proteins
... • 20 % of AA in portal blood are branched AA • In liver, most AA are utilized for synthesis of proteins, Glc, FA. • Val, Leu, Ile are not metabolized in liver due to the lack of aminotrasferases they predominate (70 %) in central circulation • High content of ammonia in portal blood is removed by ...
... • 20 % of AA in portal blood are branched AA • In liver, most AA are utilized for synthesis of proteins, Glc, FA. • Val, Leu, Ile are not metabolized in liver due to the lack of aminotrasferases they predominate (70 %) in central circulation • High content of ammonia in portal blood is removed by ...
Chapter 16 The Citric Acid Cycle
... • A 2-carbon unit Acetyl-CoA is added to the cycle • And two CO2 molecules leave (but they are different carbons…) • During the course of changes in the carbon skeleton and its oxidation state • And the transfer of energy to form GTP (aka. the “Canadian $”) and reducing power, as NADH and FADH2 • It ...
... • A 2-carbon unit Acetyl-CoA is added to the cycle • And two CO2 molecules leave (but they are different carbons…) • During the course of changes in the carbon skeleton and its oxidation state • And the transfer of energy to form GTP (aka. the “Canadian $”) and reducing power, as NADH and FADH2 • It ...
Cellular Respiration - Napa Valley College
... oxygen, produces carbon dioxide. § Anaerobic Fermentation – does not require oxygen, does not produce carbon dioxide. ...
... oxygen, produces carbon dioxide. § Anaerobic Fermentation – does not require oxygen, does not produce carbon dioxide. ...
kidney 6
... 6) Removal of reabsorbed materials by PTC: • The dynamics of reabsorption in PTC is determined by Starling ...
... 6) Removal of reabsorbed materials by PTC: • The dynamics of reabsorption in PTC is determined by Starling ...
Neonatal nutrition
... • Once milk supply good and baby back to birth weight can allow baby to go 5 hours during a 24 hour period without a feed ...
... • Once milk supply good and baby back to birth weight can allow baby to go 5 hours during a 24 hour period without a feed ...
Lecture 27
... • Propionyl-CoA is converted to S-Methylmalonyl-CoA by propionyl-CoA carboxylase with ATP and CO2. Uses a carboxybiotynyl cofactor for the mechanism. • S-Methylmalonyl-CoA is converted to R-MethylmalonylCoA by methylmalonyl-CoA racemase. • R-Methylmalonyl-CoA is converted to Succinyl-CoA by methylma ...
... • Propionyl-CoA is converted to S-Methylmalonyl-CoA by propionyl-CoA carboxylase with ATP and CO2. Uses a carboxybiotynyl cofactor for the mechanism. • S-Methylmalonyl-CoA is converted to R-MethylmalonylCoA by methylmalonyl-CoA racemase. • R-Methylmalonyl-CoA is converted to Succinyl-CoA by methylma ...
E. Transport of certain drugs
... This theme introduces the aromatic heterocyclic purine and pyrimidine and their major derivatives, the nucleosides and nucleotides, which supply the monomer units or building blocks of nucleic acids and serve additional diverse functions essential for life and health. Major biochemical functions of ...
... This theme introduces the aromatic heterocyclic purine and pyrimidine and their major derivatives, the nucleosides and nucleotides, which supply the monomer units or building blocks of nucleic acids and serve additional diverse functions essential for life and health. Major biochemical functions of ...
Details of the scope analysis for each organism
... The list of externally available molecules is supplanted by 4 macromolecules (cytoplasmic and mitochondrial oxidized thioredoxin; ferricytochrome c; and dolichol) and mitochondrial hydrogen ion to define the initial seed for the scope analysis. The scope of these molecules does not contain all produ ...
... The list of externally available molecules is supplanted by 4 macromolecules (cytoplasmic and mitochondrial oxidized thioredoxin; ferricytochrome c; and dolichol) and mitochondrial hydrogen ion to define the initial seed for the scope analysis. The scope of these molecules does not contain all produ ...
enzyme substrate
... reaction (use water and break chemical bonds). • Exergonic – produce more energy than consume • Anabolism is the energy-using processes, anabolic, biosynthetic, building of complex molecules from simpler ones, involve dehydration synthesis reactions (reactions that release water) • Endergonic – cons ...
... reaction (use water and break chemical bonds). • Exergonic – produce more energy than consume • Anabolism is the energy-using processes, anabolic, biosynthetic, building of complex molecules from simpler ones, involve dehydration synthesis reactions (reactions that release water) • Endergonic – cons ...
Nucleotide Metabolism - Oregon State University
... Inosine is Converted to Hypoxanthine and Ribose-1P by a Purine Phosphorylase Hypoxanthine (Xanthine Oxidase) and Guanine (Guanase) are Converted to Xanthine Xanthine is Converted to Uric Acid by Xanthine Oxidase Uric Acid Crystals are the Cause of Gout Gout Treated With the Xanthine Oxidase Inhibito ...
... Inosine is Converted to Hypoxanthine and Ribose-1P by a Purine Phosphorylase Hypoxanthine (Xanthine Oxidase) and Guanine (Guanase) are Converted to Xanthine Xanthine is Converted to Uric Acid by Xanthine Oxidase Uric Acid Crystals are the Cause of Gout Gout Treated With the Xanthine Oxidase Inhibito ...
