View PDF - CiteSeerX
... is called a defined medium. A defined medium can contain just a minimal set of nutrients such that the microorganism can grow only if each and every one of those nutrients is present. It is then called a minimal growth medium. The culture media known for many microorganisms are not defined media, bu ...
... is called a defined medium. A defined medium can contain just a minimal set of nutrients such that the microorganism can grow only if each and every one of those nutrients is present. It is then called a minimal growth medium. The culture media known for many microorganisms are not defined media, bu ...
3.-electron-transport-chain-ATP-synthesis
... Electron Transport Chain 3 things to note: • MOVEMENT OF ELECTRONS High energy electrons pass from one protein molecule in the chain to another • MOVEMENT OF HYDROGEN IONS The energy received allows the proteins to pump hydrogen across the membrane, so that they can be pumped back across by ATP ...
... Electron Transport Chain 3 things to note: • MOVEMENT OF ELECTRONS High energy electrons pass from one protein molecule in the chain to another • MOVEMENT OF HYDROGEN IONS The energy received allows the proteins to pump hydrogen across the membrane, so that they can be pumped back across by ATP ...
You Light Up My Life
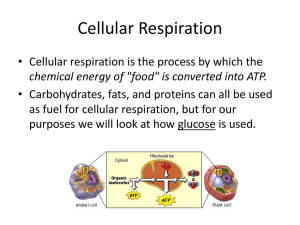
... Chemical Energy Chapter 7 Slide with a red dot may be tested upon, those without are for information purposes only ...
... Chemical Energy Chapter 7 Slide with a red dot may be tested upon, those without are for information purposes only ...
chapter 23
... of saturated fatty acids, fats are solids at room temperature. Oils have more unsaturated fatty acids than fats, so they are liquids. Like other animals, humans make fat, which is stored in adipose tissue until it is needed as an energy source. Fat has about twice as much energy per gram as carbohyd ...
... of saturated fatty acids, fats are solids at room temperature. Oils have more unsaturated fatty acids than fats, so they are liquids. Like other animals, humans make fat, which is stored in adipose tissue until it is needed as an energy source. Fat has about twice as much energy per gram as carbohyd ...
Cellular Respiration
... Acetyl coA is stripped via enzymes: coA is recycle and the remaining acetyl (2-C) is combined with oxaloacetate already present in the mitochondria forming citrate (6-C) Step 2 and 3 Redox reactions take place stripping hydrogen atoms from organic intermediates producing NADH molecules and dispo ...
... Acetyl coA is stripped via enzymes: coA is recycle and the remaining acetyl (2-C) is combined with oxaloacetate already present in the mitochondria forming citrate (6-C) Step 2 and 3 Redox reactions take place stripping hydrogen atoms from organic intermediates producing NADH molecules and dispo ...
PPT - Med Study Group
... A few inherited as Autosomal dominant trait including: porphyria, hyperlipedemia, hereditary angioedema. ...
... A few inherited as Autosomal dominant trait including: porphyria, hyperlipedemia, hereditary angioedema. ...
... Should athletes with high energy demands, such a sprinters, go on this diet? Why or why not? Sprinters need a fast source of energy. This can only be provided from glucose in glycolysis. The glucose is released from glycogen. Glycogen storage is elevated in high carbohydrate diets. Fats and proteins ...
slides#8 - DENTISTRY 2012
... A few inherited as Autosomal dominant trait including: porphyria, hyperlipedemia, hereditary angioedema. ...
... A few inherited as Autosomal dominant trait including: porphyria, hyperlipedemia, hereditary angioedema. ...
Chapter 19
... Cells and Mitochondria Animal cells have many components, each with specific functions; some components along with one or more of their functions are: • Nucleus: Where replication of DNA takes place. • Lysosomes: Remove damaged cellular components and some unwanted foreign materials. • Golgi bodies ...
... Cells and Mitochondria Animal cells have many components, each with specific functions; some components along with one or more of their functions are: • Nucleus: Where replication of DNA takes place. • Lysosomes: Remove damaged cellular components and some unwanted foreign materials. • Golgi bodies ...
Mitochondrial Lab - University of Colorado Denver
... substrate -but cannot be turned into product—so they tie up enzymes by binding to their active site. Malonate is a molecule that looks like succinate, but it cannot be made into fumaric acid (product) so malonate is a competitive inhibitor. Malonate is in a COMPETITION for the active site of the enz ...
... substrate -but cannot be turned into product—so they tie up enzymes by binding to their active site. Malonate is a molecule that looks like succinate, but it cannot be made into fumaric acid (product) so malonate is a competitive inhibitor. Malonate is in a COMPETITION for the active site of the enz ...
Lecture Notes BS1090
... Glycogen synthesis and degradation involve a different set of enzymes to allow the separate regulation of the two pathways. The key enzymes of glycogen synthesis are UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase and Glycogen Synthase (589-90) whilst the key regulatory enzyme of glycogen degradation is (Glycogen) Ph ...
