Localized in vivo 13C-NMR of Glutamate Metabolism in the Human
... Glucose is the main substrate used for energy metabolism by the normal human brain. Once transported across the blood-brain barrier, glucose is readily metabolized [1, 2]. Studies of nervous tissue have shown that label from glucose accumulates in the intermediates of glycolysis and of the TCA cycle ...
... Glucose is the main substrate used for energy metabolism by the normal human brain. Once transported across the blood-brain barrier, glucose is readily metabolized [1, 2]. Studies of nervous tissue have shown that label from glucose accumulates in the intermediates of glycolysis and of the TCA cycle ...
Biochemistry of exercise-induced metabolic acidosis
... seems that on the topic of lactic acidosis, the world’s leading scientists and academics have and continue to make this error. As such, there is a need to define what is a fact and what is a construct. A fact is defined as “something that has actual existence; that has objective reality” (58). Conve ...
... seems that on the topic of lactic acidosis, the world’s leading scientists and academics have and continue to make this error. As such, there is a need to define what is a fact and what is a construct. A fact is defined as “something that has actual existence; that has objective reality” (58). Conve ...
Unit 8A
... A more oxidized cytosolic redox state in autism could favor anaerobic glycolysis over oxidative phosphorylation as a source of adenosine triphosphate. Although skeletal muscle can tolerate this shift in metabolism, consequences for brain function could be devastating due to its heavy reliance on mit ...
... A more oxidized cytosolic redox state in autism could favor anaerobic glycolysis over oxidative phosphorylation as a source of adenosine triphosphate. Although skeletal muscle can tolerate this shift in metabolism, consequences for brain function could be devastating due to its heavy reliance on mit ...
Document
... acetyl-CoA + NADH + CO2 • One of the carbons from pyruvate is released in CO2 • Two carbons are attached to coenzyme A and continue on to the Krebs cycle ...
... acetyl-CoA + NADH + CO2 • One of the carbons from pyruvate is released in CO2 • Two carbons are attached to coenzyme A and continue on to the Krebs cycle ...
Practical part
... The calculation of transaminase activity. 1 unit of alanine aminotransferase is such quantity of enzyme, which produce 1 g of pyruvate under described conditions. The calculation of enzyme activity to micromoles of pyruvate, formed by 1 ml of serum in one hour is provided according to formula: A = ...
... The calculation of transaminase activity. 1 unit of alanine aminotransferase is such quantity of enzyme, which produce 1 g of pyruvate under described conditions. The calculation of enzyme activity to micromoles of pyruvate, formed by 1 ml of serum in one hour is provided according to formula: A = ...
Cellular Respiration (Text Book)
... phosphorylation, chemiosmosis couples electron transport to ATP synthesis • Following glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, NADH and FADH2 account for most of the energy extracted from food • These two electron carriers donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via ...
... phosphorylation, chemiosmosis couples electron transport to ATP synthesis • Following glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, NADH and FADH2 account for most of the energy extracted from food • These two electron carriers donate electrons to the electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthesis via ...
Chapter 9
... • In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps • Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme • As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration • Each NADH (the reduce ...
... • In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps • Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme • As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration • Each NADH (the reduce ...
HBMuscle
... ii. contraction period (10 - 100 ms) - from beginning of contraction to maximum force (tension) iii. relaxation period (10 - 100 ms) - time from maximum force to original relaxed state C. Graded Muscle Responses (smooth, not All-or-None) 1. Frequency of Stimulation (Wave Summation) - when motor unit ...
... ii. contraction period (10 - 100 ms) - from beginning of contraction to maximum force (tension) iii. relaxation period (10 - 100 ms) - time from maximum force to original relaxed state C. Graded Muscle Responses (smooth, not All-or-None) 1. Frequency of Stimulation (Wave Summation) - when motor unit ...
Enzymes - Coleg y Cymoedd Moodle
... internal system can be regulated to provide the optimum conditions for the enzyme. 8. Their job is to take in and destroy foreign organisms and debris. The destruction is caused by digestive enzymes in the lysosomes of these cells. 9. Enzymes regulate metabolic processes by catalysing reactions at a ...
... internal system can be regulated to provide the optimum conditions for the enzyme. 8. Their job is to take in and destroy foreign organisms and debris. The destruction is caused by digestive enzymes in the lysosomes of these cells. 9. Enzymes regulate metabolic processes by catalysing reactions at a ...
15. The Importance of Energy Changes and Electron Transfer in
... Play in Metabolism ◈ Evolution of aerobic metabolism - Nutrients are oxidized to carbon dioxide and water. - Organisms can obtain far more energy from nutrient by aerobic metabolism. - Three process: citric acid cycle, electron transport, and oxidative phosphorylation ...
... Play in Metabolism ◈ Evolution of aerobic metabolism - Nutrients are oxidized to carbon dioxide and water. - Organisms can obtain far more energy from nutrient by aerobic metabolism. - Three process: citric acid cycle, electron transport, and oxidative phosphorylation ...
mechanism of photosynthesis
... In cyclic photophosphorylation the electrons lost by PS-I is cycled back to it, whereas in non-cyclic photophosphorylation, one electron is lost it doesn’t enter into PS-II, thus it involves both PS-I and PS-II. (i) Non-cyclic photophosphorylation : Hill and Bendal (1960) and Robinowitch and Govindj ...
