macromolecule webquest
... http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP13204 1. Lipids are ___________________molecules that are insoluble in water. 2. What are fatty acid chains? 3. Define saturated fatty acids 4. In what structures are phospholipids found? 5. What is cholesterol used for in our bodies? From www. ...
... http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP13204 1. Lipids are ___________________molecules that are insoluble in water. 2. What are fatty acid chains? 3. Define saturated fatty acids 4. In what structures are phospholipids found? 5. What is cholesterol used for in our bodies? From www. ...
RG 6 - Digestion and Respiration
... 20. Summarize the total energy yield from glucose in human cells in the presence versus the absence of O2. Metabolic Pool Define: CATABOLISM ...
... 20. Summarize the total energy yield from glucose in human cells in the presence versus the absence of O2. Metabolic Pool Define: CATABOLISM ...
chapter8powerpointle
... Pass energy rich electrons along Complex arrays of protein and cytochromes - Cytochromes are respiratory molecules - Complex carbon rings with metal atoms in center ...
... Pass energy rich electrons along Complex arrays of protein and cytochromes - Cytochromes are respiratory molecules - Complex carbon rings with metal atoms in center ...
Energy in cells
... inside living cells which releases energy to drive the metabolic activities that take place in cells Aerobic respiration – takes place in the presence of oxygen ...
... inside living cells which releases energy to drive the metabolic activities that take place in cells Aerobic respiration – takes place in the presence of oxygen ...
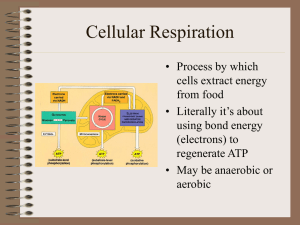
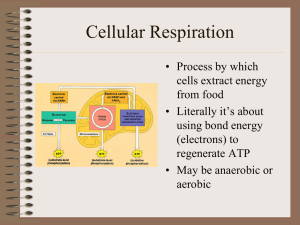
Notes-Cellular Respiration
... • use the energy stored in the chemical bonds to produce compounds • ATP powers activities of the cell ...
... • use the energy stored in the chemical bonds to produce compounds • ATP powers activities of the cell ...
Central energy metabolism remains robust in acute
... lism and, in particular, for the low activity of β-oxidation under applied conditions might be related to the control of metabolism, e.g. through insulin (19), which was present in the culture, or intracellular mediators (20). Insulin is known to influence fatty acid oxidation and might antagonize p ...
... lism and, in particular, for the low activity of β-oxidation under applied conditions might be related to the control of metabolism, e.g. through insulin (19), which was present in the culture, or intracellular mediators (20). Insulin is known to influence fatty acid oxidation and might antagonize p ...
Fuel Basics
... Can supply ATP to muscle for up to 1 -2 minutes Carbohydrate (glucose) is the only energy nutrient that can be used to make the ATP As ATP is produced, lactic acid accumulates & can impair muscle function, cause fatigue. When oxygen is available, lactic acid is burned as fuel. ...
... Can supply ATP to muscle for up to 1 -2 minutes Carbohydrate (glucose) is the only energy nutrient that can be used to make the ATP As ATP is produced, lactic acid accumulates & can impair muscle function, cause fatigue. When oxygen is available, lactic acid is burned as fuel. ...
Supporting Information S1 Metabolic Subsystems How the enzymes
... oscillations and quasi-steady state patterns can spontaneously emerge. In addition, the self-organization and the self-assembly processes may allow for reversible interactions between the multienzymatic system and other molecular structures, leading to the formation of a metabolic microcompartment, ...
... oscillations and quasi-steady state patterns can spontaneously emerge. In addition, the self-organization and the self-assembly processes may allow for reversible interactions between the multienzymatic system and other molecular structures, leading to the formation of a metabolic microcompartment, ...
Sec_2_3 Carbon Compunds
... structure is the complete, three-dimensional arrangement of a polypeptide chain. Proteins with more than one chain have a fourth level of structure (quaternary), which describes the way in which the different polypeptide chains are arranged with respect to each other. For example, the protein show ...
... structure is the complete, three-dimensional arrangement of a polypeptide chain. Proteins with more than one chain have a fourth level of structure (quaternary), which describes the way in which the different polypeptide chains are arranged with respect to each other. For example, the protein show ...
Multiple Choice Questions - Elmwood Park Public Schools
... 1. Some bacteria are strict aerobes and others are strict anaerobes. Some bacteria, however, are facultative anaerobes and can live with or without oxygen. If given the choice of using oxygen or not, which should a facultative anaerobe perform? A) Use oxygen since aerobic metabolism provides more AT ...
