Digestion and Absorption of the Food Nutrients
... Enzymes don’t get changed during the reaction ...
... Enzymes don’t get changed during the reaction ...
Fetal Pig Information
... The area where the stomach narrows to join to the small intestine is known as the pyloric region. There are two sphincters which are muscles used to regulate the movement of food in adult mammals. The cardiac sphincter is a muscle found where the esophagus and stomach meet and ensures food does not ...
... The area where the stomach narrows to join to the small intestine is known as the pyloric region. There are two sphincters which are muscles used to regulate the movement of food in adult mammals. The cardiac sphincter is a muscle found where the esophagus and stomach meet and ensures food does not ...
alimentary canal
... The salivary glands are accessory organs of digestion associated with the mouth. The teeth and tongue cooperate in chewing movements to reduce the size of food particles and mix food with saliva. These chewing movements, termed mastication (mas″-ti-ka-′shun), initiate the mechanical part of digest ...
... The salivary glands are accessory organs of digestion associated with the mouth. The teeth and tongue cooperate in chewing movements to reduce the size of food particles and mix food with saliva. These chewing movements, termed mastication (mas″-ti-ka-′shun), initiate the mechanical part of digest ...
File
... is approximately 4.5, while the pH of the surrounding cytoplasm is approximately 7. The average pH of the human stomach during digestion is approximately 2.5, while the average pH of the small intestine during digestion is about 8. The graph below shows how pH affects the enzyme activity of four dif ...
... is approximately 4.5, while the pH of the surrounding cytoplasm is approximately 7. The average pH of the human stomach during digestion is approximately 2.5, while the average pH of the small intestine during digestion is about 8. The graph below shows how pH affects the enzyme activity of four dif ...
aminoacids 2
... The diseases are inherited as autosomal recessive illnesses,due to a defect in the enzyme cystathionine β-synthase, Characteristics of Homocystinuria high plasma and urinary levels of homocysteine and methionine and low levels of cysteine. ectopia lentis (displacement of the lens of the eye), skelet ...
... The diseases are inherited as autosomal recessive illnesses,due to a defect in the enzyme cystathionine β-synthase, Characteristics of Homocystinuria high plasma and urinary levels of homocysteine and methionine and low levels of cysteine. ectopia lentis (displacement of the lens of the eye), skelet ...
Amylase
... Digestive Enzymes: are used in the lumen of the GI tract to break down complex molecules into absorbable subunits Enzymes are biological catalysts which increase the rate of a chemical reaction without themselves becoming part of the product: ...
... Digestive Enzymes: are used in the lumen of the GI tract to break down complex molecules into absorbable subunits Enzymes are biological catalysts which increase the rate of a chemical reaction without themselves becoming part of the product: ...
BIOMOLECULES UNIT 3 Chemistry Review: Atoms
... Van der Waal’s forces- attraction between positive and negatively charged ions that cumulatively are strong, (Gecko feet), but not as strong as the other types. Hydrogen bonds- attraction between water molecules, and other molecules Elements- pure substances that cannot be broken down by physical or ...
... Van der Waal’s forces- attraction between positive and negatively charged ions that cumulatively are strong, (Gecko feet), but not as strong as the other types. Hydrogen bonds- attraction between water molecules, and other molecules Elements- pure substances that cannot be broken down by physical or ...
a source of carbon , essential amino acids , essential fatty acids
... source since they cannot be synthesized from other dietary nutrients or metabolic precursors. ...
... source since they cannot be synthesized from other dietary nutrients or metabolic precursors. ...
Biochemistry Presentation Notes Pre-AP 14-15
... 1. energy storage – twice as much energy / g. as carbohydrates 2. makes up part of the cell membrane 3. hormones are lipids – estrogen and testosterone B. Examples: 1. Fats – solid at room temperature – butter, lard (animal fat) 2. Oils – liquid at room temperature – corn oil, olive oil (plant fats) ...
