Oxidative phosphorylation (mitochondria)
... First, the entire process then I’ll break it Cytosol down into its parts. Pyruvate Aceyl CoA ...
... First, the entire process then I’ll break it Cytosol down into its parts. Pyruvate Aceyl CoA ...
POSITIONS AVAILABLE 1. Position Title: Postdoctoral Research
... The Sloboda Lab group (www.slobodalab.com) in the Dept of Biochemistry and Biomedical Sciences at McMaster University seeks a post-doctoral basic science research scientist. The successful candidate will have grounding in developmental programming, animal modeling and molecular biology in pursuit of ...
... The Sloboda Lab group (www.slobodalab.com) in the Dept of Biochemistry and Biomedical Sciences at McMaster University seeks a post-doctoral basic science research scientist. The successful candidate will have grounding in developmental programming, animal modeling and molecular biology in pursuit of ...
Chapter 5
... 1. What is the difference between an organic and inorganic molecule? 2. What are the 4 functional groups? 3. Monomers make polymers…what are examples of polymer Biomolecules? 4. What kind of reaction occurs in the formation of a polymer? 5. What kind of reaction occurs in the break-down of a polymer ...
... 1. What is the difference between an organic and inorganic molecule? 2. What are the 4 functional groups? 3. Monomers make polymers…what are examples of polymer Biomolecules? 4. What kind of reaction occurs in the formation of a polymer? 5. What kind of reaction occurs in the break-down of a polymer ...
2.1 KEY CONCEPT All living things are based on atoms and their
... Living things consist of atoms of different elements. • An atom is the smallest basic unit of matter. • An element is one type of atom. Hydrogen atom (H) ...
... Living things consist of atoms of different elements. • An atom is the smallest basic unit of matter. • An element is one type of atom. Hydrogen atom (H) ...
You will need to read on the aging process in your textbook
... • Coenzymes: are large organic molecules such as NAD+, FAD, and NADP+ that transfer protons and electrons from one substrate to another. • Electrons are similar to staircases where the electrons flow down the steps from the top (most energy available) to the bottom (least amount of energy) • The ene ...
... • Coenzymes: are large organic molecules such as NAD+, FAD, and NADP+ that transfer protons and electrons from one substrate to another. • Electrons are similar to staircases where the electrons flow down the steps from the top (most energy available) to the bottom (least amount of energy) • The ene ...
carbonmacromolintro_price
... compounds are classified as organic, with the exception of: • Simple oxides of carbon: ...
... compounds are classified as organic, with the exception of: • Simple oxides of carbon: ...
Aerobic Cellular Respiration
... • Since 2 molecules of acetyl-CoA are formed from one molecule of glucose, the Krebs cycle occurs twice for each molecule of glucose processed • As acetyl-CoA enters the cycle, the CoA is released and can be used for the next pyruvate •During one complete cycle a total of 3 NAD+s and 1 FAD are reduc ...
... • Since 2 molecules of acetyl-CoA are formed from one molecule of glucose, the Krebs cycle occurs twice for each molecule of glucose processed • As acetyl-CoA enters the cycle, the CoA is released and can be used for the next pyruvate •During one complete cycle a total of 3 NAD+s and 1 FAD are reduc ...
Ch. 5 Enzyme Review
... intermediate B arginine. Each reaction is catalyzed by a different enzyme. This metabolic pathway is controlled by feedback inhibition with arginine inhibiting the conversion of precursor A to intermediate B. In this case, arginine almost certainly acts as a _____ of the first enzyme in the pathway. ...
... intermediate B arginine. Each reaction is catalyzed by a different enzyme. This metabolic pathway is controlled by feedback inhibition with arginine inhibiting the conversion of precursor A to intermediate B. In this case, arginine almost certainly acts as a _____ of the first enzyme in the pathway. ...
EXAM 2 Fall2007.doc
... 36. Molecules which permeate a plasma membrane by facilitated diffusion A) require an expenditure of energy. B) require the aid of transport proteins. C) move from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. D) do so much more quickly than those crossing by simple diffusion. E) al ...
... 36. Molecules which permeate a plasma membrane by facilitated diffusion A) require an expenditure of energy. B) require the aid of transport proteins. C) move from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. D) do so much more quickly than those crossing by simple diffusion. E) al ...
