BRNO UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY FACULTY OF
... climates. Historically, barley has been an important food source in many parts of the world. However, only 2 % of barley is used for human food at present, mainly in the developing world. It is used as an animal feed more likely, and the worldwide greatest use of barley is for malting purposes, most ...
... climates. Historically, barley has been an important food source in many parts of the world. However, only 2 % of barley is used for human food at present, mainly in the developing world. It is used as an animal feed more likely, and the worldwide greatest use of barley is for malting purposes, most ...
27. GE_7.27 Gluconeo.. - College of Pharmacy at Howard University
... phosphoryl group transfer from glucose 6-phosphate to ADP, forming ATP, an energetically unfavorable reaction. The reaction catalyzed by glucose 6-phosphatase does not require synthesis of ATP; it is a simple hydrolysis of a phosphate ester. ...
... phosphoryl group transfer from glucose 6-phosphate to ADP, forming ATP, an energetically unfavorable reaction. The reaction catalyzed by glucose 6-phosphatase does not require synthesis of ATP; it is a simple hydrolysis of a phosphate ester. ...
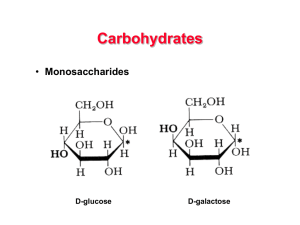
Carbohydrates
... • peroxidase reaction interference by uric acid, vitamin C, bilirubin • suitable for spinal fluid ...
... • peroxidase reaction interference by uric acid, vitamin C, bilirubin • suitable for spinal fluid ...
6 - rguhs
... systems. Glucose oxidase is used in fluorescence enzymatic determinations.4 Glucose oxidase is considered as an antibiotic due to peroxide formation. It is applied as an antimicrobial agent in oral care and other products. ...
... systems. Glucose oxidase is used in fluorescence enzymatic determinations.4 Glucose oxidase is considered as an antibiotic due to peroxide formation. It is applied as an antimicrobial agent in oral care and other products. ...
Chapter 25: Urinary System
... • In GI tract and kidney tubules, Na+/glucose symporters • Most other cells, GluT facilitated diffusion transporters move glucose into cells – insulin increases number of GluT transporters in the membrane of most cells – in liver & brain, always lots of GluT ...
... • In GI tract and kidney tubules, Na+/glucose symporters • Most other cells, GluT facilitated diffusion transporters move glucose into cells – insulin increases number of GluT transporters in the membrane of most cells – in liver & brain, always lots of GluT ...
Gellan-related polysaccharides and the genus
... 1991). Similarity between the general characteristics of *Tel. 619 455 8500; fax 619 587 2716. ...
... 1991). Similarity between the general characteristics of *Tel. 619 455 8500; fax 619 587 2716. ...
Gellan-related polysaccharides and the genus
... 1991). Similarity between the general characteristics of *Tel. 619 455 8500; fax 619 587 2716. ...
... 1991). Similarity between the general characteristics of *Tel. 619 455 8500; fax 619 587 2716. ...
Lecture 6 - TCA cycle I - University of Lethbridge
... Why such a complex set of enzymes? 1. Enzymatic reaction rates are limited by diffusion, with shorter distance between subunits in an enzyme, the substrate can be directed from one subunit (catalytic site) to another. ...
... Why such a complex set of enzymes? 1. Enzymatic reaction rates are limited by diffusion, with shorter distance between subunits in an enzyme, the substrate can be directed from one subunit (catalytic site) to another. ...
Chapter 10 Enzymes - Angelo State University
... • An enzyme inhibitor is a substance that decreases the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. – Many poisons and medicines inhibit one or more enzymes and thereby decrease the rate of the reactions they carry out. – Some substances normally found in cells inhibit specific enzymes, providing a means ...
... • An enzyme inhibitor is a substance that decreases the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. – Many poisons and medicines inhibit one or more enzymes and thereby decrease the rate of the reactions they carry out. – Some substances normally found in cells inhibit specific enzymes, providing a means ...
secondary metabolic processes and products
... Improper handling and storage conditions prior to cooking can significantly increase the level of free reducing sugars, leading to a lower quality product. Carbohydrates can be further classified, based on their degree of polymerization, into monosaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides. Si ...
... Improper handling and storage conditions prior to cooking can significantly increase the level of free reducing sugars, leading to a lower quality product. Carbohydrates can be further classified, based on their degree of polymerization, into monosaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides. Si ...
cholesterol and lipo..