... 1. energy storage – twice as much energy / g. as carbohydrates 2. makes up part of the cell membrane 3. hormones are lipids – estrogen and testosterone B. Examples: 1. Fats – solid at room temperature – butter, lard (animal fat) 2. Oils – liquid at room temperature – corn oil, olive oil (plant fats) ...
Human Anatomy Digestive System
... of the sigmoid colon and ends at the anal canal. Anal Canal The last 2–3 cm of the digestive tract is the anal canal. It begins at the inferior end of the rectum and ends at the anus. Anus: Is the external digestive tract opening. ...
... of the sigmoid colon and ends at the anal canal. Anal Canal The last 2–3 cm of the digestive tract is the anal canal. It begins at the inferior end of the rectum and ends at the anus. Anus: Is the external digestive tract opening. ...
What more do we need to know to optimize the
... – Look at water pH/diet buffering capacity • Lowering pH, especially in young birds, can help with protease efficacy ...
... – Look at water pH/diet buffering capacity • Lowering pH, especially in young birds, can help with protease efficacy ...
biochemistry-16
... • How are large macromolecules formed? Smaller sugars combine to make larger molecules. ...
... • How are large macromolecules formed? Smaller sugars combine to make larger molecules. ...
10 BIO By dr. bp karn Q1.What do you mean by nutrition?
... Q14.Differentiate between holozoic-nutrition and saprophytic nutrition ? Q 15.How photosynthesis occurs in desert plant as their stomata are close during day time ? Q16.Write the three events occurring during the process of photosynthesis ? Q17.Write the function of the following in the digestive pr ...
... Q14.Differentiate between holozoic-nutrition and saprophytic nutrition ? Q 15.How photosynthesis occurs in desert plant as their stomata are close during day time ? Q16.Write the three events occurring during the process of photosynthesis ? Q17.Write the function of the following in the digestive pr ...
NF96-251 A Comparative Study of Fiber Digestion and Subsequent
... from the diet. Microbes leaving the rumen provide a protein source to the animal (host). "By-pass protein" is a term for protein that passes protected from microbial breakdown through the rumen to the small intestine where it is absorbed and utilized by the animal (host) use (not for microbes). Fibe ...
... from the diet. Microbes leaving the rumen provide a protein source to the animal (host). "By-pass protein" is a term for protein that passes protected from microbial breakdown through the rumen to the small intestine where it is absorbed and utilized by the animal (host) use (not for microbes). Fibe ...
Document
... ◦ The anterior vagal trunk mainly from the left vagus nerve supply the anterior surface of the stomach and the pyrolus. It also carries nerve fibres for pain transmission. ◦ The posterior vagal trunk mainly from the right vagus nerve supply the posterior surface of the stomach. It also carries secre ...
... ◦ The anterior vagal trunk mainly from the left vagus nerve supply the anterior surface of the stomach and the pyrolus. It also carries nerve fibres for pain transmission. ◦ The posterior vagal trunk mainly from the right vagus nerve supply the posterior surface of the stomach. It also carries secre ...
Biochemistry Ch 37 696-706 [4-20
... Digestion of Proteins in the Stomach – pepsinogen is secreted by chief cells in the stomach -gastric acid secreted by parietal cells, which alters conformation of pepsinogen for autocatalysis -dietary proteins denatured by stomach acid, which denatures proteins and unfold them to make them better su ...
... Digestion of Proteins in the Stomach – pepsinogen is secreted by chief cells in the stomach -gastric acid secreted by parietal cells, which alters conformation of pepsinogen for autocatalysis -dietary proteins denatured by stomach acid, which denatures proteins and unfold them to make them better su ...
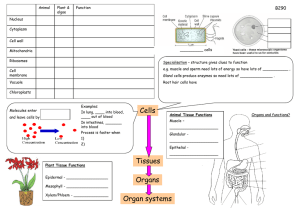
Chapter 2 SWBATS Content Standards Cell Biology 1. The
... What are the two main types of chemical bonds? Give an example of each. Why are water molecules polar? What are acidic solutions? What are basic solutions? Give an example of each. What are the functions of each group of organic compounds? What happens to chemical bonds during chemical reactions? Ho ...
