respiration - Sakshieducation.com
... Anaerobes that can tolerate aerobic conditions are called as facultative anaerobes. e.g. Yeasts. There are two stages in anaerobic respiration known as Glycolysis and Fermentation. Glycolysis results in the formation of 2 molecules of Pyruvic acid, 2 NADH2 and net gain of 2 ATP. Ethyl alcohol is for ...
... Anaerobes that can tolerate aerobic conditions are called as facultative anaerobes. e.g. Yeasts. There are two stages in anaerobic respiration known as Glycolysis and Fermentation. Glycolysis results in the formation of 2 molecules of Pyruvic acid, 2 NADH2 and net gain of 2 ATP. Ethyl alcohol is for ...
Cellular Respiration Notes (8.3)
... • Final step in the breakdown of glucose Purpose: Converts ADP to ATP by transferring electrons Location: Mitochondria ...
... • Final step in the breakdown of glucose Purpose: Converts ADP to ATP by transferring electrons Location: Mitochondria ...
NUCLEOTIDES METABOLISM Nucleotide
... Humans and other primates excrete uric acid in the urine, but most N goes out as urea Birds, reptiles and insects excrete uric acid and for them it is the major nitrogen excretory compound Gout occurs from accumulation of uric acid crystals in the extremities Allopurinol, which inhibits XO, is a tre ...
... Humans and other primates excrete uric acid in the urine, but most N goes out as urea Birds, reptiles and insects excrete uric acid and for them it is the major nitrogen excretory compound Gout occurs from accumulation of uric acid crystals in the extremities Allopurinol, which inhibits XO, is a tre ...
Enzymes
... • [S] generally < than its Km – Only uses fraction of enzyme catalytic ability – Enzyme is able to respond to changes in [S] ...
... • [S] generally < than its Km – Only uses fraction of enzyme catalytic ability – Enzyme is able to respond to changes in [S] ...
Lecture Power Point
... Glycogen is a polysaccharide of glucose (Glc) which functions as the primary short term energy storage in muscle cells (myofiber). Glycogen is found in the form of granules in the sarcoplasm, and plays an important role in the glucose cycle. ...
... Glycogen is a polysaccharide of glucose (Glc) which functions as the primary short term energy storage in muscle cells (myofiber). Glycogen is found in the form of granules in the sarcoplasm, and plays an important role in the glucose cycle. ...
Factors that affect Drug Metabolism
... the enzymatic addition of oxygen or removal of hydrogen, carried out by mixed function oxidases, often in the liver. These oxidative reactions typically involve a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase (often abbreviated CYP), NADPH and oxygen. The classes of pharmaceutical drugs that utilize this method for ...
... the enzymatic addition of oxygen or removal of hydrogen, carried out by mixed function oxidases, often in the liver. These oxidative reactions typically involve a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase (often abbreviated CYP), NADPH and oxygen. The classes of pharmaceutical drugs that utilize this method for ...
Cellular Respiration Introduction Energy flow Overall Equation for
... More than one fuel Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins can all be used as the fuel, but it is traditional to start learning with glucose. C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP + heat) The catabolism of glucose is exergonic with a delta G of - 686 kcal per mole of glucose. Some of this energy ...
... More than one fuel Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins can all be used as the fuel, but it is traditional to start learning with glucose. C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP + heat) The catabolism of glucose is exergonic with a delta G of - 686 kcal per mole of glucose. Some of this energy ...
S1 Text Section A Annotation by structural analysis In case of aldose
... Comparison of knockout predictions between the L. infantum iAS142 and L. major iAC560 models Given below is a table (Table SC) that compares the knockout predictions of the iAS142 with the iAC560 model lethal predictions and their relation to known phenotypes identified from experiments. The results ...
... Comparison of knockout predictions between the L. infantum iAS142 and L. major iAC560 models Given below is a table (Table SC) that compares the knockout predictions of the iAS142 with the iAC560 model lethal predictions and their relation to known phenotypes identified from experiments. The results ...
Medical Nutrition Therapy of Gastrointestinal Disorder
... • Functional dyspepsia is a term that de- scribes unexplained persistent or recurrent upper GI discomfort. It may also be described as non-ulcer dyspepsia • Symptoms of functional dyspepsia are reported in about 15%-20% of adults over a year's time and may include vague abdominal discomfort, bloatin ...
... • Functional dyspepsia is a term that de- scribes unexplained persistent or recurrent upper GI discomfort. It may also be described as non-ulcer dyspepsia • Symptoms of functional dyspepsia are reported in about 15%-20% of adults over a year's time and may include vague abdominal discomfort, bloatin ...
Bio 6B Lecture Slides - R1
... • Catabolic pathway (catabolism): breaking down of macromolecules. Releases energy which may be used to produce ATP. • Anabolic pathway (anabolism): building up of macromolecules. Requires energy from ATP. • Metabolism: the balance of catabolism and anabolism in the body. ...
... • Catabolic pathway (catabolism): breaking down of macromolecules. Releases energy which may be used to produce ATP. • Anabolic pathway (anabolism): building up of macromolecules. Requires energy from ATP. • Metabolism: the balance of catabolism and anabolism in the body. ...