... chenodeoxycholic acid and cholic acid are called primary bile acids. Within the intestines the primary bile acids are converted by intestinal bacteria to the secondary bile acids, identified as deoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid. Both primary and secondary bile acids are reabsorbed by the intesti ...
... chenodeoxycholic acid and cholic acid are called primary bile acids. Within the intestines the primary bile acids are converted by intestinal bacteria to the secondary bile acids, identified as deoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid. Both primary and secondary bile acids are reabsorbed by the intesti ...
Organic Chemistry Notes Student
... • The bonds between amino acid monomers – Are called _______________ bonds Carboxyl group ...
... • The bonds between amino acid monomers – Are called _______________ bonds Carboxyl group ...
Biology: Concepts and Connections, 6e
... B) is most common in people of European descent. C) can currently be treated by gene therapy to treat the underlying cause. D) does not affect the consumption of beverages made from soy or rice. E) is a fatal disease with no known treatment. Answer: D Topic: Opening Essay Skill: Factual Recall ...
... B) is most common in people of European descent. C) can currently be treated by gene therapy to treat the underlying cause. D) does not affect the consumption of beverages made from soy or rice. E) is a fatal disease with no known treatment. Answer: D Topic: Opening Essay Skill: Factual Recall ...
Hydrolytic Fate of 3/15-Acetyldeoxynivalenol in Humans: Specific
... than an hour) at the level of the duodenum and jejunum, where only few bacteria are present; and (ii) in vitro experiments have shown that 3/15ADON could efficiently be absorbed by the IEC [8,21,25]. Thus, it seems more plausible that without the need of a luminal deacetylation, 3/15ADON are absorbe ...
... than an hour) at the level of the duodenum and jejunum, where only few bacteria are present; and (ii) in vitro experiments have shown that 3/15ADON could efficiently be absorbed by the IEC [8,21,25]. Thus, it seems more plausible that without the need of a luminal deacetylation, 3/15ADON are absorbe ...
as a PDF - PubAg
... Bioactive proteins, such as digestive proteinase inhibitors, have potential to be used for insect control (Duan et al., 1996). Genes producing bioactive proteins can be used to transform host plants to suppress insect growth and reduce pest insect population size (Baker and Kramer, 1996), which can ...
... Bioactive proteins, such as digestive proteinase inhibitors, have potential to be used for insect control (Duan et al., 1996). Genes producing bioactive proteins can be used to transform host plants to suppress insect growth and reduce pest insect population size (Baker and Kramer, 1996), which can ...
ENZYMES at Lew Port`s Biology Place
... 2. Without enzymes, many of the important processes of life could not happen. Enzymes are very __________ in their functions. Each enzyme has only __________ reaction that it can help. (ANIMATION b) 3. Enzymes are __________ __________ when they perform their function. This means that the same enzym ...
... 2. Without enzymes, many of the important processes of life could not happen. Enzymes are very __________ in their functions. Each enzyme has only __________ reaction that it can help. (ANIMATION b) 3. Enzymes are __________ __________ when they perform their function. This means that the same enzym ...
Artifact 1
... carbohydrate metabolism as it catalyzes this major step of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. This enzyme is particularly important for fructose metabolism. Genetic mutations leading to a lack of functional aldolase B result in a condition called hereditary fructose intolerance. F1P accumulation is ...
... carbohydrate metabolism as it catalyzes this major step of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. This enzyme is particularly important for fructose metabolism. Genetic mutations leading to a lack of functional aldolase B result in a condition called hereditary fructose intolerance. F1P accumulation is ...
MB ChB PHASE I
... These enzymes have different specificities: they cleave adjacent to different amino-acids. Together, they break polypeptides to free amino-acids and short peptides. In addition, a mucosal cell-surface aminopeptidase removes amino-acids one at a time from N termini. ...
... These enzymes have different specificities: they cleave adjacent to different amino-acids. Together, they break polypeptides to free amino-acids and short peptides. In addition, a mucosal cell-surface aminopeptidase removes amino-acids one at a time from N termini. ...
Daily Recommendations For Folic Acid
... Folic acid supplements and food fortification Despite strong recommendations many women fail to increase folic acid intake in pregnancy. Routine fortification of UK flour with folic acid would be a simple way of supplementing the diet, increasing baseline folic acid intake from flour-based foods. Ma ...
... Folic acid supplements and food fortification Despite strong recommendations many women fail to increase folic acid intake in pregnancy. Routine fortification of UK flour with folic acid would be a simple way of supplementing the diet, increasing baseline folic acid intake from flour-based foods. Ma ...
