Metabolic hypothesis for human altriciality
... beyond its current dimensions would significantly diminish locomotor performance. The OD hypothesis suggests that the sexual dimorphism evident in human pelves evolved because childbirth in Pleistocene hominins was difficult and dangerous, and selection favored a wider pelvis to lower the risks associ ...
... beyond its current dimensions would significantly diminish locomotor performance. The OD hypothesis suggests that the sexual dimorphism evident in human pelves evolved because childbirth in Pleistocene hominins was difficult and dangerous, and selection favored a wider pelvis to lower the risks associ ...
Metabolic hypothesis for human altriciality
... beyond its current dimensions would significantly diminish locomotor performance. The OD hypothesis suggests that the sexual dimorphism evident in human pelves evolved because childbirth in Pleistocene hominins was difficult and dangerous, and selection favored a wider pelvis to lower the risks associ ...
... beyond its current dimensions would significantly diminish locomotor performance. The OD hypothesis suggests that the sexual dimorphism evident in human pelves evolved because childbirth in Pleistocene hominins was difficult and dangerous, and selection favored a wider pelvis to lower the risks associ ...
Document
... Bio 1 study guide Exam #2 Fall 2009 This as a guide and does not replace your notes! Fig. 9.11 overview of citric acid cycle (NADH, FADH2, ATP and CO2 produced) Fig. 9.12 closer look at the Citric acid cycle 9.4 Oxidative phosphorylation, chemiosmosis couples electron transport to ATP synthesis Mos ...
... Bio 1 study guide Exam #2 Fall 2009 This as a guide and does not replace your notes! Fig. 9.11 overview of citric acid cycle (NADH, FADH2, ATP and CO2 produced) Fig. 9.12 closer look at the Citric acid cycle 9.4 Oxidative phosphorylation, chemiosmosis couples electron transport to ATP synthesis Mos ...
SI Worksheet 7
... 6. The ultimate source of the energy the enables cellular respiration to occur is a. glucose b. fermentation c. oxygen d. biosynthesis e. the sun 7. Unlike turkey breast, the breast of duck is “dark meat.” Why? a. ducks fly longer distances, so their breast muscles consist of fast fibers b. ducks fl ...
... 6. The ultimate source of the energy the enables cellular respiration to occur is a. glucose b. fermentation c. oxygen d. biosynthesis e. the sun 7. Unlike turkey breast, the breast of duck is “dark meat.” Why? a. ducks fly longer distances, so their breast muscles consist of fast fibers b. ducks fl ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules
... 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules • Carbohydrates can be broken down to provide energy for cells. • Some carbohydrates are part of cell structure. Polymer (starch) Starch is a polymer of glucose monomers that often has a branched structure. ...
... 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules • Carbohydrates can be broken down to provide energy for cells. • Some carbohydrates are part of cell structure. Polymer (starch) Starch is a polymer of glucose monomers that often has a branched structure. ...
Cell Respiration Key
... 7. Like aerobic respiration, alcoholic fermentation produces CO2 8. The ATP yield of fermentation is much 9. The buildup of lactic acid ...
... 7. Like aerobic respiration, alcoholic fermentation produces CO2 8. The ATP yield of fermentation is much 9. The buildup of lactic acid ...
Energy Metabolism Review
... Plants make ATP during photosynthesis. All other organisms, including plants, must produce ATP by breaking down molecules such as glucose ...
... Plants make ATP during photosynthesis. All other organisms, including plants, must produce ATP by breaking down molecules such as glucose ...
Chapter 12 Pathways to biomolecules
... Explain how your body maintains a fairly constant concentration of glucose in the blood even though you don’t eat foods that supply glucose constantly throughout the day. A30. When the body digests food and absorbs glucose, the glucose is transported by the blood to the liver where it is converted t ...
... Explain how your body maintains a fairly constant concentration of glucose in the blood even though you don’t eat foods that supply glucose constantly throughout the day. A30. When the body digests food and absorbs glucose, the glucose is transported by the blood to the liver where it is converted t ...
Slide 1
... the pyruvate is reduced directly by NADH to form lactate (ionized form of lactic acid). – Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt. – Muscle cells switch from aerobic respiration to lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce نادر. • The ...
... the pyruvate is reduced directly by NADH to form lactate (ionized form of lactic acid). – Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt. – Muscle cells switch from aerobic respiration to lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce نادر. • The ...
Yr12Ch12 - ChemistryVCE
... Explain how your body maintains a fairly constant concentration of glucose in the blood even though you don’t eat foods that supply glucose constantly throughout the day. A30. When the body digests food and absorbs glucose, the glucose is transported by the blood to the liver where it is converted t ...
... Explain how your body maintains a fairly constant concentration of glucose in the blood even though you don’t eat foods that supply glucose constantly throughout the day. A30. When the body digests food and absorbs glucose, the glucose is transported by the blood to the liver where it is converted t ...