... In cyclic photophosphorylation the electrons lost by PS-I is cycled back to it, whereas in non-cyclic photophosphorylation, one electron is lost it doesn’t enter into PS-II, thus it involves both PS-I and PS-II. (i) Non-cyclic photophosphorylation : Hill and Bendal (1960) and Robinowitch and Govindj ...
1 Proteins: Workshop I Amino Acids
... investigate the structure of amino acids and how they affect the structure of a protein. We will also investigate the affect of structure on the function of a protein. Why learn about proteins? Of the three classes of biomolecules - lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins – proteins have some of the mos ...
... investigate the structure of amino acids and how they affect the structure of a protein. We will also investigate the affect of structure on the function of a protein. Why learn about proteins? Of the three classes of biomolecules - lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins – proteins have some of the mos ...
439EnPanc13
... Increases production of glucose from amino acids (gluconeogenesis). Also increases lipolysis, to free fatty acids for metabolism. Result: maintenance of blood glucose levels ...
... Increases production of glucose from amino acids (gluconeogenesis). Also increases lipolysis, to free fatty acids for metabolism. Result: maintenance of blood glucose levels ...
Transport and Utilization of Lipids in Insect Flight
... shuttle mechanism. Through ligand blotting techniques, a number of flight muscle membrane proteins were shown to bind to HDLp or LDLp, most prominently a 30-kDa protein. At present, it is unclear whether this or another lipophorin-binding protein is involved in the lipid delivery to the flight muscl ...
... shuttle mechanism. Through ligand blotting techniques, a number of flight muscle membrane proteins were shown to bind to HDLp or LDLp, most prominently a 30-kDa protein. At present, it is unclear whether this or another lipophorin-binding protein is involved in the lipid delivery to the flight muscl ...
Oxidative Phosphorylation in Homogenates of
... phosphate is being removed from the reaction. This stationary phase of the ammonia curves in kidney homogenates is much more pronounced in individual experiments, e.g., as shown in Chart 6, than in Chart 5, which represents the average of five homogenates. The data suggest that ATP, as such, cannot ...
... phosphate is being removed from the reaction. This stationary phase of the ammonia curves in kidney homogenates is much more pronounced in individual experiments, e.g., as shown in Chart 6, than in Chart 5, which represents the average of five homogenates. The data suggest that ATP, as such, cannot ...
Metabolic processes of Methanococcus maripaludis and potential
... [17]. Although the specific roles of the pili in M. mariplaudis are still unknown [18], if archaeal pili are similar to their bacterial counterparts, then they could be involved in functions related to cell-to-cell twitching, motility, attachment, biofilm formation, etc. Figure 2 provides a comprehe ...
... [17]. Although the specific roles of the pili in M. mariplaudis are still unknown [18], if archaeal pili are similar to their bacterial counterparts, then they could be involved in functions related to cell-to-cell twitching, motility, attachment, biofilm formation, etc. Figure 2 provides a comprehe ...
medbiochem exam 1, 2000
... D. increasing the concentration of BPG in erythrocytes decreases the oxygen affinity of hemoglobin. 46. Your have just admitted a male infant with a congenital deficiency for pyruvate dehydrogenase. Which of the following pathways in his brain will be accelerated after he is fed? A. Electron transpo ...
... D. increasing the concentration of BPG in erythrocytes decreases the oxygen affinity of hemoglobin. 46. Your have just admitted a male infant with a congenital deficiency for pyruvate dehydrogenase. Which of the following pathways in his brain will be accelerated after he is fed? A. Electron transpo ...
Respiration - Biology Junction
... • The overall process is: • Organic compounds + O2 -> CO2 + H2O + Energy ...
... • The overall process is: • Organic compounds + O2 -> CO2 + H2O + Energy ...
ppt
... An individual with a deficiency of an enzyme in the pathway for carnitine synthesis is not eating adequate amounts of carnitine in the diet. Which of the following effectw would you expect during fasting as compared with an individual with an adequate intake and synthesis of carnitine? a. Fatty acid ...
... An individual with a deficiency of an enzyme in the pathway for carnitine synthesis is not eating adequate amounts of carnitine in the diet. Which of the following effectw would you expect during fasting as compared with an individual with an adequate intake and synthesis of carnitine? a. Fatty acid ...
chapter 21
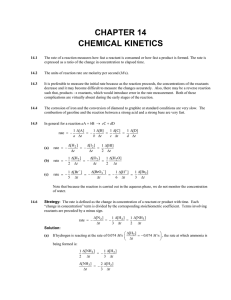
... (a) Strategy: We are given information as to how the concentrations of X2, Y, and Z affect the rate of the reaction and are asked to determine the rate law. We assume that the rate law takes the form rate k[X2]x[Y]y[Z]z How do we use the information to determine x, y, and z? Solution: Since the re ...
... (a) Strategy: We are given information as to how the concentrations of X2, Y, and Z affect the rate of the reaction and are asked to determine the rate law. We assume that the rate law takes the form rate k[X2]x[Y]y[Z]z How do we use the information to determine x, y, and z? Solution: Since the re ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.