BCHM 2300 Test III - Lipids and Metabolism
... 63. True or False? Taking protein supplements or eating high-protein diet is only the effective way to lose fat and gain muscle mass. A) True B) False 64. True or False? Kidney beans are considered to be a source of complete and high quality protein. A) True B) False 65. True or False? Diets high in ...
... 63. True or False? Taking protein supplements or eating high-protein diet is only the effective way to lose fat and gain muscle mass. A) True B) False 64. True or False? Kidney beans are considered to be a source of complete and high quality protein. A) True B) False 65. True or False? Diets high in ...
Small-molecule metabolism: an enzyme mosaic
... are very rare. If duplication of large portions of the bacterial chromosome takes place, and all the genes in a duplicated portion were used to form a new pathway, serial recruitment would be expected. In fact, only 89 out of 26 341 (0.3%) possible pairs of enzymes are homologous in both the first a ...
... are very rare. If duplication of large portions of the bacterial chromosome takes place, and all the genes in a duplicated portion were used to form a new pathway, serial recruitment would be expected. In fact, only 89 out of 26 341 (0.3%) possible pairs of enzymes are homologous in both the first a ...
A1121 SD1 - Food Standards Australia New Zealand
... Cobalt. Strain P-52 is not genetically modified and has been confirmed as belonging to the species A. melleus. A. melleus has not been previously assessed by FSANZ. However, A. melleus has been used for many years for food or feed purposes or in the production of enzymes used as processing aids in D ...
... Cobalt. Strain P-52 is not genetically modified and has been confirmed as belonging to the species A. melleus. A. melleus has not been previously assessed by FSANZ. However, A. melleus has been used for many years for food or feed purposes or in the production of enzymes used as processing aids in D ...
Protein hydrolysates in sports nutrition
... acid balance across the leg improved in both groups, but a net anabolic effect was observed only with supraphysiologically high doses. ...
... acid balance across the leg improved in both groups, but a net anabolic effect was observed only with supraphysiologically high doses. ...
Enzymes in jasmonate biosynthesis – Structure, function, regulation
... 2002)) mediates import of OPDA, and thus contributes to the biosynthesis of JAs (Theodoulou et al., 2005). CTS catalyzes the ATPdependent uptake of multiple b-oxidation substrates into peroxisomes. Reduced levels of JAs, impaired wound-induced JA accumulation, and reduced expression of the JA-depend ...
... 2002)) mediates import of OPDA, and thus contributes to the biosynthesis of JAs (Theodoulou et al., 2005). CTS catalyzes the ATPdependent uptake of multiple b-oxidation substrates into peroxisomes. Reduced levels of JAs, impaired wound-induced JA accumulation, and reduced expression of the JA-depend ...
Digestion

Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into small water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the watery blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into the blood stream. Digestion is a form of catabolism that is often divided into two processes based on how food is broken down: mechanical and chemical digestion. The term mechanical digestion refers to the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces which can subsequently be accessed by digestive enzymes. In chemical digestion, enzymes break down food into the small molecules the body can use.In the human digestive system, food enters the mouth and mechanical digestion of the food starts by the action of mastication (chewing), a form of mechanical digestion, and the wetting contact of saliva. Saliva, a liquid secreted by the salivary glands, contains salivary amylase, an enzyme which starts the digestion of starch in the food; the saliva also contains mucus, which lubricates the food, and hydrogen carbonate, which provides the ideal conditions of pH (alkaline) for amylase to work. After undergoing mastication and starch digestion, the food will be in the form of a small, round slurry mass called a bolus. It will then travel down the esophagus and into the stomach by the action of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach starts protein digestion. Gastric juice mainly contains hydrochloric acid and pepsin. As these two chemicals may damage the stomach wall, mucus is secreted by the stomach, providing a slimy layer that acts as a shield against the damaging effects of the chemicals. At the same time protein digestion is occurring, mechanical mixing occurs by peristalsis, which is waves of muscular contractions that move along the stomach wall. This allows the mass of food to further mix with the digestive enzymes.After some time (typically 1–2 hours in humans, 4–6 hours in dogs, 3–4 hours in house cats), the resulting thick liquid is called chyme. When the pyloric sphincter valve opens, chyme enters the duodenum where it mixes with digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile juice from the liver and then passes through the small intestine, in which digestion continues. When the chyme is fully digested, it is absorbed into the blood. 95% of absorption of nutrients occurs in the small intestine. Water and minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood in the colon (large intestine) where the pH is slightly acidic about 5.6 ~ 6.9. Some vitamins, such as biotin and vitamin K (K2MK7) produced by bacteria in the colon are also absorbed into the blood in the colon. Waste material is eliminated from the rectum during defecation.