Fatty Acid Synthesis Chapter 28, Stryer Short Course
... • Opposite of beta oxidation in the sense that 2carbon acetate units are linked to form evenchain, saturated fatty acids • Differs from Fatty acid degradation – In cytoplasm, not matrix – Acyl carrier protein rather than CoA – Enzymes linked in a complex – Utilizes NADPH – Energetically linked to AT ...
... • Opposite of beta oxidation in the sense that 2carbon acetate units are linked to form evenchain, saturated fatty acids • Differs from Fatty acid degradation – In cytoplasm, not matrix – Acyl carrier protein rather than CoA – Enzymes linked in a complex – Utilizes NADPH – Energetically linked to AT ...
Lipogenesis (2014)
... Palmitic acid - the end product of FA synthesis in cytoplasm can be elongated in mitochondria by the addition of two carbon atoms to give other long chain saturated FA e.g. stearic acid Unsaturation: occur also in mitochondria by desaturase enzyme to give unsaturated fatty acids e.g. oleic acid ...
... Palmitic acid - the end product of FA synthesis in cytoplasm can be elongated in mitochondria by the addition of two carbon atoms to give other long chain saturated FA e.g. stearic acid Unsaturation: occur also in mitochondria by desaturase enzyme to give unsaturated fatty acids e.g. oleic acid ...
Lecture 1 Course overview and intro to enzymes
... CO2 removed to give amine H removed and replaced to give D form N removed to give alpha keto acid Glutamine as N carrier glutamine synthetase and glutaminase Aspartate as N carrier The urea cycle, also called the ornithine cycle two compartments ...
... CO2 removed to give amine H removed and replaced to give D form N removed to give alpha keto acid Glutamine as N carrier glutamine synthetase and glutaminase Aspartate as N carrier The urea cycle, also called the ornithine cycle two compartments ...
Targeted Chemical Libraries
... Finally, the SynPhase lanterns use grafted polymers to create solid supports that are easy to handle, track, and can be loaded at 75 μmol. 2.4. Chemical Planning for a Targeted Library: In 1997 Spaller et al. published an important review that clearly illustrated a key difference between focuse ...
... Finally, the SynPhase lanterns use grafted polymers to create solid supports that are easy to handle, track, and can be loaded at 75 μmol. 2.4. Chemical Planning for a Targeted Library: In 1997 Spaller et al. published an important review that clearly illustrated a key difference between focuse ...
1 - u.arizona.edu
... dihydrofolate reductase - THF is backbone for production of other active forms of folate; must be in this form to carry carbon - N5,N10-methyleneTHF gains a carbon from side chain of serine yielding glycine product; required for TMP synthesis from dUMP - N5,N10-methenylTHF is a precursor for formati ...
... dihydrofolate reductase - THF is backbone for production of other active forms of folate; must be in this form to carry carbon - N5,N10-methyleneTHF gains a carbon from side chain of serine yielding glycine product; required for TMP synthesis from dUMP - N5,N10-methenylTHF is a precursor for formati ...
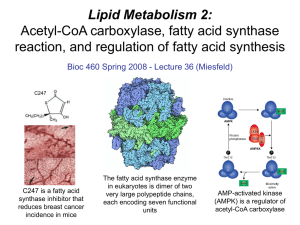
Lecture 36 - Lipid Metabolism 2
... • The fatty acid synthase protein complex consists of six enzymatic activities and the acyl carrier protein; each reaction cycle adds two carbons that are derived from malonyl-CoA following decarboxylation. ...
... • The fatty acid synthase protein complex consists of six enzymatic activities and the acyl carrier protein; each reaction cycle adds two carbons that are derived from malonyl-CoA following decarboxylation. ...
Chapter 4
... No primer required Nucleoside triphosphates: ATP, GTP, CTP, UTP Synthesis is 5’ to 3’ ...
... No primer required Nucleoside triphosphates: ATP, GTP, CTP, UTP Synthesis is 5’ to 3’ ...
Azospirillum and related microorganisms.
... many bacteria contaíns a sequence which crossreacts with the chosen 23S rRNA sequence of A. lipoferum. Another possible problem arrises in the non-radioactive detection system with DIG-labelled probes. NA-preparations obtained with the method of Stahl & Flesher (1987) cannot be used, because the rib ...
... many bacteria contaíns a sequence which crossreacts with the chosen 23S rRNA sequence of A. lipoferum. Another possible problem arrises in the non-radioactive detection system with DIG-labelled probes. NA-preparations obtained with the method of Stahl & Flesher (1987) cannot be used, because the rib ...
purine
... Purine Catabolism and Salvage • All purine degradation leads to uric acid • Ingested nucleic acids are degraded to nucleotides by pancreatic nucleases, and intestinal phosphodiesterases in the intestine • Group-specific nucleotidases and non-specific phosphatases degrade nucleotides into nucleoside ...