Bios 302 FINAL FOR 1999.
... You suggest that she analyze the enzyme for the presence of cobalt. Why do you make this suggestion? f. What one slight modification would you make to one enzyme already present in the glycolytic path so that glucose and mannose could be used equally well as starting points for glycolysis? g. The ge ...
... You suggest that she analyze the enzyme for the presence of cobalt. Why do you make this suggestion? f. What one slight modification would you make to one enzyme already present in the glycolytic path so that glucose and mannose could be used equally well as starting points for glycolysis? g. The ge ...
Cellular respiration Review: 1. Why is ATP the “energy currency” of
... 15. Using the diagram below and your knowledge, put these compounds in order they are produced: Pyruvate, Co-A, Oxaloacetate, Acetyl-Co A, Citric Acid, PGAL, and Glucose. 16. Write the formula for the more expensive, but efficient carrier when it is reduced. 17. What is the difference between a comp ...
... 15. Using the diagram below and your knowledge, put these compounds in order they are produced: Pyruvate, Co-A, Oxaloacetate, Acetyl-Co A, Citric Acid, PGAL, and Glucose. 16. Write the formula for the more expensive, but efficient carrier when it is reduced. 17. What is the difference between a comp ...
Chemistry SL HL Assessment Statements 2009 Revised
... The aim of this option is to give students an understanding of the chemistry of important molecules found in the human body, and the need for a balanced and healthy diet. Although the role that these molecules play in the body should be appreciated, the emphasis is placed on their chemistry, and stu ...
... The aim of this option is to give students an understanding of the chemistry of important molecules found in the human body, and the need for a balanced and healthy diet. Although the role that these molecules play in the body should be appreciated, the emphasis is placed on their chemistry, and stu ...
Document
... 1. The Chemistry of Life Broad Concept: Chemical elements form organic molecules that interact to perform the basic functions of life. 1.1 Recognize that biological organisms are composed primarily of very few elements. The six most common are C, H, N, O, P, S. 1.2 Describe the basic molecular stru ...
... 1. The Chemistry of Life Broad Concept: Chemical elements form organic molecules that interact to perform the basic functions of life. 1.1 Recognize that biological organisms are composed primarily of very few elements. The six most common are C, H, N, O, P, S. 1.2 Describe the basic molecular stru ...
Chapter 13
... cytosol, whereas the citric acid cycle and the oxidative phosphorylation processes occur in mitochondria. Important metabolic functions are listed in Table 15-2. 4. ATP is the most important cellular energy currency because 1. ATP hydrolysis produces ∆G°’ = -30.5 kJ/mol which can be used as an input ...
... cytosol, whereas the citric acid cycle and the oxidative phosphorylation processes occur in mitochondria. Important metabolic functions are listed in Table 15-2. 4. ATP is the most important cellular energy currency because 1. ATP hydrolysis produces ∆G°’ = -30.5 kJ/mol which can be used as an input ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Nerve activates contraction
... – Also known as functional proteins – Function as antibodies or enzymes – Can be denatured ...
... – Also known as functional proteins – Function as antibodies or enzymes – Can be denatured ...
Foundations in Microbiology
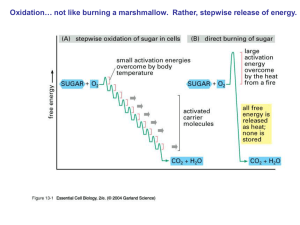
... that make or break bonds and transfer electrons • Endergonic reactions – consume energy • Exergonic reactions – release energy • Energy present in chemical bonds of nutrients are trapped by specialized enzyme systems as the bonds of the nutrients are broken • Energy released is temporarily stored in ...
... that make or break bonds and transfer electrons • Endergonic reactions – consume energy • Exergonic reactions – release energy • Energy present in chemical bonds of nutrients are trapped by specialized enzyme systems as the bonds of the nutrients are broken • Energy released is temporarily stored in ...
Microbiology: A Systems Approach, 2nd ed.
... – Three-part molecule • Nitrogen base (adenine) • 5-carbon sugar (ribose) • Chain of three phosphate groups ...
... – Three-part molecule • Nitrogen base (adenine) • 5-carbon sugar (ribose) • Chain of three phosphate groups ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.