Document
... The main pathway for glucose oxidation. It forms pyruvate anaerobically. Phosphogluconate pathway An auxiliary route for glucose oxidation in animals. It produces ribose-5-phosphate. Gluconeogenesis Pathway for the synthesis of glucose from pyruvate. ...
... The main pathway for glucose oxidation. It forms pyruvate anaerobically. Phosphogluconate pathway An auxiliary route for glucose oxidation in animals. It produces ribose-5-phosphate. Gluconeogenesis Pathway for the synthesis of glucose from pyruvate. ...
2 ATP - HCC Learning Web
... • Reactions that result in the transfer of one or more electrons (e−) from one reactant to another are oxidation-reduction reactions, or redox reactions. • The loss of electrons from a substance is called oxidation or is oxidized. • The addition of electrons to another substance is called reduction ...
... • Reactions that result in the transfer of one or more electrons (e−) from one reactant to another are oxidation-reduction reactions, or redox reactions. • The loss of electrons from a substance is called oxidation or is oxidized. • The addition of electrons to another substance is called reduction ...
Nucleotide Metabolism
... Inosine is Converted to Hypoxanthine and Ribose-1P by a Purine Phosphorylase Hypoxanthine (Xanthine Oxidase) and Guanine (Guanase) are Converted to Xanthine Xanthine is Converted to Uric Acid by Xanthine Oxidase Uric Acid Crystals are the Cause of Gout Gout Treated With the Xanthine Oxidase Inhibito ...
... Inosine is Converted to Hypoxanthine and Ribose-1P by a Purine Phosphorylase Hypoxanthine (Xanthine Oxidase) and Guanine (Guanase) are Converted to Xanthine Xanthine is Converted to Uric Acid by Xanthine Oxidase Uric Acid Crystals are the Cause of Gout Gout Treated With the Xanthine Oxidase Inhibito ...
Problem-Set Solutions
... form bilirubin and removal of bilirubin from the blood by the liver is upset. 26.80 liver diseases, spleen malfunction, gallbladder malfunction 26.81 The numerous metabolic pathways of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins are linked by various compounds that participate in more than one pathway. Duri ...
... form bilirubin and removal of bilirubin from the blood by the liver is upset. 26.80 liver diseases, spleen malfunction, gallbladder malfunction 26.81 The numerous metabolic pathways of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins are linked by various compounds that participate in more than one pathway. Duri ...
Biology: Concepts and Connections, 6e (Campbell)
... A) Exergonic reactions involve ionic bonds; endergonic reactions involve covalent bonds. B) Exergonic reactions involve the breaking of bonds; endergonic reactions involve the formation of bonds. C) Exergonic reactions involve the formation of bonds; endergonic reactions involve the breaking of bond ...
... A) Exergonic reactions involve ionic bonds; endergonic reactions involve covalent bonds. B) Exergonic reactions involve the breaking of bonds; endergonic reactions involve the formation of bonds. C) Exergonic reactions involve the formation of bonds; endergonic reactions involve the breaking of bond ...
FREE Sample Here
... except one. Which one is the exception? a. AMDRs were established to ensure sufficient intakes of the micronutrients. b. One focus of the AMDRs is reduction of chronic disease. c. Macronutrients are fat, carbohydrate, protein, and two polyunsaturated fatty acids. d. Consuming amounts outside the AMD ...
... except one. Which one is the exception? a. AMDRs were established to ensure sufficient intakes of the micronutrients. b. One focus of the AMDRs is reduction of chronic disease. c. Macronutrients are fat, carbohydrate, protein, and two polyunsaturated fatty acids. d. Consuming amounts outside the AMD ...
M01
... - secondary to many genetic / acquired disorders (episodic hypoketotic hypoglycemia, starting in infancy) Carnitine supplementation : supposed to increase energy production, because it facilitates the FA transport into mitochondria for oxidation, sparing glycogen from the muscles during exercise; co ...
... - secondary to many genetic / acquired disorders (episodic hypoketotic hypoglycemia, starting in infancy) Carnitine supplementation : supposed to increase energy production, because it facilitates the FA transport into mitochondria for oxidation, sparing glycogen from the muscles during exercise; co ...
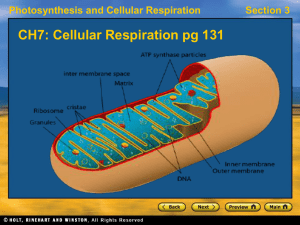
CH7Cellular-Respiration
... • The first stage of aerobic respiration is the Krebs cycle, a series of reactions that produce electron carriers (NADH and FADH2). • The electron carriers enter an electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthase. • Up to 38 ATP molecules can be produced from one glucose molecule in aerobic resp ...
... • The first stage of aerobic respiration is the Krebs cycle, a series of reactions that produce electron carriers (NADH and FADH2). • The electron carriers enter an electron transport chain, which powers ATP synthase. • Up to 38 ATP molecules can be produced from one glucose molecule in aerobic resp ...
Biochemistry_Written_Tests.doc
... multienzyme means several enzymes that catalyzes successive steps in a series of reactions which are associated together as a complex, also: fatty acid synthase complex ...
... multienzyme means several enzymes that catalyzes successive steps in a series of reactions which are associated together as a complex, also: fatty acid synthase complex ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.