... Purine Catabolism and Salvage • All purine degradation leads to uric acid • Ingested nucleic acids are degraded to nucleotides by pancreatic nucleases, and intestinal phosphodiesterases in the intestine • Group-specific nucleotidases and non-specific phosphatases degrade nucleotides into nucleoside ...
Document
... 1. Synthesis of PE and PC from preexisting choline and ethanolamine These synthetic pathways involve the phosphorylation of choline or ethanolamine by انزيمkinases, followed by conversion to the activated form, CDP-choline or CDP-ethanolamine ارجع الى الطريقه الثانيه لتصنيع الفسفولبدز لكي تتو ...
... 1. Synthesis of PE and PC from preexisting choline and ethanolamine These synthetic pathways involve the phosphorylation of choline or ethanolamine by انزيمkinases, followed by conversion to the activated form, CDP-choline or CDP-ethanolamine ارجع الى الطريقه الثانيه لتصنيع الفسفولبدز لكي تتو ...
ROCZNIKI FILOZOFICZNE Tom XXXI, zeszyt 3 — 1983
... of them, e.g. pyrrole and benzaldehyde, had to originate in the earlier stages of chemical evolution, and be accessible in sufficient concentrations. Some investigators were able to synthetize these compounds in simulated abiotic conditions. The reactions leading to the synthesis of porphyrins can t ...
... of them, e.g. pyrrole and benzaldehyde, had to originate in the earlier stages of chemical evolution, and be accessible in sufficient concentrations. Some investigators were able to synthetize these compounds in simulated abiotic conditions. The reactions leading to the synthesis of porphyrins can t ...
Heme- Fe 2+ (ferrous) - LSU School of Medicine
... Note: Uroporphyrinogen I synthase is alternate name for Hydroxymethylbilane ...
... Note: Uroporphyrinogen I synthase is alternate name for Hydroxymethylbilane ...
NME2.28: fat and carbohydrate metabolism in the
... Pyruvate from glycolysis enters the hepatocyte/adipocyte mitochondria o Pyruvate is converted to acetyl-CoA by pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) o Acetyl-CoA enters the first part of the TCA cycle (see NME 2.31) o Acetyl-CoA with oxaloacetate is converted to citrate o Citrate is exported from the mitocho ...
... Pyruvate from glycolysis enters the hepatocyte/adipocyte mitochondria o Pyruvate is converted to acetyl-CoA by pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) o Acetyl-CoA enters the first part of the TCA cycle (see NME 2.31) o Acetyl-CoA with oxaloacetate is converted to citrate o Citrate is exported from the mitocho ...
Uric acid
... binding to them. b. Allopurinol increases excretion of uric acid by the kidneys. c. Allopurinol inhibits the enzyme that makes uric acid. d. Allopurinol decreases the inflammatory response. ...
... binding to them. b. Allopurinol increases excretion of uric acid by the kidneys. c. Allopurinol inhibits the enzyme that makes uric acid. d. Allopurinol decreases the inflammatory response. ...
Slide 1
... • Favorable reaction because ΔH for complex formation = -3 x H-bond energy • ΔS is unfavorable → complex is organized 3 H-bonds overcome the entropy of complex formation • **Note: In synthetic DNAs other interactions can occur ...
... • Favorable reaction because ΔH for complex formation = -3 x H-bond energy • ΔS is unfavorable → complex is organized 3 H-bonds overcome the entropy of complex formation • **Note: In synthetic DNAs other interactions can occur ...
Fatty Acid Biosynthesis
... degraded to Acetyl CoA Acetyl CoA provides biologic energy Excess acetyl CoA is stored as Fatty Acids (FA’s) FA’s are assembled into more complex lipids like triglycerides (TG’s) ...
... degraded to Acetyl CoA Acetyl CoA provides biologic energy Excess acetyl CoA is stored as Fatty Acids (FA’s) FA’s are assembled into more complex lipids like triglycerides (TG’s) ...
Metabolic fate of amino acid
... (6)Urea Synthesis • Urea is the major end product of nitrogen catabolism in humans. • Urea is formed from ammonia, carbon dioxide, and aspartate, synthesis of I mol each of ammonium ion and the a -amino nitrogen of aspartate. • The biosythesis of urea involves 5 important ...
... (6)Urea Synthesis • Urea is the major end product of nitrogen catabolism in humans. • Urea is formed from ammonia, carbon dioxide, and aspartate, synthesis of I mol each of ammonium ion and the a -amino nitrogen of aspartate. • The biosythesis of urea involves 5 important ...
