LAB: (Day 1) Macromolecules/Enzymes
... When we eat, we consume macromolecules, vitamins, and minerals needed for our body to function normally. When macromolecules are consumed, it is necessary to break them down into smaller monomers to use them. Carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars, such as glucose, that are used to create ...
... When we eat, we consume macromolecules, vitamins, and minerals needed for our body to function normally. When macromolecules are consumed, it is necessary to break them down into smaller monomers to use them. Carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars, such as glucose, that are used to create ...
FOOD PRESERVATION BY SALT, ACID, SUGAR AND CHEMICAL
... • Salt produces a number of effects when added to fresh plant tissues • Salt exerts a selective inhibitory action on certain contaminating microorganisms. • Salt also affects the water activity (aw) of the substrate, thus controlling microbial growth by a method independent of its toxic effects. ...
... • Salt produces a number of effects when added to fresh plant tissues • Salt exerts a selective inhibitory action on certain contaminating microorganisms. • Salt also affects the water activity (aw) of the substrate, thus controlling microbial growth by a method independent of its toxic effects. ...
Class XIX Tissues and organ systems I – Epithelial tissues To Grow
... -Require large amounts of minerals (Calcium, Iron, etc.) Therefore, animals need to ingest (eat) another living organisms which make or contains these substances ...
... -Require large amounts of minerals (Calcium, Iron, etc.) Therefore, animals need to ingest (eat) another living organisms which make or contains these substances ...
Probiotic Complex
... everyone. Healthy microorganisms, called microflora, are found in the digestive tract and have a protective role in the body. Yet, even when we eat well, stress, age, certain medications, the environment and other factors can reduce the proportion of this friendly bacteria in our bodies. This can le ...
... everyone. Healthy microorganisms, called microflora, are found in the digestive tract and have a protective role in the body. Yet, even when we eat well, stress, age, certain medications, the environment and other factors can reduce the proportion of this friendly bacteria in our bodies. This can le ...
Document
... We say the particles diffuse down a concentration _________. In cells, the cell membrane has small holes that allow small particles through, but not large molecules. We call this membrane ________ ________. The bigger the difference in concentration, the faster the rate of ________. ...
... We say the particles diffuse down a concentration _________. In cells, the cell membrane has small holes that allow small particles through, but not large molecules. We call this membrane ________ ________. The bigger the difference in concentration, the faster the rate of ________. ...
Review Sheet - Phillips Scientific Methods
... of water. Glucose + Fructose is sucrose o Polysaccharides Polymers of many monosaccharides Starch is a storage polysaccharide found in plants. Entirely of glucose. Amylose and amylpectin. Animals use glycogen (liver and muscles) Cellulose has Beta glycosidic linkages; we only have enz for ...
... of water. Glucose + Fructose is sucrose o Polysaccharides Polymers of many monosaccharides Starch is a storage polysaccharide found in plants. Entirely of glucose. Amylose and amylpectin. Animals use glycogen (liver and muscles) Cellulose has Beta glycosidic linkages; we only have enz for ...
Catabolic Pathways and Glycolysis
... Catabolic Pathways and Glycolysis • The ability to do that work depends on catabolic process that harvest the potential energy found in organic molecules. The 2 catabolic processes that occur in organisms are fermentation (breakdown without O2)and cellular respiration (breakdown with O2). ...
... Catabolic Pathways and Glycolysis • The ability to do that work depends on catabolic process that harvest the potential energy found in organic molecules. The 2 catabolic processes that occur in organisms are fermentation (breakdown without O2)and cellular respiration (breakdown with O2). ...
Energy - My CCSD
... D. Every enzyme catalyzes only one reaction or one type of reaction E. Enzymes …. 1. break down toxins (a lot in liver) 2. speed up digestion ...
... D. Every enzyme catalyzes only one reaction or one type of reaction E. Enzymes …. 1. break down toxins (a lot in liver) 2. speed up digestion ...
Complex carbohydrates
... However, organisms differ greatly in terms of how much water they need and how they get it. A human will survive for about three days without water. ...
... However, organisms differ greatly in terms of how much water they need and how they get it. A human will survive for about three days without water. ...
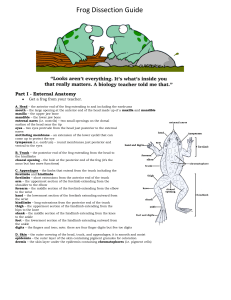
Frog Dissection Guide
... Lift and cut through the muscles and breast bone to open up the body cavity. If your frog is a female, the abdominal cavity may be filled with dark-colored eggs. If so, remove the eggs on one side so you can see the organs underlying them. heart (atria and ventricle) – in the center at the anterior ...
