5.2 Molecular Models for Fungi Growing: Digestion and
... How are molecules in food changed chemically so that fungal cells can use them? ...
... How are molecules in food changed chemically so that fungal cells can use them? ...
Chapter 25
... • Organic molecules that exist in minute quantities in food – Essential vitamins must be obtained by diet ...
... • Organic molecules that exist in minute quantities in food – Essential vitamins must be obtained by diet ...
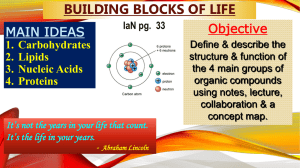
Macromolecules and the Molecules of Life
... Macromolecules • Macromolecules • Made of CHNOP • Large molecules formed by joining polymers • Monomers • The basic units that bond together to form molecules essential to life • Bond via condensation reaction • Monomer + monomer = polymer + water • Polymers • Several monomers joined together • Sep ...
... Macromolecules • Macromolecules • Made of CHNOP • Large molecules formed by joining polymers • Monomers • The basic units that bond together to form molecules essential to life • Bond via condensation reaction • Monomer + monomer = polymer + water • Polymers • Several monomers joined together • Sep ...
Rat Dissection Guide
... the job for them. Separate out the small intestine, clipping gently through the mesentery holding it together, until you have separated out a long single tube (you're going to measure them for question 10). At a certain, clearly recognizable point, the small intestine joins the large intestine, or c ...
... the job for them. Separate out the small intestine, clipping gently through the mesentery holding it together, until you have separated out a long single tube (you're going to measure them for question 10). At a certain, clearly recognizable point, the small intestine joins the large intestine, or c ...
Food Safety & Toxicology (3) - Share My Knowledge & Experience
... • Reduction: Consumption of foods rich in calcium, such as dairy products and seafood, and enhanced vitamin D intake ...
... • Reduction: Consumption of foods rich in calcium, such as dairy products and seafood, and enhanced vitamin D intake ...
AMA 108 PowerPoint
... The Amino Acids (For each amino acid, both the three-letter and single-letter codes are given. CLICK the NAME to see the structural formula)Alanine Ala A hydrophobic Arginine Arg R free amino group makes it basic and hydrophilic Asparagine Asn N carbohydrate can be covalently linked ("N-linked) to i ...
... The Amino Acids (For each amino acid, both the three-letter and single-letter codes are given. CLICK the NAME to see the structural formula)Alanine Ala A hydrophobic Arginine Arg R free amino group makes it basic and hydrophilic Asparagine Asn N carbohydrate can be covalently linked ("N-linked) to i ...
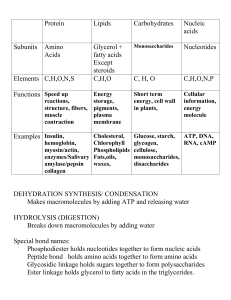
Macromolecules chart
... DEHYDRATION SYNTHESIS/ CONDENSATION Makes macromolecules by adding ATP and releasing water HYDROLYSIS (DIGESTION) Breaks down macromolecules by adding water Special bond names: Phosphodiester holds nucleotides together to form nucleic acids Peptide bond holds amino acids together to form amino acids ...
... DEHYDRATION SYNTHESIS/ CONDENSATION Makes macromolecules by adding ATP and releasing water HYDROLYSIS (DIGESTION) Breaks down macromolecules by adding water Special bond names: Phosphodiester holds nucleotides together to form nucleic acids Peptide bond holds amino acids together to form amino acids ...
TABLE 3–1 Some Common Types of Enzymes
... catalyze the rearrangement of bonds within a single molecule. catalyze polymerization reactions such as the synthesis of DNA and RNA. catalyze the addition of phosphate groups to molecules. Protein kinases are an important group of kinases that attach phosphate groups to proteins. catalyze the hydro ...
... catalyze the rearrangement of bonds within a single molecule. catalyze polymerization reactions such as the synthesis of DNA and RNA. catalyze the addition of phosphate groups to molecules. Protein kinases are an important group of kinases that attach phosphate groups to proteins. catalyze the hydro ...
Biochemistry Jeopardy C.P. Bio.
... Chitin is found in the exoskeleton of animals known as Arthropods. This group includes these kinds of animals. ...
... Chitin is found in the exoskeleton of animals known as Arthropods. This group includes these kinds of animals. ...
protein/power point
... HAPPY TUESDAY Bellwork: Compare and Contrast Carbohydrates vs Lipids ...
... HAPPY TUESDAY Bellwork: Compare and Contrast Carbohydrates vs Lipids ...