... Glycogen synthesis and degradation involve a different set of enzymes to allow the separate regulation of the two pathways. The key enzymes of glycogen synthesis are UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase and Glycogen Synthase (589-90) whilst the key regulatory enzyme of glycogen degradation is (Glycogen) Ph ...
Lecture 18
... Energy Balance Energy input equals energy output Energy output = work + heat Transport work: moving molecules across cell membrane Mechanical work: movement Chemical work: used for growth, maintenance, and storage of information and energy (ATP bonds, glycogen bonds). ...
... Energy Balance Energy input equals energy output Energy output = work + heat Transport work: moving molecules across cell membrane Mechanical work: movement Chemical work: used for growth, maintenance, and storage of information and energy (ATP bonds, glycogen bonds). ...
Notes - The University of Sydney
... of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act). The material in this communication may be subject to copyright under the Act. Any further reproduction or communication of this material by you may be the subject of copyright protection under the Act. Do not remove this notice. ...
... of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act). The material in this communication may be subject to copyright under the Act. Any further reproduction or communication of this material by you may be the subject of copyright protection under the Act. Do not remove this notice. ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... Both involve gas exchange by taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide. They differ in where the process takes place. In breathing, the exchange takes place in the alveoli of the lungs; in cellular respiration, it takes place in the cells themselves. 2. How are photosynthesis and cellular respir ...
... Both involve gas exchange by taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide. They differ in where the process takes place. In breathing, the exchange takes place in the alveoli of the lungs; in cellular respiration, it takes place in the cells themselves. 2. How are photosynthesis and cellular respir ...
Cellular Respiration
... Aerobic Respiration • Aerobic Respiration has three distinct parts: – Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm (yields 2 ATP) – Krebs cycle takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria (yields 2 ATP) – Electron transport chain is carried out on the inner mitochondrial membrane (yields 34 ATP) ...
... Aerobic Respiration • Aerobic Respiration has three distinct parts: – Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm (yields 2 ATP) – Krebs cycle takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria (yields 2 ATP) – Electron transport chain is carried out on the inner mitochondrial membrane (yields 34 ATP) ...
1 Lecture 27: Metabolic Pathways Part I: Glycolysis
... This completes the “first stage” of glycolysis. Overall Δ G for the first 5 steps under cellular conditions is -53 kJ/mol. So far, 2 ATP molecules have been consumed. ...
... This completes the “first stage” of glycolysis. Overall Δ G for the first 5 steps under cellular conditions is -53 kJ/mol. So far, 2 ATP molecules have been consumed. ...
fgfgrc022814 - Texas A&M University
... Under starvation conditions that cause hepatic stress and steatosis, adipose FGFR1 concurrently imposes restrictions on adipocyte lipolysis and indirectly hepatic lipogenesis. This serves to attenuate extent of compensatory hepatic steatosis that often occurs during hepatic stress. Lipolysis and lip ...
... Under starvation conditions that cause hepatic stress and steatosis, adipose FGFR1 concurrently imposes restrictions on adipocyte lipolysis and indirectly hepatic lipogenesis. This serves to attenuate extent of compensatory hepatic steatosis that often occurs during hepatic stress. Lipolysis and lip ...
Hand Outs B 1 - University of Wisconsin–Madison
... is also in the body in muscles and enzymes. Amino Acid=a small unit that makes up protein Phenylalanine=one of 20 amino acids. Called “phe” for short. Tyrosine=another amino acid. In someone who does not have PKU, phe gets changed into tyrosine. PKU=Phenylketonuria=a genetic disorder in which the bo ...
... is also in the body in muscles and enzymes. Amino Acid=a small unit that makes up protein Phenylalanine=one of 20 amino acids. Called “phe” for short. Tyrosine=another amino acid. In someone who does not have PKU, phe gets changed into tyrosine. PKU=Phenylketonuria=a genetic disorder in which the bo ...
lecture CH23 chem131pikul
... produce reduced coenzymes (NADH and FADH2). These molecules enter the electron transport chain and ultimately produce ATP. Smith, Janice Gorzynski. General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry 2nd Ed. ...
... produce reduced coenzymes (NADH and FADH2). These molecules enter the electron transport chain and ultimately produce ATP. Smith, Janice Gorzynski. General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry 2nd Ed. ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules
... • Fats and oils have different types of fatty acids. – saturated fatty acids – unsaturated fatty acids ...
... • Fats and oils have different types of fatty acids. – saturated fatty acids – unsaturated fatty acids ...
Regents Biology
... Organic vs. Inorganic • Organic Molecules: Contains Carbon AND associated with life. Inorganic Molecules: Not associated with life… may, or may not contain carbon ...
... Organic vs. Inorganic • Organic Molecules: Contains Carbon AND associated with life. Inorganic Molecules: Not associated with life… may, or may not contain carbon ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.