... What are the two main types of chemical bonds? Give an example of each. Why are water molecules polar? What are acidic solutions? What are basic solutions? Give an example of each. What are the functions of each group of organic compounds? What happens to chemical bonds during chemical reactions? Ho ...
2 Biochemistry
... • chemicals that do not contain carbon • water- most abundant & important, 60-80% of most cells • salts- ionic compounds containing ions other than H+ & OH• salts of many metals are common in the body ex: NaCl, Ca2CO3, KCl • Ca3PO4 most plentiful salt, hardness of bones & teeth, nerve transmission, ...
... • chemicals that do not contain carbon • water- most abundant & important, 60-80% of most cells • salts- ionic compounds containing ions other than H+ & OH• salts of many metals are common in the body ex: NaCl, Ca2CO3, KCl • Ca3PO4 most plentiful salt, hardness of bones & teeth, nerve transmission, ...
Document
... Describe examples of enzymes that work outside of body cells, such as digestive enzymes, including details of where they are produced, where they go, and what reactions they catalyse Describe the function and sites of production of amylase, protease enzymes and lipase enzymes Relate the acidic condi ...
... Describe examples of enzymes that work outside of body cells, such as digestive enzymes, including details of where they are produced, where they go, and what reactions they catalyse Describe the function and sites of production of amylase, protease enzymes and lipase enzymes Relate the acidic condi ...
digestive tract
... the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract), digestive tract, guts or gut is the system of organs within multicellular organisms that takes in food, digests it to extract energy and nutrients, and expels the remaining matter. The major functions of the gastrointestinal tract are ingestion, digestion, abso ...
... the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract), digestive tract, guts or gut is the system of organs within multicellular organisms that takes in food, digests it to extract energy and nutrients, and expels the remaining matter. The major functions of the gastrointestinal tract are ingestion, digestion, abso ...
Digestion

Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into small water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the watery blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into the blood stream. Digestion is a form of catabolism that is often divided into two processes based on how food is broken down: mechanical and chemical digestion. The term mechanical digestion refers to the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces which can subsequently be accessed by digestive enzymes. In chemical digestion, enzymes break down food into the small molecules the body can use.In the human digestive system, food enters the mouth and mechanical digestion of the food starts by the action of mastication (chewing), a form of mechanical digestion, and the wetting contact of saliva. Saliva, a liquid secreted by the salivary glands, contains salivary amylase, an enzyme which starts the digestion of starch in the food; the saliva also contains mucus, which lubricates the food, and hydrogen carbonate, which provides the ideal conditions of pH (alkaline) for amylase to work. After undergoing mastication and starch digestion, the food will be in the form of a small, round slurry mass called a bolus. It will then travel down the esophagus and into the stomach by the action of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach starts protein digestion. Gastric juice mainly contains hydrochloric acid and pepsin. As these two chemicals may damage the stomach wall, mucus is secreted by the stomach, providing a slimy layer that acts as a shield against the damaging effects of the chemicals. At the same time protein digestion is occurring, mechanical mixing occurs by peristalsis, which is waves of muscular contractions that move along the stomach wall. This allows the mass of food to further mix with the digestive enzymes.After some time (typically 1–2 hours in humans, 4–6 hours in dogs, 3–4 hours in house cats), the resulting thick liquid is called chyme. When the pyloric sphincter valve opens, chyme enters the duodenum where it mixes with digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile juice from the liver and then passes through the small intestine, in which digestion continues. When the chyme is fully digested, it is absorbed into the blood. 95% of absorption of nutrients occurs in the small intestine. Water and minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood in the colon (large intestine) where the pH is slightly acidic about 5.6 ~ 6.9. Some vitamins, such as biotin and vitamin K (K2MK7) produced by bacteria in the colon are also absorbed into the blood in the colon. Waste material is eliminated from the rectum during defecation.