L-Methylfolate: A Vitamin for Your Monoamines
... • Eating disorders • Pregnancy • Gastrointestinal disorders • Documented low levels of MTHFR (methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase) or being from a group (Hispanic and Mediterranean populations) at high risk for decreased levels of this enzyme • Documented high homocysteine levels, which tend to ris ...
... • Eating disorders • Pregnancy • Gastrointestinal disorders • Documented low levels of MTHFR (methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase) or being from a group (Hispanic and Mediterranean populations) at high risk for decreased levels of this enzyme • Documented high homocysteine levels, which tend to ris ...
pcc-sio2.alcohol.oxi..
... make the purification of products lengthy. The anhydrous conditions maintained by a PCC/silica gel oxidation serve to minimize the formation of carboxylic acids as products of the side reaction involving aldehyde hydrate oxidation. Many other oxochromium(VI) amine oxidants have been developed (20) i ...
... make the purification of products lengthy. The anhydrous conditions maintained by a PCC/silica gel oxidation serve to minimize the formation of carboxylic acids as products of the side reaction involving aldehyde hydrate oxidation. Many other oxochromium(VI) amine oxidants have been developed (20) i ...
The Roles of Amino Acids in Milk Yield and Components
... corresponding keto-acid is provided in the diet. Racemic mixtures of D and L-isomers of AAs can provide an effective source of supplemental AA to balance rations. The ketoacid produced following action of D-oxidase has no racemic center and so it can be reaminated to yield the L-isomer. Therefore, k ...
... corresponding keto-acid is provided in the diet. Racemic mixtures of D and L-isomers of AAs can provide an effective source of supplemental AA to balance rations. The ketoacid produced following action of D-oxidase has no racemic center and so it can be reaminated to yield the L-isomer. Therefore, k ...
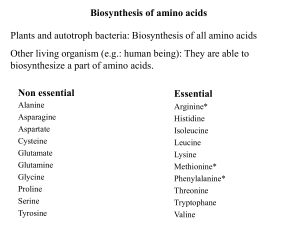
Biosynthesis of amino acids
... 1. All the amino nitrogen from amino acids that undergo transamination can be concentrated in glutamate. 2. Release of nitrogen as ammonia is catalyzed by hepatic Lglutamate dehydrogenase (GDH), 3. Glutamine synthase fixes ammonia as glutamine. Hydrolytic release of the amide nitrogen of glutamine a ...
... 1. All the amino nitrogen from amino acids that undergo transamination can be concentrated in glutamate. 2. Release of nitrogen as ammonia is catalyzed by hepatic Lglutamate dehydrogenase (GDH), 3. Glutamine synthase fixes ammonia as glutamine. Hydrolytic release of the amide nitrogen of glutamine a ...
B) Contain an alcohol - LSU School of Medicine
... 2) fatty acid forms amide linkage with amino group of sphingosine = a ceramide (this is also a precursor for glycolipids) 3) esterification of carbon 1 of ceramide by phosphorylcholine = sphingomyelin (important component of myelin in nerves) ...
... 2) fatty acid forms amide linkage with amino group of sphingosine = a ceramide (this is also a precursor for glycolipids) 3) esterification of carbon 1 of ceramide by phosphorylcholine = sphingomyelin (important component of myelin in nerves) ...
File - Wk 1-2
... ‘reducing’ equivalents and ATP). In aerobic conditions, the pyruvate will go on to be further metabolised in the TCA cycle, whilst in anaerobic conditions, the pyruvate will be converted into lactate to later take part in gluconeogenesis. Glycolysis itself is anaerobic. Depending on which book you l ...
... ‘reducing’ equivalents and ATP). In aerobic conditions, the pyruvate will go on to be further metabolised in the TCA cycle, whilst in anaerobic conditions, the pyruvate will be converted into lactate to later take part in gluconeogenesis. Glycolysis itself is anaerobic. Depending on which book you l ...
Dominant Dietary Fatty Acids
... CoA is the carrier o Fatty acid synthesis Acyl group carrier is ACP Contains part of the CoA molecule Homology in acyl carrier group and CoA molecule (?) Acetyl CoA slide… Fig 14.1 o Priming reaction at first Reactions catalyzed by fatty acid synthase (Diagram) o Two business enzymes o Ying- ...