Fatty acid catabolism leture2-3
... Now the rest of the chain can be oxidized as described before. ...
... Now the rest of the chain can be oxidized as described before. ...
Bio AP chp 9 notes
... In the combustion of methane to form water and carbon dioxide, the nonpolar covalent bonds of methane (C-H) and oxygen (O=O) are converted to polar covalent bonds (C=O and O-H). ...
... In the combustion of methane to form water and carbon dioxide, the nonpolar covalent bonds of methane (C-H) and oxygen (O=O) are converted to polar covalent bonds (C=O and O-H). ...
TCA Cycle
... pick up protons from one side and release then on the other side 2. Ionophores • Hydrophobic molecules that disspate osmotic gradients by inserting them selves into the membrane and form a channel ...
... pick up protons from one side and release then on the other side 2. Ionophores • Hydrophobic molecules that disspate osmotic gradients by inserting them selves into the membrane and form a channel ...
Sample exam
... 14. Which molecules drawn above would you attribute the property of amphipathic. 15. Which processes below consume more energy than they produce? (consume ATP, NADPH etc ) Gluconeogenesis Glycolysis Citric acid cycle Cholesterol synthesis Pentose phosphate pathway Fatty acid oxidation Fatty acid bio ...
... 14. Which molecules drawn above would you attribute the property of amphipathic. 15. Which processes below consume more energy than they produce? (consume ATP, NADPH etc ) Gluconeogenesis Glycolysis Citric acid cycle Cholesterol synthesis Pentose phosphate pathway Fatty acid oxidation Fatty acid bio ...
Water - University of California, Los Angeles
... • Reduced charge repulsion in products • Better resonance stabilization of products • More favored solvation of products ΔG'° is -30.5 kJ/mol • Cells keep [ATP] relatively high ΔG < -30.5 kJ/mol ...
... • Reduced charge repulsion in products • Better resonance stabilization of products • More favored solvation of products ΔG'° is -30.5 kJ/mol • Cells keep [ATP] relatively high ΔG < -30.5 kJ/mol ...
Microbial ecosystem in the oral cavity: Metabolic diversity in an
... Subgingival sites provide a stable tooth surface and an unstable epithelial surface, the latter of which continuously desquamates. Both surfaces are bathed with a continuous efflux of gingival crevicular fluid (GCF), derived from blood plasma and thus nutritionally rich in nitrogenous compounds such ...
... Subgingival sites provide a stable tooth surface and an unstable epithelial surface, the latter of which continuously desquamates. Both surfaces are bathed with a continuous efflux of gingival crevicular fluid (GCF), derived from blood plasma and thus nutritionally rich in nitrogenous compounds such ...
Lipids General function
... a- Insolubility in water and solubility in organic solvents like chloroform-,etc b- some relation to fatty acids esters, either actual or potential phospholipids have very little solubility in water total body lipid in man is ...
... a- Insolubility in water and solubility in organic solvents like chloroform-,etc b- some relation to fatty acids esters, either actual or potential phospholipids have very little solubility in water total body lipid in man is ...
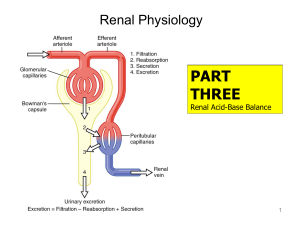
18 Renal Acid-Base Balance
... • Your patient’s blood pH is too high (alkalosis). • This can be caused by either respiratory alkalosis or metabolic alkalosis. Let’s say it was respiratory alkalosis (abnormal breathing rate). • We need to look at the patient’s partial pressures of carbon dioxide and bicarbonate to see if they are ...
... • Your patient’s blood pH is too high (alkalosis). • This can be caused by either respiratory alkalosis or metabolic alkalosis. Let’s say it was respiratory alkalosis (abnormal breathing rate). • We need to look at the patient’s partial pressures of carbon dioxide and bicarbonate to see if they are ...
A modified Atkin`s diet for an infant with pyruvate dehydrogenase
... Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex deficiency (PDCD) is one of the most common neurodegenerative disorders associated with abnormal mitochondrial metabolism. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex plays an important role in glucose metabolism and generation of energy from carbohydrates. Potential therapies for ...
... Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex deficiency (PDCD) is one of the most common neurodegenerative disorders associated with abnormal mitochondrial metabolism. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex plays an important role in glucose metabolism and generation of energy from carbohydrates. Potential therapies for ...
Copyright Information of the Article Published Online
... human urine samples based on our previously published protocols [24,25]. The raw data was processed using the TargetLynx application manager (Waters Corp., Milford, MA) to obtain calibration equations and the measured concentration of each bile acid in the samples. The quality control samples were p ...
... human urine samples based on our previously published protocols [24,25]. The raw data was processed using the TargetLynx application manager (Waters Corp., Milford, MA) to obtain calibration equations and the measured concentration of each bile acid in the samples. The quality control samples were p ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.