... 1. Some bacteria are strict aerobes and others are strict anaerobes. Some bacteria, however, are facultative anaerobes and can live with or without oxygen. If given the choice of using oxygen or not, which should a facultative anaerobe perform? A) Use oxygen since aerobic metabolism provides more AT ...
Enzymes
... When many simple sugars are linked together, they form a polysaccharide Polysaccharides store large amounts of energy Humans use the polysaccharide glycogen Plants use the polysaccharide starch ...
... When many simple sugars are linked together, they form a polysaccharide Polysaccharides store large amounts of energy Humans use the polysaccharide glycogen Plants use the polysaccharide starch ...
Ch 7 outline
... 4. If the cell has plenty of energy, acetyl-CoA is transferred to a fat-depositing pathway; otherwise it enters the Krebs cycle. C. Step Two: The Krebs Cycle 1. The Krebs cycle takes place in the mitochondria, and its nine reactions can be grouped into three stages. 2. In the first stage, acetyl-CoA ...
... 4. If the cell has plenty of energy, acetyl-CoA is transferred to a fat-depositing pathway; otherwise it enters the Krebs cycle. C. Step Two: The Krebs Cycle 1. The Krebs cycle takes place in the mitochondria, and its nine reactions can be grouped into three stages. 2. In the first stage, acetyl-CoA ...
Inorganic vs. Organic Compounds Carbon Compounds Polymerize
... – Common examples: fats, oils, and waxes. – Lipids are made of C, H, and O (no ratio H to O). – Lipids function in energy storage, form biological membranes, and act as chemical messengers. Lipids have more energy than carbohydrates because lipids have more hydrogens bonded to the carbon chain. ...
... – Common examples: fats, oils, and waxes. – Lipids are made of C, H, and O (no ratio H to O). – Lipids function in energy storage, form biological membranes, and act as chemical messengers. Lipids have more energy than carbohydrates because lipids have more hydrogens bonded to the carbon chain. ...
Halloween Candy Calories
... Introduction: Supplying enough energy to support the many functions of the body at work and play is one of the chief functions of food. This energy comes from the fats, carbohydrates, and proteins in the food you eat. Of the three, fat is the most concentrated source of energy because it furnished m ...
... Introduction: Supplying enough energy to support the many functions of the body at work and play is one of the chief functions of food. This energy comes from the fats, carbohydrates, and proteins in the food you eat. Of the three, fat is the most concentrated source of energy because it furnished m ...
Muscle
... b-hydroxybutyrate is formed from fatty acids in the liver and converted to acetyl-CoA → enter TCA cycle This allows the brain to use fat as fuel ...
... b-hydroxybutyrate is formed from fatty acids in the liver and converted to acetyl-CoA → enter TCA cycle This allows the brain to use fat as fuel ...
What Do Enzymes Do
... (phosphoenolpyruvate) to another substrate (ADP), thereby generating pyruvate and ATP as products (Figure 1). ...
... (phosphoenolpyruvate) to another substrate (ADP), thereby generating pyruvate and ATP as products (Figure 1). ...
SCI_7726_files/Cellular Respiration
... • 10 reaction steps, each catalyzed by specific enzymes. ...
... • 10 reaction steps, each catalyzed by specific enzymes. ...
Inked Outline
... In many cases the sugar monomers are ultimately metabolized either by glycolysis or another pathway to generate pyruvate. ...
... In many cases the sugar monomers are ultimately metabolized either by glycolysis or another pathway to generate pyruvate. ...
Specifications sheet Energy Pure
... maltodextrin, dextrose, coloring: caramelised sugar (caramelised glucose syrup, maltodextrin); chicory inulin (FOS)) (4.44 g/100 g), aqueous extract of green tea leaves Camelia sinensis (4.32 g/100 g), natural flavoring, fibers of acacia (0.44 g/ 100 g), acidity regulator: citric acid, salt, vitamin ...
... maltodextrin, dextrose, coloring: caramelised sugar (caramelised glucose syrup, maltodextrin); chicory inulin (FOS)) (4.44 g/100 g), aqueous extract of green tea leaves Camelia sinensis (4.32 g/100 g), natural flavoring, fibers of acacia (0.44 g/ 100 g), acidity regulator: citric acid, salt, vitamin ...
Notes Chapter 3 Biochemistry
... a) Cholesterol is steroid that is needed by the body for nerve cells and other cells to function normally b) Added to cell membrane to make it more fluid – fluid mosaic model 3. Nucleic Acids – very large and complex organic molecules that store information in cells made of long chains of nucleotide ...
... a) Cholesterol is steroid that is needed by the body for nerve cells and other cells to function normally b) Added to cell membrane to make it more fluid – fluid mosaic model 3. Nucleic Acids – very large and complex organic molecules that store information in cells made of long chains of nucleotide ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.