... CoA is the carrier o Fatty acid synthesis Acyl group carrier is ACP Contains part of the CoA molecule Homology in acyl carrier group and CoA molecule (?) Acetyl CoA slide… Fig 14.1 o Priming reaction at first Reactions catalyzed by fatty acid synthase (Diagram) o Two business enzymes o Ying- ...
Slide ()
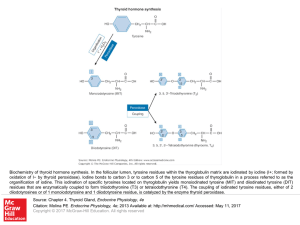
... Biochemistry of thyroid hormone synthesis. In the follicular lumen, tyrosine residues within the thyroglobulin matrix are iodinated by iodine (I+; formed by oxidation of I− by thyroid peroxidase). Iodine bonds to carbon 3 or to carbon 5 of the tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin in a process referred ...
... Biochemistry of thyroid hormone synthesis. In the follicular lumen, tyrosine residues within the thyroglobulin matrix are iodinated by iodine (I+; formed by oxidation of I− by thyroid peroxidase). Iodine bonds to carbon 3 or to carbon 5 of the tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin in a process referred ...
NUCLEOTIDE metabolism class of 2016
... the key regulatory steps) • the key steps in the degradation of purines • causes of primary and secondary hyperuricemia Also familiarize yourselves with • the basis of other disorders associated with the nucleotide metabolism (Lesch-Nyhan syndrome, adenosine deaminase deficiency) • why/how nucleotid ...
... the key regulatory steps) • the key steps in the degradation of purines • causes of primary and secondary hyperuricemia Also familiarize yourselves with • the basis of other disorders associated with the nucleotide metabolism (Lesch-Nyhan syndrome, adenosine deaminase deficiency) • why/how nucleotid ...
CHOLESTEROL 10/02-03/07 LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1) To
... B) Synthesis of bile acids (Fig. 18.9) 1) liver, multistep process starting with cholesterol 2) hydroxyl groups inserted, double bond in B ring reduced, hydrocarbon chain shortened by three carbons, carboxyl group added to end of chain 3) rate-limiting committed step catalyzed by cholesterol 7-a hy ...
... B) Synthesis of bile acids (Fig. 18.9) 1) liver, multistep process starting with cholesterol 2) hydroxyl groups inserted, double bond in B ring reduced, hydrocarbon chain shortened by three carbons, carboxyl group added to end of chain 3) rate-limiting committed step catalyzed by cholesterol 7-a hy ...
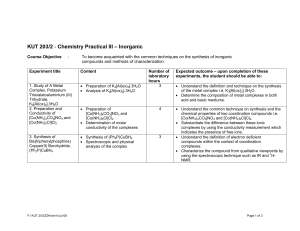
KUT 203/2 - Chemistry Practical III (Inorganic Chemistry)
... of the metal complex i.e. K3[Al(ox)3].3H2O. • Determine the composition of metal complexes in both acid and basic mediums. • Understand the common technique on synthesis and the chemical properties of two coordination compounds i.e. [Co(NH3)4CO3]NO3 and [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2. • Substantiate the difference ...
... of the metal complex i.e. K3[Al(ox)3].3H2O. • Determine the composition of metal complexes in both acid and basic mediums. • Understand the common technique on synthesis and the chemical properties of two coordination compounds i.e. [Co(NH3)4CO3]NO3 and [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2. • Substantiate the difference ...
40_Biochemical functions of liver
... the bound O2 to the peroxide. [4] A hydroxyl ion is now cleaved from this intermediate. Uptake of a proton gives rise to H2O and the reactive form of oxygen mentioned above. In this ferryl radical, the iron is formally tetravalent. [5] The activated oxygen atom inserts itself into a C–H bond in the ...
... the bound O2 to the peroxide. [4] A hydroxyl ion is now cleaved from this intermediate. Uptake of a proton gives rise to H2O and the reactive form of oxygen mentioned above. In this ferryl radical, the iron is formally tetravalent. [5] The activated oxygen atom inserts itself into a C–H bond in the ...
