The History
... – Used for anabolism and catabolism – Conserve materials to build new compounds – Break down remaining compounds ...
... – Used for anabolism and catabolism – Conserve materials to build new compounds – Break down remaining compounds ...
Chapter 8
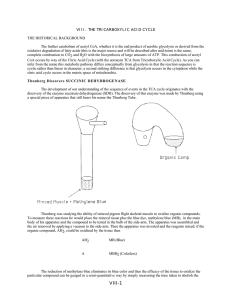
... THE HISTORICAL BACKGROUND The further catabolism of acetyl CoA, whether it is the end product of aerobic glycolysis or derived from the oxidative degradation of fatty acids (this is the major source and will be described after mid-term) is the same; complete combustion to CO2 and H2O with the biosyn ...
... THE HISTORICAL BACKGROUND The further catabolism of acetyl CoA, whether it is the end product of aerobic glycolysis or derived from the oxidative degradation of fatty acids (this is the major source and will be described after mid-term) is the same; complete combustion to CO2 and H2O with the biosyn ...
Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis
... The first reaction is thermodynamically quite favorable, with a standard freeenergy change, ⌬G°⬘, of approximately ⫺50 kJ mol⫺1 (⫺12 kcal mol⫺1), whereas the second reaction is quite unfavorable, with a standard free-energy change of the same magnitude but the opposite sign. If these two reactions s ...
... The first reaction is thermodynamically quite favorable, with a standard freeenergy change, ⌬G°⬘, of approximately ⫺50 kJ mol⫺1 (⫺12 kcal mol⫺1), whereas the second reaction is quite unfavorable, with a standard free-energy change of the same magnitude but the opposite sign. If these two reactions s ...
Owens et al., 1998, Acidosis in cattle: a review.
... higher when cattle are limit- or program-fed. To date, acidosis incidence has not been reported to be increased by limit feeding, perhaps because the total quantity of feed supplied is not excessive. However, when excessive amounts of feed are provided, either mistakenly or during the switch from li ...
... higher when cattle are limit- or program-fed. To date, acidosis incidence has not been reported to be increased by limit feeding, perhaps because the total quantity of feed supplied is not excessive. However, when excessive amounts of feed are provided, either mistakenly or during the switch from li ...
respiration
... 2b Differences between burning and respiration: vi In burning, energy is released in the forms of heat and light while in respiration, energy released is used to form ATP while some is lost as heat . ...
... 2b Differences between burning and respiration: vi In burning, energy is released in the forms of heat and light while in respiration, energy released is used to form ATP while some is lost as heat . ...
UNIVERSITAT DE BARCELONA Divisió de Ciències Experimentals i Matemàtiques Facultat de Biologia
... urea cycle (Barber et al., 1985), as well as a wider nitrogen gap than comparable animals fed a standard diet (Esteve et al., 1992). Several reports show that cafeteria-fed rats accrue more protein —in addition to much more fat— than control reference diet-fed animals (Esteve et al., 1992), and it h ...
... urea cycle (Barber et al., 1985), as well as a wider nitrogen gap than comparable animals fed a standard diet (Esteve et al., 1992). Several reports show that cafeteria-fed rats accrue more protein —in addition to much more fat— than control reference diet-fed animals (Esteve et al., 1992), and it h ...
ppt for
... Assis et. al, U Michigan) 1) 43% of all rodent piR clusters arose after rodent-primate divergence. While the highest known expansion rate for olfactory receptors is ...
... Assis et. al, U Michigan) 1) 43% of all rodent piR clusters arose after rodent-primate divergence. While the highest known expansion rate for olfactory receptors is ...
Engineering of Aromatic Amino Acid Metabolism in
... The main application field of amino acids nowadays is in food. About fifty percent of amino acids manufactured worldwide are applied in human food production (Fig. 2). The amino acids with the largest market volumes are glutamic acid, lysine and methionine (64) (Table 1). The microbial production of ...