Chapter 26 - s3.amazonaws.com
... G for ATP hydrolysis says that at equilibrium the concentrations of ADP and Pi should be vastly greater than that of ATP However, a cell where this is true is dead Kinetic controls over catabolic pathways ensure that the [ATP]/[ADP][Pi] ratio stays very high This allows ATP hydrolysis to serve as t ...
... G for ATP hydrolysis says that at equilibrium the concentrations of ADP and Pi should be vastly greater than that of ATP However, a cell where this is true is dead Kinetic controls over catabolic pathways ensure that the [ATP]/[ADP][Pi] ratio stays very high This allows ATP hydrolysis to serve as t ...
LECTURE OUTLINE
... An imbalance of globin chain production results in the accumulation of free globin chains in the red blood cell precursors, which, being insoluble, precipitate, resulting in hemolysis of the red blood cells ...
... An imbalance of globin chain production results in the accumulation of free globin chains in the red blood cell precursors, which, being insoluble, precipitate, resulting in hemolysis of the red blood cells ...
Chemical synthesis of proteins
... existed for over 30 years. However, the construction of proteins has become more accessible recently because of improvements in peptide-synthesis efficiency, including the development of rapid coupling reagents and the minimization of deleterious side reactions1. The creation of protein-like molecul ...
... existed for over 30 years. However, the construction of proteins has become more accessible recently because of improvements in peptide-synthesis efficiency, including the development of rapid coupling reagents and the minimization of deleterious side reactions1. The creation of protein-like molecul ...
Document
... Analogues and Synthesis: A rich array of puromycin analogues with modified amino acid, carbohydrate, and/or base moieties has been prepared and evaluated biologically to study the structure-activity correlations….. ...
... Analogues and Synthesis: A rich array of puromycin analogues with modified amino acid, carbohydrate, and/or base moieties has been prepared and evaluated biologically to study the structure-activity correlations….. ...
1 Respiration efficiency Respiration summary
... From Glutamate to... Glutamate can be enzymatically transformed into glutamine, proline and arginine. Other amino acids are formed by a transamination from glutamate and another Krebs cycle intermediate: – glutamate + pyruvate ↔ alanine + α-ketoglutarate – glutamate + oxaloacetate ↔ aspartate + α-ke ...
... From Glutamate to... Glutamate can be enzymatically transformed into glutamine, proline and arginine. Other amino acids are formed by a transamination from glutamate and another Krebs cycle intermediate: – glutamate + pyruvate ↔ alanine + α-ketoglutarate – glutamate + oxaloacetate ↔ aspartate + α-ke ...
Protein Synthesis - Workforce Solutions
... amino acid differ only in the third base; therefore fewer different tRNAs are needed because a given tRNA can base-pair with several codons – the existence of wobble minimizes the damage that can be caused by a misreading of the code; for example, if the Leu codon CUU were misread as CUC or CUA or C ...
... amino acid differ only in the third base; therefore fewer different tRNAs are needed because a given tRNA can base-pair with several codons – the existence of wobble minimizes the damage that can be caused by a misreading of the code; for example, if the Leu codon CUU were misread as CUC or CUA or C ...
Oligonucleotide synthesis

Oligonucleotide synthesis is the chemical synthesis of relatively short fragments of nucleic acids with defined chemical structure (sequence). The technique is extremely useful in current laboratory practice because it provides a rapid and inexpensive access to custom-made oligonucleotides of the desired sequence. Whereas enzymes synthesize DNA and RNA only in a 5' to 3' direction, chemical oligonucleotide synthesis does not suffer from this limitation, although it is, most often, carried out in the opposite, 3' to 5' direction. Currently, the process is implemented as solid-phase synthesis using phosphoramidite method and phosphoramidite building blocks derived from protected 2'-deoxynucleosides (dA, dC, dG, and T), ribonucleosides (A, C, G, and U), or chemically modified nucleosides, e.g. LNA, BNA.To obtain the desired oligonucleotide, the building blocks are sequentially coupled to the growing oligonucleotide chain in the order required by the sequence of the product (see Synthetic cycle below). The process has been fully automated since the late 1970s. Upon the completion of the chain assembly, the product is released from the solid phase to solution, deprotected, and collected. The occurrence of side reactions sets practical limits for the length of synthetic oligonucleotides (up to about 200 nucleotide residues) because the number of errors accumulates with the length of the oligonucleotide being synthesized. Products are often isolated by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to obtain the desired oligonucleotides in high purity. Typically, synthetic oligonucleotides are single-stranded DNA or RNA molecules around 15–25 bases in length.Oligonucleotides find a variety of applications in molecular biology and medicine. They are most commonly used as antisense oligonucleotides, small interfering RNA, primers for DNA sequencing and amplification, probes for detecting complementary DNA or RNA via molecular hybridization, tools for the targeted introduction of mutations and restriction sites, and for the synthesis of artificial genes.