Sydney
... • When glycogen has run out, only fatty acid oxidation can be used for ATP generation • Power output is lower when using only fatty acids • “Hitting the Wall” • Cannot sprint if there’s no glycogen ...
... • When glycogen has run out, only fatty acid oxidation can be used for ATP generation • Power output is lower when using only fatty acids • “Hitting the Wall” • Cannot sprint if there’s no glycogen ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.