Porous silicon-based nanostructured microparticles as degradable
... EtOH and DCM before being completely dried under vacuum. The particles were then immersed in 10 mL of pyridine containing 500 mg (1.48 mmol) of DMT-Cl and a catalytic amount of DMAP. The mixture was shaken overnight at RT after which the particles were washed extensively with THF and dried under vac ...
... EtOH and DCM before being completely dried under vacuum. The particles were then immersed in 10 mL of pyridine containing 500 mg (1.48 mmol) of DMT-Cl and a catalytic amount of DMAP. The mixture was shaken overnight at RT after which the particles were washed extensively with THF and dried under vac ...
21_Pentose phosphate pathway of carbohydrates metabolism
... The pentose phosphate pathway ends with these five reactions in some tissue. In others it continue in nonoxidative mode to make fructose 6-phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. These reactions link pentose phosphate pathway with glycolysis. ...
... The pentose phosphate pathway ends with these five reactions in some tissue. In others it continue in nonoxidative mode to make fructose 6-phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. These reactions link pentose phosphate pathway with glycolysis. ...
AMINOACID METABOLISM
... Thus GLUTAMATE serves as ‘COLLECTION CENTRE’ for amino groups in the biological system. GDH can utilise NAD or NADP. * This reaction is important as it reversibly links glutamate metabolism with TCA CYCLE through α Ketoglutarate. GDH – regulated allosterically – GTP & ATP inhibits & viceversa ...
... Thus GLUTAMATE serves as ‘COLLECTION CENTRE’ for amino groups in the biological system. GDH can utilise NAD or NADP. * This reaction is important as it reversibly links glutamate metabolism with TCA CYCLE through α Ketoglutarate. GDH – regulated allosterically – GTP & ATP inhibits & viceversa ...
SYNTHESIS OF FATTY ACID Acetyl
... Double bonds are introduced into long-chain acyl-CoAs through an electron-transfer process coupled to the reduction of molecular oxygen Reaction catalyzed by a complex of membrane-bound enzymes Double bonds inserted such that the new double bond is three carbons closer to the CoA group, and never be ...
... Double bonds are introduced into long-chain acyl-CoAs through an electron-transfer process coupled to the reduction of molecular oxygen Reaction catalyzed by a complex of membrane-bound enzymes Double bonds inserted such that the new double bond is three carbons closer to the CoA group, and never be ...
Lipids (lect 5, 6))
... Phosphatidyl inositol: structure not required It is one of cell membrane lipids (but less common) In addition it plays a role in cell signaling ...
... Phosphatidyl inositol: structure not required It is one of cell membrane lipids (but less common) In addition it plays a role in cell signaling ...
Hao Nguyen
... 7. Please, explain the Wobble theory (hypothesis). Include the following facts: a) tell me what it is; b) what are the non-Watson-Crick basepairs; c) location; and d) why is this necessary (that is, what is the function). (20 points) The Wobble hypothesis (or theory) stated that non-Watson-Crick ba ...
... 7. Please, explain the Wobble theory (hypothesis). Include the following facts: a) tell me what it is; b) what are the non-Watson-Crick basepairs; c) location; and d) why is this necessary (that is, what is the function). (20 points) The Wobble hypothesis (or theory) stated that non-Watson-Crick ba ...
Camp 1
... • These sources are most commonly pyruvate, citric acid cycle intermediates, and glucogenic amino acids. • Gluconeogenesis is not the exact reversal of glycolysis; that is, pyruvate to glucose does not occur by reversing the steps of glucose to pyruvate. • There are three irreversible steps in glyco ...
... • These sources are most commonly pyruvate, citric acid cycle intermediates, and glucogenic amino acids. • Gluconeogenesis is not the exact reversal of glycolysis; that is, pyruvate to glucose does not occur by reversing the steps of glucose to pyruvate. • There are three irreversible steps in glyco ...
Protein mteabolism L..
... Folic acid is a member of vitamin B complex. It plays an important role in synthesis of purines and thymidine monophosphate (TMP) and so DNA synthesis. Deficiency of folic acid leads to diminished DNA synthesis and inhibit cell division resulting in meglaoblastic anemia (accumulation of large, immat ...
