3-Major Veins of the body
... and lies behind the medial border of the patella. Passes behind the knee and curves forward around the medial side of the thigh. Hooks through the lower part of the saphenous opening in the deep fascia to joins the femoral vein about 1.5 in. (4 cm) below and lateral to the pubic tubercle. ...
... and lies behind the medial border of the patella. Passes behind the knee and curves forward around the medial side of the thigh. Hooks through the lower part of the saphenous opening in the deep fascia to joins the femoral vein about 1.5 in. (4 cm) below and lateral to the pubic tubercle. ...
Arteries and Veins Worksheet
... and the renal veins drain the kidneys. 4) The hepatic portal vein drains the digestive tract organs and carries this blood through the liver before it enters the systemic circulation. The hepatic veins drain the liver. 5) The internal iliac vein drains blood from the rectum and tissue of the bladder ...
... and the renal veins drain the kidneys. 4) The hepatic portal vein drains the digestive tract organs and carries this blood through the liver before it enters the systemic circulation. The hepatic veins drain the liver. 5) The internal iliac vein drains blood from the rectum and tissue of the bladder ...
Amazing anatomy: roadmaps of venous collateral circulation in
... presentation is to review the most important pathways of collateral circulation in patients with obstruction of SVC, as well as to provide tips for easy identification. Four main systems of collateral venous circulation include: (1) azygos system of veins, which provides communication between SVC an ...
... presentation is to review the most important pathways of collateral circulation in patients with obstruction of SVC, as well as to provide tips for easy identification. Four main systems of collateral venous circulation include: (1) azygos system of veins, which provides communication between SVC an ...
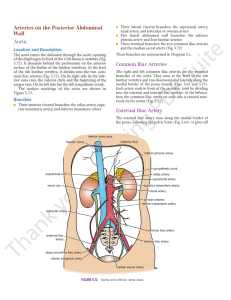
Common Iliac Arteries External Iliac Artery EMBRYOLOGIC NOTES
... The inferior vena cava is commonly compressed by the enlarged uterus during the later stages of pregnancy. This produces edema of the ankles and feet and temporary varicose veins. Malignant retroperitoneal tumors can cause severe compression and eventual blockage of the inferior vena cava. This resu ...
... The inferior vena cava is commonly compressed by the enlarged uterus during the later stages of pregnancy. This produces edema of the ankles and feet and temporary varicose veins. Malignant retroperitoneal tumors can cause severe compression and eventual blockage of the inferior vena cava. This resu ...
Bilateral alar thoracic artery
... During a routine dissection a superficial artery was observed coursing subcutaneously at the anterior border of the axillary base towards the thoracic wall and bilaterally at the lower border of the pectoralis major muscle. On the right side it originated from the 3rd part of the axillary artery but ...
... During a routine dissection a superficial artery was observed coursing subcutaneously at the anterior border of the axillary base towards the thoracic wall and bilaterally at the lower border of the pectoralis major muscle. On the right side it originated from the 3rd part of the axillary artery but ...
The deep veins
... 3. To investigate swollen legs where the differential diagnosis between lymph edema, cellulitis and venous incompetence (or obstruction) is not clear. 4. To outline venous malformations. 5. In some cases, however, for example in patients with repeated pulmonary emboli but no obvious source, the inve ...
... 3. To investigate swollen legs where the differential diagnosis between lymph edema, cellulitis and venous incompetence (or obstruction) is not clear. 4. To outline venous malformations. 5. In some cases, however, for example in patients with repeated pulmonary emboli but no obvious source, the inve ...
INTRODUCTION - Austin Community College
... The following is a list of structures that students should identify on a dissected animal. The items on this list also appear along with the related lab topics below and are included here for easy reference. List of structures that students will locate through the dissection of a whole animal (cat, ...
... The following is a list of structures that students should identify on a dissected animal. The items on this list also appear along with the related lab topics below and are included here for easy reference. List of structures that students will locate through the dissection of a whole animal (cat, ...
biology 2304/2101 human anatomy
... The following is a list of structures that students should identify on a dissected animal. The items on this list also appear along with the related lab topics below and are included here for easy reference. List of structures that students will locate through the dissection of a whole animal (cat, ...
... The following is a list of structures that students should identify on a dissected animal. The items on this list also appear along with the related lab topics below and are included here for easy reference. List of structures that students will locate through the dissection of a whole animal (cat, ...
Chapter 26-Part 2-Digestive System
... Diverticulosis (a) An external view of the sigmoid colon showing diverticula. (b) An endoscopic view of diverticula. b: Photo courtesy Interactive Atlas of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy by Edgar Jaramillo, available free of charge at www.gastrosource.com ...
... Diverticulosis (a) An external view of the sigmoid colon showing diverticula. (b) An endoscopic view of diverticula. b: Photo courtesy Interactive Atlas of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy by Edgar Jaramillo, available free of charge at www.gastrosource.com ...
Femoral triangle
... Contains: a little loose fatty tissue, a small lymph node, and some lymph vessels. The boundaries of the femoral ring Anteriorly: the inguinal ligament ...