... The main application field of amino acids nowadays is in food. About fifty percent of amino acids manufactured worldwide are applied in human food production (Fig. 2). The amino acids with the largest market volumes are glutamic acid, lysine and methionine (64) (Table 1). The microbial production of ...
Download: 7.2 MB PDF
... pioneering a systems approach that supports healthcare providers in the personalized treatment and prevention of chronic disease. Chronic diseases are often complex and Genova’s system-based testing helps physicians develop targeted treatments for their patients. Easy-to-read color graphic reports s ...
... pioneering a systems approach that supports healthcare providers in the personalized treatment and prevention of chronic disease. Chronic diseases are often complex and Genova’s system-based testing helps physicians develop targeted treatments for their patients. Easy-to-read color graphic reports s ...
A Systematic Approach to Enzyme Assay Optimization, Illustrated by
... for assay design begins with developing a mathematical representation, or model, of the enzyme kinetics of the assay. The parameters of the model, which are the enzymes’ Michaehis constants, are derived from experimental data. For each of the two assays, these data consist of activity measurements a ...
... for assay design begins with developing a mathematical representation, or model, of the enzyme kinetics of the assay. The parameters of the model, which are the enzymes’ Michaehis constants, are derived from experimental data. For each of the two assays, these data consist of activity measurements a ...
The malonyl-CoA insensitive fraction of muscle CPT1 is greater in
... Malonyl-CoA sensitivity in homogenates of red and white gastrocnemius. To better evaluate fiber-type dependent differences in malonyl-CoA sensitivity, palmitate oxidation to CO2 was studied in the presence of increasing malonyl-CoA in whole homogenates of red and white gastrocnemius (Figure 3A). In ...
... Malonyl-CoA sensitivity in homogenates of red and white gastrocnemius. To better evaluate fiber-type dependent differences in malonyl-CoA sensitivity, palmitate oxidation to CO2 was studied in the presence of increasing malonyl-CoA in whole homogenates of red and white gastrocnemius (Figure 3A). In ...
Glutamine and the bowel
... For amino sugar synthesis : 1. glutamine may be one factor in the maintenance of mucosal structure, especially the maintenance of tight junction. (Panigrahi et al. 1997) 2. a precursor for N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylglactosamine synthesis, glutamine could play a critical role in intestinal muci ...
... For amino sugar synthesis : 1. glutamine may be one factor in the maintenance of mucosal structure, especially the maintenance of tight junction. (Panigrahi et al. 1997) 2. a precursor for N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylglactosamine synthesis, glutamine could play a critical role in intestinal muci ...
Stressrelated challenges in pentose fermentation to ethanol
... the optimum temperature for the currently available cellulases. However, a lower temperature must be used in the SSF to stay within the allowable temperature for the yeast. An improved yeast thermotolerance would thus be beneficial from a process point of view. Also the end-product of the fermentati ...
... the optimum temperature for the currently available cellulases. However, a lower temperature must be used in the SSF to stay within the allowable temperature for the yeast. An improved yeast thermotolerance would thus be beneficial from a process point of view. Also the end-product of the fermentati ...
Connection of Propionyl-CoA Metabolism to Polyketide
... Manuscript received February 16, 2004 Accepted for publication April 25, 2004 ABSTRACT Propionyl-CoA is an intermediate metabolite produced through a variety of pathways including thioesterification of propionate and catabolism of odd chain fatty acids and select amino acids. Previously, we found th ...
... Manuscript received February 16, 2004 Accepted for publication April 25, 2004 ABSTRACT Propionyl-CoA is an intermediate metabolite produced through a variety of pathways including thioesterification of propionate and catabolism of odd chain fatty acids and select amino acids. Previously, we found th ...
Medical Nutrition Therapy Nutrient
... 4. What are food sources of the nutrient? -Thiamin is found in enriched, fortified, and whole grain products including bread, cereals, rice, pasta, and flour. Beef liver and pork, dried milk, eggs, legumes and peas, as well as nuts and seeds, are additional sources of thiamin. Dairy products, fruits ...
