Mock Exam 2 BY 123 – Dr. Biga Supplemental Instruction 1. Which
... 38. Which of the following is not true? A) Reducing agents are electron donors. B) Oxidizing agents are electron acceptors. C) Oxidation is the loss of electrons. D) Reduction is the gain of electrons. E) NAD+ is a reducing agent. 39. A mutation prevents the formation of cristae in the mitochondriA ...
... 38. Which of the following is not true? A) Reducing agents are electron donors. B) Oxidizing agents are electron acceptors. C) Oxidation is the loss of electrons. D) Reduction is the gain of electrons. E) NAD+ is a reducing agent. 39. A mutation prevents the formation of cristae in the mitochondriA ...
G 0 - Lucinda Supernavage
... • According to the first law of thermodynamics, the energy of the universe is constant – Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed ...
... • According to the first law of thermodynamics, the energy of the universe is constant – Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed ...
File - May-Lissa Faustin Eportfolio
... Chloroplasts take in sunlight and convert it into energy. The chloroplasts contain chlorophyll which gives the plants the green color that plants usually have. In photosynthesis, Organisms split water as a source of electrons, and then they release O2. Electrons also reduce CO2 to sugars. There are ...
... Chloroplasts take in sunlight and convert it into energy. The chloroplasts contain chlorophyll which gives the plants the green color that plants usually have. In photosynthesis, Organisms split water as a source of electrons, and then they release O2. Electrons also reduce CO2 to sugars. There are ...
1.Oxidative phosphorylation
... tissue is abundant in the newborn and in some adult mammals, and it is brown because of its high content of mitochondria. In humans, brown adipose tissue is abundant in infants, but it gradually diminishes and is barely detectable in adults. • UCP1 provides body heat during cold stress in the young ...
... tissue is abundant in the newborn and in some adult mammals, and it is brown because of its high content of mitochondria. In humans, brown adipose tissue is abundant in infants, but it gradually diminishes and is barely detectable in adults. • UCP1 provides body heat during cold stress in the young ...
Sugar
... mg. However, a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, in addition to several other studies, refute this. This study looked at the effects of egg consumption in 100,000 men and women, and concluded that eggs alone do not contribute to high cholesterol. In fact, when chole ...
... mg. However, a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, in addition to several other studies, refute this. This study looked at the effects of egg consumption in 100,000 men and women, and concluded that eggs alone do not contribute to high cholesterol. In fact, when chole ...
Amino Acid Metabolism
... 【目的与要求】 • 掌握脱氨基作用、氨的来源、去路,氨的转运…… • 掌握尿素合成的部位和全过程 • 掌握一碳单位的概念、来源、载体和功能 • 需要掌握的概念: 必需氨基酸、蛋白质的互补作用、氨基酸库、 联合脱氨基作用.…… ...
... 【目的与要求】 • 掌握脱氨基作用、氨的来源、去路,氨的转运…… • 掌握尿素合成的部位和全过程 • 掌握一碳单位的概念、来源、载体和功能 • 需要掌握的概念: 必需氨基酸、蛋白质的互补作用、氨基酸库、 联合脱氨基作用.…… ...
Study Guide Cellular Respiration
... 2. Respiration and Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis uses CO2 and H2O molecules to form C6H12O6 (glucose) and O2. Respiration is just the opposite, it uses O2 to breakdown glucose into CO2 and H2O. It results in chemical cycling in biosphere. 3. Respiration and Breathing: Respiration takes place in cel ...
... 2. Respiration and Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis uses CO2 and H2O molecules to form C6H12O6 (glucose) and O2. Respiration is just the opposite, it uses O2 to breakdown glucose into CO2 and H2O. It results in chemical cycling in biosphere. 3. Respiration and Breathing: Respiration takes place in cel ...
Photosynthesis Powerpoint review
... water Yellow and orange pigment molecules that broaden the spectrum of colors used to drive photosynthesis and also protect chlorophyll by ...
... water Yellow and orange pigment molecules that broaden the spectrum of colors used to drive photosynthesis and also protect chlorophyll by ...
Energy and Metabolism
... Enzymes are proteins that carry out most catalysis in living organisms. • Unlike heat, enzymes are highly specific. Each enzyme typically speeds up only one or a few chemical reactions. • Unique three-dimensional shape enables an enzyme to stabilize a temporary association between substrates. • Beca ...
... Enzymes are proteins that carry out most catalysis in living organisms. • Unlike heat, enzymes are highly specific. Each enzyme typically speeds up only one or a few chemical reactions. • Unique three-dimensional shape enables an enzyme to stabilize a temporary association between substrates. • Beca ...
Respiration and Photosynthesis Class Work Where does the energy
... a. Respiration: C6H12O6 + CO2 6CO2 + 6H20 + ATP Photosynthesis: 6CO2 + 6H20 + Energy C6H12O6 + CO2 b. Photosynthesis converts solar energy to chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH, which is then used to create glucose and carbon dioxide. As glucose is broken down through the catabolic pro ...
... a. Respiration: C6H12O6 + CO2 6CO2 + 6H20 + ATP Photosynthesis: 6CO2 + 6H20 + Energy C6H12O6 + CO2 b. Photosynthesis converts solar energy to chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH, which is then used to create glucose and carbon dioxide. As glucose is broken down through the catabolic pro ...