... Folic acid is a member of vitamin B complex. It plays an important role in synthesis of purines and thymidine monophosphate (TMP) and so DNA synthesis. Deficiency of folic acid leads to diminished DNA synthesis and inhibit cell division resulting in meglaoblastic anemia (accumulation of large, immat ...
Lipids (lect 4))
... Acetyl CoA is the precursor of fatty acid synthesis. It is produced from oxidation of glucose (by oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate), βoxidation of fatty acids and metabolism of ketogenic and mixed amino acids. Acetyl CoA is produced in mitochondria, and FA synthesis occurs in cytoplasm, so acet ...
... Acetyl CoA is the precursor of fatty acid synthesis. It is produced from oxidation of glucose (by oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate), βoxidation of fatty acids and metabolism of ketogenic and mixed amino acids. Acetyl CoA is produced in mitochondria, and FA synthesis occurs in cytoplasm, so acet ...
Amino Acid and Nucleobase Synthesis in Meteoritic Parent Bodies
... - Fischer-Tropsch (FT): H2, CO, NH3 in presence of a catalyst (eg. nickel-iron alloy) can make all 5 - Non-catalytic (NC): reactants, usually involving HCN heated and cooled, no catalyst. Can make all 5 - Catalytic (CA): typically use formamide as sole reactant in presence of catalysts n ...
... - Fischer-Tropsch (FT): H2, CO, NH3 in presence of a catalyst (eg. nickel-iron alloy) can make all 5 - Non-catalytic (NC): reactants, usually involving HCN heated and cooled, no catalyst. Can make all 5 - Catalytic (CA): typically use formamide as sole reactant in presence of catalysts n ...
Translation of Cyclin mRNA Is Necessary for Extracts of Activated
... possibility that translation of cyclin 82 mRNA starts at an AUG upstream of the XlcycP sequence, although, as shown below (Figure 4), the translation product of synthetic mRNA from this clone migrates very close to that of authentic egg mRNA. Cyclin Bl polypeptide contains 398 amino acids and has a ...
... possibility that translation of cyclin 82 mRNA starts at an AUG upstream of the XlcycP sequence, although, as shown below (Figure 4), the translation product of synthetic mRNA from this clone migrates very close to that of authentic egg mRNA. Cyclin Bl polypeptide contains 398 amino acids and has a ...
Oligonucleotide synthesis

Oligonucleotide synthesis is the chemical synthesis of relatively short fragments of nucleic acids with defined chemical structure (sequence). The technique is extremely useful in current laboratory practice because it provides a rapid and inexpensive access to custom-made oligonucleotides of the desired sequence. Whereas enzymes synthesize DNA and RNA only in a 5' to 3' direction, chemical oligonucleotide synthesis does not suffer from this limitation, although it is, most often, carried out in the opposite, 3' to 5' direction. Currently, the process is implemented as solid-phase synthesis using phosphoramidite method and phosphoramidite building blocks derived from protected 2'-deoxynucleosides (dA, dC, dG, and T), ribonucleosides (A, C, G, and U), or chemically modified nucleosides, e.g. LNA, BNA.To obtain the desired oligonucleotide, the building blocks are sequentially coupled to the growing oligonucleotide chain in the order required by the sequence of the product (see Synthetic cycle below). The process has been fully automated since the late 1970s. Upon the completion of the chain assembly, the product is released from the solid phase to solution, deprotected, and collected. The occurrence of side reactions sets practical limits for the length of synthetic oligonucleotides (up to about 200 nucleotide residues) because the number of errors accumulates with the length of the oligonucleotide being synthesized. Products are often isolated by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to obtain the desired oligonucleotides in high purity. Typically, synthetic oligonucleotides are single-stranded DNA or RNA molecules around 15–25 bases in length.Oligonucleotides find a variety of applications in molecular biology and medicine. They are most commonly used as antisense oligonucleotides, small interfering RNA, primers for DNA sequencing and amplification, probes for detecting complementary DNA or RNA via molecular hybridization, tools for the targeted introduction of mutations and restriction sites, and for the synthesis of artificial genes.