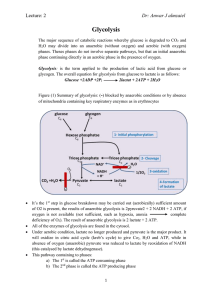
Dr: Anwar J almzaiel Glycolysis
... Glycolysis is not only the principle route for glucose metabolism, but it also provides the main pathway for the metabolism of fructose and galactose derived from the diet. The ability of glycolysis to provide energy in the absence of oxygen allows muscle contraction in which oxygen supply insuffici ...
... Glycolysis is not only the principle route for glucose metabolism, but it also provides the main pathway for the metabolism of fructose and galactose derived from the diet. The ability of glycolysis to provide energy in the absence of oxygen allows muscle contraction in which oxygen supply insuffici ...
4.1 Chemical Energy and ATP
... The chemical energy used for most cell processes is carried by ATP. • Molecules in food store chemical energy in their bonds. – Called chemical energy • This chemical energy can be converted into the chemical energy of ATP • Carbohydrates are the molecules most commonly broken down to make ATP. – 36 ...
... The chemical energy used for most cell processes is carried by ATP. • Molecules in food store chemical energy in their bonds. – Called chemical energy • This chemical energy can be converted into the chemical energy of ATP • Carbohydrates are the molecules most commonly broken down to make ATP. – 36 ...
Treatment of inherited metabolic disorders
... There is no effective therapy for many inherited metabolic disorders - Symptoms developing in utero - Primary affection of central nervous system For many disorders only symptomatic therapy --------------------Effective therapy for a number of disorders Novel developments : Enzyme replacement thera ...
... There is no effective therapy for many inherited metabolic disorders - Symptoms developing in utero - Primary affection of central nervous system For many disorders only symptomatic therapy --------------------Effective therapy for a number of disorders Novel developments : Enzyme replacement thera ...
Chapter 9. Cellular Respiration STAGE 1: Glycolysis
... Cellular Respiration (harvesting ATP from glucose) in the absence of Oxygen. ...
... Cellular Respiration (harvesting ATP from glucose) in the absence of Oxygen. ...
electron transport chain
... lactate, may cause muscle fatigue, but ultimately it is converted back to pyruvate in the liver. Fig. 9.17b ...
... lactate, may cause muscle fatigue, but ultimately it is converted back to pyruvate in the liver. Fig. 9.17b ...
Amino Acid Regulation of RNA Synthesis
... 2- Catabolite Regulation Carbon catabolite regulation In penicillin production it had been known for a long time that penicillin is not produced in a glucose-containing medium until after the exhaustion of the glucose, when the idiophase sets in; the same effect has been observed with cephalospori ...
... 2- Catabolite Regulation Carbon catabolite regulation In penicillin production it had been known for a long time that penicillin is not produced in a glucose-containing medium until after the exhaustion of the glucose, when the idiophase sets in; the same effect has been observed with cephalospori ...
lecture6-BW
... Glycogen is about 1 % of the body’s energy reserve Proteins is 21% of energy reserve Fat makes up the bulk of reserves (78 %) Note: In lecture 4 we discussed polysaccharides, proteins and lipids. ...
... Glycogen is about 1 % of the body’s energy reserve Proteins is 21% of energy reserve Fat makes up the bulk of reserves (78 %) Note: In lecture 4 we discussed polysaccharides, proteins and lipids. ...
Lecture 27
... Chapter 26: Amino acid metabolism Quiz Monday on Transamination mechanism Quiz on Wed. for Urea Cycle ...
... Chapter 26: Amino acid metabolism Quiz Monday on Transamination mechanism Quiz on Wed. for Urea Cycle ...
Lecture 15
... - Electron Transport Chain accepts e- from NADH and passes these efrom one protein molecule to another. - At the end of the chain, e- combine with both H+ and O2 to form H2O and release energy. - These energy are used by mitochondria to synthesis 90% of the cellular ATP via ATP-synthase, a process c ...
... - Electron Transport Chain accepts e- from NADH and passes these efrom one protein molecule to another. - At the end of the chain, e- combine with both H+ and O2 to form H2O and release energy. - These energy are used by mitochondria to synthesis 90% of the cellular ATP via ATP-synthase, a process c ...
The Physiological Roles of Enzymes
... the RNA molecule is removed while the parts on either side of this intron are reconnected. b. Other RNA molecules that do not undergo self-splicing can act on other molecules as substrates are true catalysts. i. Ribonuclease P cleaves transfer RNA precursors to their mature ...
... the RNA molecule is removed while the parts on either side of this intron are reconnected. b. Other RNA molecules that do not undergo self-splicing can act on other molecules as substrates are true catalysts. i. Ribonuclease P cleaves transfer RNA precursors to their mature ...
Fitness Weight Training Centennial Physical Education
... resistance exercises (e.g., weight training, yoga). What is Weight Training? Weight training is an effective tool for improving or maintaining strength, endurance, and overall fitness. It involves controlled movements of skeletal muscle in an effort to move an external load. This can be accomplished ...
... resistance exercises (e.g., weight training, yoga). What is Weight Training? Weight training is an effective tool for improving or maintaining strength, endurance, and overall fitness. It involves controlled movements of skeletal muscle in an effort to move an external load. This can be accomplished ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.