... Contains: a little loose fatty tissue, a small lymph node, and some lymph vessels. The boundaries of the femoral ring Anteriorly: the inguinal ligament ...
INTRODUCTION - Austin Community College
... The following is a list of structures that students should identify on a dissected animal. The items on this list also appear along with the related lab topics below and are included here for easy reference. List of structures that students will locate through the dissection of a whole animal (cat, ...
... The following is a list of structures that students should identify on a dissected animal. The items on this list also appear along with the related lab topics below and are included here for easy reference. List of structures that students will locate through the dissection of a whole animal (cat, ...
PAROTID REGION.
... Branches of the external carotid artery traverse the glandular tissue and supply the parotid. The main branch to supply the gland is the transverse facial artery. numerous local veins drain the organ. These veins drain into tributaries of external and internal jugular veins. The maxillary ...
... Branches of the external carotid artery traverse the glandular tissue and supply the parotid. The main branch to supply the gland is the transverse facial artery. numerous local veins drain the organ. These veins drain into tributaries of external and internal jugular veins. The maxillary ...
ANATOMY
... By permission of JE Skandalakis, SW Gray, and JR Rowe. Anatomical Complications in General Surgery. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1983. ...
... By permission of JE Skandalakis, SW Gray, and JR Rowe. Anatomical Complications in General Surgery. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1983. ...
Chest Hybrid Imaging: Anatomy, Variants, Urgent Findings
... – Decreases with fasting as cardiac muscle shifts to fatty acid source of energy • In fed state, glucose metabolism prevails ...
... – Decreases with fasting as cardiac muscle shifts to fatty acid source of energy • In fed state, glucose metabolism prevails ...
Pelvic Viscera
... The superior rectal artery is a continuation of the inferior mesenteric artery. It splits into two branches supplying the proximal portion of the rectum. The two middle rectal arteries arise from the inferior vesical arteries; supply the middle and inferior portions. The inferior rectal artery forms ...
... The superior rectal artery is a continuation of the inferior mesenteric artery. It splits into two branches supplying the proximal portion of the rectum. The two middle rectal arteries arise from the inferior vesical arteries; supply the middle and inferior portions. The inferior rectal artery forms ...
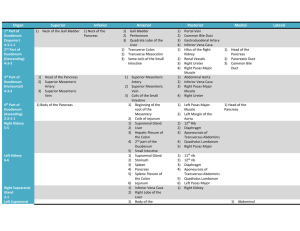
Thoracic wall, abdominal region, muscles
... 6) Increases intra-abdominal pressure, including parturition (childbirth), urination, defecation (expulsion of feces from the rectum),vomiting, and coughing. 2 muscles @ posterior abdominal wall 1) Iliopsoas Psoas major + Iliacus Main flexor of thigh, Moves the body up from supine position to erec ...
... 6) Increases intra-abdominal pressure, including parturition (childbirth), urination, defecation (expulsion of feces from the rectum),vomiting, and coughing. 2 muscles @ posterior abdominal wall 1) Iliopsoas Psoas major + Iliacus Main flexor of thigh, Moves the body up from supine position to erec ...
Dr.Kaan Yücel http://yeditepeanatomy.org Thoracic Wall THORACIC
... The transversus thoracis muscles are found on the deep surface of the anterior thoracic wall and in the same plane as the innermost intercostals. They lie deep to the internal thoracic vessels and secure these vessels to the wall. The subcostales are in the same plane as the innermost intercostals, ...
... The transversus thoracis muscles are found on the deep surface of the anterior thoracic wall and in the same plane as the innermost intercostals. They lie deep to the internal thoracic vessels and secure these vessels to the wall. The subcostales are in the same plane as the innermost intercostals, ...
Concise Guide to HUMAN ANATOMY 2
... 3. Flat bones: broad and flat, for example, ribs, sternum, scapulae, and many bones of the skull . 4. Irregular bones: varied in shape, include many of the cranial bones, vertebrae, hip bones and so on . Ⅱ. The Structure of bones: Living bones consist of bony substance, periesteum and bony marrow, a ...
... 3. Flat bones: broad and flat, for example, ribs, sternum, scapulae, and many bones of the skull . 4. Irregular bones: varied in shape, include many of the cranial bones, vertebrae, hip bones and so on . Ⅱ. The Structure of bones: Living bones consist of bony substance, periesteum and bony marrow, a ...
The Histology of the Pulp
... Recognize, Capture Foreign Ag Non-Phagocytic Increased in Carious Teeth Class II MHC Positive ...
... Recognize, Capture Foreign Ag Non-Phagocytic Increased in Carious Teeth Class II MHC Positive ...
Introduction of the nervous system
... septum股环隔 superiorly. The canal contains a little loose fatty tissue, a small lymph node, and some lymph vessels. ...
... septum股环隔 superiorly. The canal contains a little loose fatty tissue, a small lymph node, and some lymph vessels. ...