... Lift and cut through the muscles and breast bone to open up the body cavity. If your frog is a female, the abdominal cavity may be filled with dark-colored eggs. If so, remove the eggs on one side so you can see the organs underlying them. heart (atria and ventricle) – in the center at the anterior ...
Anatomy handout
... changes this substance to secretin. The secretin is absorbed by the blood and carried to the liver and pancreas which are stimulated to secrete their fluids. Secretin belongs to a class of activators known as hormones. The pancreatic juice contains three enzymes which act upon proteins, carbohydrate ...
... changes this substance to secretin. The secretin is absorbed by the blood and carried to the liver and pancreas which are stimulated to secrete their fluids. Secretin belongs to a class of activators known as hormones. The pancreatic juice contains three enzymes which act upon proteins, carbohydrate ...
Document
... a. plant cells create glucose. b. cells grow and reproduce. c. cells use oxygen to produce energy from food. d. cells breakdown food without using oxygen. 2.Fermentation in muscle cells produces a. glucose. b. lactic acid. c. water. d. bacteria. 3. Photosynthesis allows a. an animal cell to get ener ...
... a. plant cells create glucose. b. cells grow and reproduce. c. cells use oxygen to produce energy from food. d. cells breakdown food without using oxygen. 2.Fermentation in muscle cells produces a. glucose. b. lactic acid. c. water. d. bacteria. 3. Photosynthesis allows a. an animal cell to get ener ...
Dissection Guide - Home Science Tools
... 6. Looking inside the mouth, find the tongue. A snake both tastes and smells with its tongue. It flickers its tongue in and out to pick up scent particles in the air. The tongue is forked because when the snake brings the tongue back into its mouth, the tips are inserted into two pockets in the mout ...
... 6. Looking inside the mouth, find the tongue. A snake both tastes and smells with its tongue. It flickers its tongue in and out to pick up scent particles in the air. The tongue is forked because when the snake brings the tongue back into its mouth, the tips are inserted into two pockets in the mout ...
29_Metabolism of amino acids. Digestion of proteins
... • Proteins of animal sources (meat, milk, eggs) have high BV because they contain all the essential amino acids. • Proteins from plant sources (wheat, corn, beans) have low BV thus combination of more than one plant protein is required (a vegetarian diet) to increase its BV. ...
... • Proteins of animal sources (meat, milk, eggs) have high BV because they contain all the essential amino acids. • Proteins from plant sources (wheat, corn, beans) have low BV thus combination of more than one plant protein is required (a vegetarian diet) to increase its BV. ...
The Necessities of Life
... Inside blood, the red protein, hemoglobin, bind to oxygen to deliver and release oxygen throughout the body Some proteins protect cells Other proteins, called enzymes start or speed up chemical reactions ...
... Inside blood, the red protein, hemoglobin, bind to oxygen to deliver and release oxygen throughout the body Some proteins protect cells Other proteins, called enzymes start or speed up chemical reactions ...
Slideshow
... *Used to build structures for the body; carry out cell metabolism Proteins come in variety of shapes and ...
... *Used to build structures for the body; carry out cell metabolism Proteins come in variety of shapes and ...
Biomolecules Fill in the crossword puzzle by using
... contains the elements carbon, hydrogen,oxygen and nitrogen and is composed of amino acids examples are insulin,hemglobin and enzymes. are the small building blocks of polymers ...
... contains the elements carbon, hydrogen,oxygen and nitrogen and is composed of amino acids examples are insulin,hemglobin and enzymes. are the small building blocks of polymers ...
topic 3 igcse biology
... enzyme is vital for the enzyme's function. High temperatures denature the enzyme, changing the shape of the active site. ...
... enzyme is vital for the enzyme's function. High temperatures denature the enzyme, changing the shape of the active site. ...
Biological Catalysts
... covalent bonds (disulphide bridges) & hydrophobic interactions between the amino acid side chains. Enzymes are tertiary structures, and not quaternary as they contain just one polypeptide chain rather than several polypeptides that make up the quaternary structure. ...
... covalent bonds (disulphide bridges) & hydrophobic interactions between the amino acid side chains. Enzymes are tertiary structures, and not quaternary as they contain just one polypeptide chain rather than several polypeptides that make up the quaternary structure. ...
Matthew Mekari
... cellular respiration, the oxygen dependent process by which cells extract energy from food molecules. B. Most eukaryotes cells (and many prokaryotic cells ) are aerobic, that is, they depend on oxygen for life. C. Many prokaryotes and a few eukaryotes can live anaerobically, without oxygen. ...