... 4. What are food sources of the nutrient? -Thiamin is found in enriched, fortified, and whole grain products including bread, cereals, rice, pasta, and flour. Beef liver and pork, dried milk, eggs, legumes and peas, as well as nuts and seeds, are additional sources of thiamin. Dairy products, fruits ...
The Metabolic Functions of Carnitine in Torulopsis
... The carnitine-responsive yeast strain Torulopsis bacina ATCC 260 14 and the wild-type strain T. bot:ina ATCC 22987 were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection, Rockville, Md., USA. Cells were maintained, inocula were prepared and bioautography was done as described by Lewin & Bieber (197 ...
... The carnitine-responsive yeast strain Torulopsis bacina ATCC 260 14 and the wild-type strain T. bot:ina ATCC 22987 were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection, Rockville, Md., USA. Cells were maintained, inocula were prepared and bioautography was done as described by Lewin & Bieber (197 ...
Characterization of carnitine and fatty acid metabolism in the long
... Half of the 80 % acetonitrile supernatant was evaporated under a stream of nitrogen at 40 ◦C. A 100 µl volume of propylation reagent, a 4:1 (v/v) mixture of propan-2-ol and acetylchloride, was added to the residue, vortex-mixed and incubated at 65 ◦C for 15 min. The propylation reagent was evaporate ...
... Half of the 80 % acetonitrile supernatant was evaporated under a stream of nitrogen at 40 ◦C. A 100 µl volume of propylation reagent, a 4:1 (v/v) mixture of propan-2-ol and acetylchloride, was added to the residue, vortex-mixed and incubated at 65 ◦C for 15 min. The propylation reagent was evaporate ...
Biochemistry 304 2014 Student Edition Glycolysis Lectures
... Pyruvate kinase controls the outflow from the glycolysis pathway. It is the third irreversible step. This final step yields ATP and pyruvate. Several mammalian isozymes of tetramer enzyme: L-form predominates in liver M-form predominates in muscle and brain ...
... Pyruvate kinase controls the outflow from the glycolysis pathway. It is the third irreversible step. This final step yields ATP and pyruvate. Several mammalian isozymes of tetramer enzyme: L-form predominates in liver M-form predominates in muscle and brain ...
Oxidation and Synthesis of Fatty Acids in Soluble Enzyme Systems
... and with appropriate additions even numbered fatty acids from C4 to C18 (Table 1) are oxidized completely to CO2 and 1120 (4). The corresponding fl-hydroxy acids, a- unsaturated acids, and -ketoacids are also oxidized to completion and at about the same rate. The odd numbered fatty acids are oxidize ...
... and with appropriate additions even numbered fatty acids from C4 to C18 (Table 1) are oxidized completely to CO2 and 1120 (4). The corresponding fl-hydroxy acids, a- unsaturated acids, and -ketoacids are also oxidized to completion and at about the same rate. The odd numbered fatty acids are oxidize ...
Involvement of Polyamine Catabolism in the Regulation of Glucose
... regulation of glucose, energy and lipid metabolism was investigated using transgenic mice overexpressing or deficient for SSAT. The characterization of SSAT mice revealed that these mice exhibited severely reduced whole body WAT mass, elevated energy expenditure, high insulin sensitivity, a low tiss ...
... regulation of glucose, energy and lipid metabolism was investigated using transgenic mice overexpressing or deficient for SSAT. The characterization of SSAT mice revealed that these mice exhibited severely reduced whole body WAT mass, elevated energy expenditure, high insulin sensitivity, a low tiss ...
... 2.3.4. Another risk factors ............................................................. 12 2.4. Etiopathology of type 2 diabetes ............................................... 12 2.5. Current treatments for type 2 diabetes ..................................... 14 2.5.1 Lifestyle interventions ... ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.