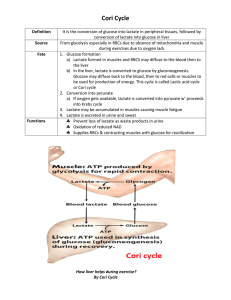
Cori Cycle - COFFEE BREAK CORNER
... or Cori cycle 2. Conversion into pyruvate a) If oxygen gets available, lactate is converted into pyruvate w’ proceeds into Krebs cycle 3. Lactate may be accumulated in muscles causing muscle fatigue ...
... or Cori cycle 2. Conversion into pyruvate a) If oxygen gets available, lactate is converted into pyruvate w’ proceeds into Krebs cycle 3. Lactate may be accumulated in muscles causing muscle fatigue ...
A) 0% B) 20% C) 50% D) 80% E) 100% 1. Naturally occurring boron
... 57. Equal numbers of moles of H2O(g), F 2(g), Cl2(g) are placed into a single container. The container has a pinhole-sized leak (1 mm), and after 10 minutes some gas has escaped from the container. What is best reason for why there is more Cl 2 gas left in the container than any other gas? (NOTE: ...
... 57. Equal numbers of moles of H2O(g), F 2(g), Cl2(g) are placed into a single container. The container has a pinhole-sized leak (1 mm), and after 10 minutes some gas has escaped from the container. What is best reason for why there is more Cl 2 gas left in the container than any other gas? (NOTE: ...
Macromolecules of Life – Lecture 1
... g. Vein i. Xylem ii. Phloem h. Chloroplasts i. Chlorophyll ...
... g. Vein i. Xylem ii. Phloem h. Chloroplasts i. Chlorophyll ...
AP Biology Chapter Objectives – Campbell 7th Edition Modified from
... 7. Name the three stages of cellular respiration and state the region of the eukaryotic cell where each stage occurs. 8. Describe how the carbon skeleton of glucose changes as it proceeds through glycolysis. 9. Explain why ATP is required for the preparatory steps of glycolysis. 10. Identify where s ...
... 7. Name the three stages of cellular respiration and state the region of the eukaryotic cell where each stage occurs. 8. Describe how the carbon skeleton of glucose changes as it proceeds through glycolysis. 9. Explain why ATP is required for the preparatory steps of glycolysis. 10. Identify where s ...
Unit 2 ~ Learning Guide Name
... well as metabolizing them. Next to glucose, _____________________ ___________________________________________________ for us. Unforunately, we store them in adipose (________) cells. They function as a _____________________________________, _______________________________, and ______________________ ...
... well as metabolizing them. Next to glucose, _____________________ ___________________________________________________ for us. Unforunately, we store them in adipose (________) cells. They function as a _____________________________________, _______________________________, and ______________________ ...
7-Keto DHEA - Scientific Bio
... environmental, physical and mental stress by secreting hormones such as adrenaline, cortisol and DHEA. The levels of these hormones can fluctuate throughout the day depending on the amount and intensity of the stressors that one encounters. Once a stressful situation has been resolved the body must ...
... environmental, physical and mental stress by secreting hormones such as adrenaline, cortisol and DHEA. The levels of these hormones can fluctuate throughout the day depending on the amount and intensity of the stressors that one encounters. Once a stressful situation has been resolved the body must ...
Załącznik nr 3 do Zarządzenia Rektora PUM…………………….. z
... and non-balanced diet knows consequences of hypovitaminosis and minerals deficiency as well as vitamin and mineral excess in human organism knows modes of action and regulatory mechanisms of all human organs and systems, incl. circulatory system, respiratory system, alimentary system, urinary system ...
... and non-balanced diet knows consequences of hypovitaminosis and minerals deficiency as well as vitamin and mineral excess in human organism knows modes of action and regulatory mechanisms of all human organs and systems, incl. circulatory system, respiratory system, alimentary system, urinary system ...
Intermediary Nitrogen Metabolism, Vol 16. Biochemistry of Plants Brochure
... Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/1766672/ ...
... Brochure More information from http://www.researchandmarkets.com/reports/1766672/ ...
Enzymes
... Structural Formula - This formula shows how the atoms are arranged (its structure!!). For example, sugar C6H12O6 looks like this. ...
... Structural Formula - This formula shows how the atoms are arranged (its structure!!). For example, sugar C6H12O6 looks like this. ...
Lactic acid fermentation
... and giving phosphates to another molecule. How does this apply to mitochondria? Let’s analyze the processes that allow this to occur. ...
... and giving phosphates to another molecule. How does this apply to mitochondria? Let’s analyze the processes that allow this to occur. ...
BIOCHEMISTRY Electron Transport Chain
... Released when blood glucose levels are low Principal function is to increase blood glucose concentration by speeding up Glycogenolysis & Gluconeogenesis in the liver • Glucagon elicits the opposite effects of insulin ...
... Released when blood glucose levels are low Principal function is to increase blood glucose concentration by speeding up Glycogenolysis & Gluconeogenesis in the liver • Glucagon elicits the opposite effects of insulin ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.