... cellular respiration, the oxygen dependent process by which cells extract energy from food molecules. B. Most eukaryotes cells (and many prokaryotic cells ) are aerobic, that is, they depend on oxygen for life. C. Many prokaryotes and a few eukaryotes can live anaerobically, without oxygen. ...
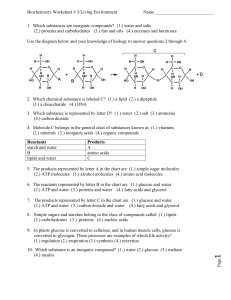
1. Which substances are inorganic compounds?
... (3.) flufferfication (4.) aerobic respiration 13. The reverse reaction indicated by arrow E illustrates (1.) chemical digestion (2.) synthesis (3.) flufferfication (4.) aerobic respiration ...
... (3.) flufferfication (4.) aerobic respiration 13. The reverse reaction indicated by arrow E illustrates (1.) chemical digestion (2.) synthesis (3.) flufferfication (4.) aerobic respiration ...
File - FOOD CHEMISTRY: Presented by Arnold
... Substance that prevents or slows down oxidation; inhibits reactions promoted by oxygen; often used as a preservative. Amylase An enzyme (protein) in saliva that breaks down starch Amino acids Contain carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and sometimes sulfur. Serves as monomers to make ...
... Substance that prevents or slows down oxidation; inhibits reactions promoted by oxygen; often used as a preservative. Amylase An enzyme (protein) in saliva that breaks down starch Amino acids Contain carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and sometimes sulfur. Serves as monomers to make ...
Lesson One: The Four Basic Food Molecules
... Proteins are made from 20 amino acids that form chains that twist, curl, fold, bend and form many different shapes. Two important shapes are the alpha helix and the beta pleated sheet. Proteins are often denatured by heat or acid. Proteins can coagulate. Enzymes are a specific type of proteins. Fats ...
... Proteins are made from 20 amino acids that form chains that twist, curl, fold, bend and form many different shapes. Two important shapes are the alpha helix and the beta pleated sheet. Proteins are often denatured by heat or acid. Proteins can coagulate. Enzymes are a specific type of proteins. Fats ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Ch. 6 Cellular Respiration
... excellent source of fuel? • The many hydrogen atoms covalently bonded to carbon, that the cell can break for energy, and of course the many energy rich electrons. • Can fats be used in cellular respiration? • Yes, by being converted to intermediates. ...
... excellent source of fuel? • The many hydrogen atoms covalently bonded to carbon, that the cell can break for energy, and of course the many energy rich electrons. • Can fats be used in cellular respiration? • Yes, by being converted to intermediates. ...
Digestion

Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into small water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the watery blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into the blood stream. Digestion is a form of catabolism that is often divided into two processes based on how food is broken down: mechanical and chemical digestion. The term mechanical digestion refers to the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces which can subsequently be accessed by digestive enzymes. In chemical digestion, enzymes break down food into the small molecules the body can use.In the human digestive system, food enters the mouth and mechanical digestion of the food starts by the action of mastication (chewing), a form of mechanical digestion, and the wetting contact of saliva. Saliva, a liquid secreted by the salivary glands, contains salivary amylase, an enzyme which starts the digestion of starch in the food; the saliva also contains mucus, which lubricates the food, and hydrogen carbonate, which provides the ideal conditions of pH (alkaline) for amylase to work. After undergoing mastication and starch digestion, the food will be in the form of a small, round slurry mass called a bolus. It will then travel down the esophagus and into the stomach by the action of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach starts protein digestion. Gastric juice mainly contains hydrochloric acid and pepsin. As these two chemicals may damage the stomach wall, mucus is secreted by the stomach, providing a slimy layer that acts as a shield against the damaging effects of the chemicals. At the same time protein digestion is occurring, mechanical mixing occurs by peristalsis, which is waves of muscular contractions that move along the stomach wall. This allows the mass of food to further mix with the digestive enzymes.After some time (typically 1–2 hours in humans, 4–6 hours in dogs, 3–4 hours in house cats), the resulting thick liquid is called chyme. When the pyloric sphincter valve opens, chyme enters the duodenum where it mixes with digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile juice from the liver and then passes through the small intestine, in which digestion continues. When the chyme is fully digested, it is absorbed into the blood. 95% of absorption of nutrients occurs in the small intestine. Water and minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood in the colon (large intestine) where the pH is slightly acidic about 5.6 ~ 6.9. Some vitamins, such as biotin and vitamin K (K2MK7) produced by bacteria in the colon are also absorbed into the blood in the colon. Waste material is eliminated from the rectum during defecation.