6-Anatomy of OMENTUM2016-12
... duct, and portal vein between its two layers. • Behind by the peritoneum covering the inferior vena cava. • Above (roof) by the peritoneum on the caudate process of the liver. • Below (floor) by the peritoneum covering the commencement of the duodenum and the hepatic ...
... duct, and portal vein between its two layers. • Behind by the peritoneum covering the inferior vena cava. • Above (roof) by the peritoneum on the caudate process of the liver. • Below (floor) by the peritoneum covering the commencement of the duodenum and the hepatic ...
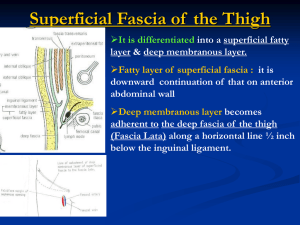
39-L.L. (Updated 21st April)
... It is funnel-shaped tube of fascia that surround the upper 1 in. of femoral vessels & lymphatics, below inguinal ligament. The upper end of sheath opens into abdomen, while lower end fuses with the walls of femoral vessels (tunica adventitia). Its anterior wall is formed of downward continuation ...
... It is funnel-shaped tube of fascia that surround the upper 1 in. of femoral vessels & lymphatics, below inguinal ligament. The upper end of sheath opens into abdomen, while lower end fuses with the walls of femoral vessels (tunica adventitia). Its anterior wall is formed of downward continuation ...
Relationships
... 2) Esophageal Hiatus: Formed by the Right Crus of the Diaphragm @ TV10 a. Esophagus b. Anterior and Posterior Vagal Trunks 3) Aortic Hiatus: @TV12 a. Aorta b. Azygos Vein c. Thoracic Duct ...
... 2) Esophageal Hiatus: Formed by the Right Crus of the Diaphragm @ TV10 a. Esophagus b. Anterior and Posterior Vagal Trunks 3) Aortic Hiatus: @TV12 a. Aorta b. Azygos Vein c. Thoracic Duct ...
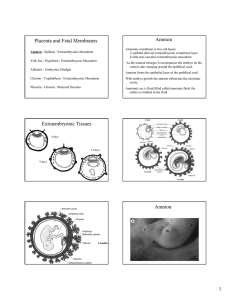
08 Placenta and Fetal Membranes total
... Making the Placenta By 8 weeks - chorionic stem villi over the entire surface of the chorionic sac Those villi associated with the decidua basalis increase in size and more villi form. Enlargement includes further branching of the anchoring villus - chorion frondosum. The villi continue to enlarge d ...
... Making the Placenta By 8 weeks - chorionic stem villi over the entire surface of the chorionic sac Those villi associated with the decidua basalis increase in size and more villi form. Enlargement includes further branching of the anchoring villus - chorion frondosum. The villi continue to enlarge d ...
Lymphatic system

The lymphatic system is part of the circulatory system and a vital part of the immune system, comprising a network of lymphatic vessels that carry a clear fluid called lymph (from Latin lympha meaning water) directionally towards the heart. The lymphatic system was first described in the seventeenth century independently by Olaus Rudbeck and Thomas Bartholin. Unlike the cardiovascular system, the lymphatic system is not a closed system. The human circulatory system processes an average of 20 litres of blood per day through capillary filtration, which removes plasma while leaving the blood cells. Roughly 17 litres of the filtered plasma are reabsorbed directly into the blood vessels, while the remaining three litres remain in the interstitial fluid. One of the main functions of the lymph system is to provide an accessory return route to the blood for the surplus three litres.The other main function is that of defense in the immune system. Lymph is very similar to blood plasma: it contains lymphocytes and other white blood cells. It also contains waste products and debris of cells together with bacteria and protein. Associated organs composed of lymphoid tissue are the sites of lymphocyte production. Lymphocytes are concentrated in the lymph nodes. The spleen and the thymus are also lymphoid organs of the immune system. The tonsils are lymphoid organs that are also associated with the digestive system. Lymphoid tissues contain lymphocytes, and also contain other types of cells for support. The system also includes all the structures dedicated to the circulation and production of lymphocytes (the primary cellular component of lymph), which also includes the bone marrow, and the lymphoid tissue associated with the digestive system.The blood does not come into direct contact with the parenchymal cells and tissues in the body (except in case of an injury causing rupture of one or more blood vessels), but constituents of the blood first exit the microvascular exchange blood vessels to become interstitial fluid, which comes into contact with the parenchymal cells of the body. Lymph is the fluid that is formed when interstitial fluid enters the initial lymphatic vessels of the lymphatic system. The lymph is then moved along the lymphatic vessel network by either intrinsic contractions of the lymphatic passages or by extrinsic compression of the lymphatic vessels via external tissue forces (e.g., the contractions of skeletal muscles), or by lymph hearts in some animals. The organization of lymph nodes and drainage follows the organization of the body into external and internal regions; therefore, the lymphatic drainage of the head, limbs, and body cavity walls follows an external route, and the lymphatic drainage of the thorax, abdomen, and pelvic cavities follows an internal route. Eventually, the lymph vessels empty into the lymphatic ducts, which drain into one of the two subclavian veins, near their junction with the internal jugular veins.