TEST Chapter 2: The Guide to Good Food
... 10. _____A form of complex carbohydrate from plants that humans cannot digest. It does not provide the body with energy, but it is important because it provides bulk in the diet and promotes normal bowel function. ...
... 10. _____A form of complex carbohydrate from plants that humans cannot digest. It does not provide the body with energy, but it is important because it provides bulk in the diet and promotes normal bowel function. ...
CHE 4310 Fall 2011
... A general note: Short answer questions are just that, short. Writing a paragraph filled with every term you can remember from class won’t improve your answer— just answer clearly, succinctly, and in your own words. Useful information: R = 8.315 J/mol*K T = 298 K ...
... A general note: Short answer questions are just that, short. Writing a paragraph filled with every term you can remember from class won’t improve your answer— just answer clearly, succinctly, and in your own words. Useful information: R = 8.315 J/mol*K T = 298 K ...
Structure and function
... • Parasites feed on living hosts • Saprophytes feed on dead matter • Decomposers breakdown dead matter and recycle the nutrients • Pathogens are disease causing organisms (most parasites are also pathogens) • Extra cellular digestion is the process by which bacteria and fungi feed • Binary fission i ...
... • Parasites feed on living hosts • Saprophytes feed on dead matter • Decomposers breakdown dead matter and recycle the nutrients • Pathogens are disease causing organisms (most parasites are also pathogens) • Extra cellular digestion is the process by which bacteria and fungi feed • Binary fission i ...
Nutrit Ecology Insects
... C. Plant Phenology: Younger tissue has higher water content D. Environmental Conditions Variations in insect performance on different plant parts & taxa Approximate digestibilities: tree foliage > forb foliage ECI’s; AD’s Seeds, Pollen > Leaves > Wood ...
... C. Plant Phenology: Younger tissue has higher water content D. Environmental Conditions Variations in insect performance on different plant parts & taxa Approximate digestibilities: tree foliage > forb foliage ECI’s; AD’s Seeds, Pollen > Leaves > Wood ...
File
... C. Purpose: provide support & speed reactions D. Enzymes are specialized proteins that function as catalysts for chemical reactions. E. Examples of those important to humans: 1. Digestive enzymes, collagen, etc. Too many to list them all – they make up 15% of your total body mass! ...
... C. Purpose: provide support & speed reactions D. Enzymes are specialized proteins that function as catalysts for chemical reactions. E. Examples of those important to humans: 1. Digestive enzymes, collagen, etc. Too many to list them all – they make up 15% of your total body mass! ...
Macro-molecule study guide / worksheet
... 3. There are two basic kinds of nucleic acids. Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) which contains the sugar ribose and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) which contains the sugar deoxyribose. 4. DNA - 2 strands of nucleotides; RNA - 1 strand of nucleotides Enzymes - with few exceptions, they are proteins Catalyst - sub ...
... 3. There are two basic kinds of nucleic acids. Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) which contains the sugar ribose and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) which contains the sugar deoxyribose. 4. DNA - 2 strands of nucleotides; RNA - 1 strand of nucleotides Enzymes - with few exceptions, they are proteins Catalyst - sub ...
B2 mindmaps File
... (each enzyme has its own favourite conditions) Only the matching Fossils are the remains of substrate will fit. ...
... (each enzyme has its own favourite conditions) Only the matching Fossils are the remains of substrate will fit. ...
Biology Unit 2
... (each enzyme has its own favourite conditions) Only the matching Fossils are the remains of substrate will fit. ...
... (each enzyme has its own favourite conditions) Only the matching Fossils are the remains of substrate will fit. ...
Biology Unit 2
... (each enzyme has its own favourite conditions) Only the matching Fossils are the remains of substrate will fit. ...
... (each enzyme has its own favourite conditions) Only the matching Fossils are the remains of substrate will fit. ...
Digestion

Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into small water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the watery blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into the blood stream. Digestion is a form of catabolism that is often divided into two processes based on how food is broken down: mechanical and chemical digestion. The term mechanical digestion refers to the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces which can subsequently be accessed by digestive enzymes. In chemical digestion, enzymes break down food into the small molecules the body can use.In the human digestive system, food enters the mouth and mechanical digestion of the food starts by the action of mastication (chewing), a form of mechanical digestion, and the wetting contact of saliva. Saliva, a liquid secreted by the salivary glands, contains salivary amylase, an enzyme which starts the digestion of starch in the food; the saliva also contains mucus, which lubricates the food, and hydrogen carbonate, which provides the ideal conditions of pH (alkaline) for amylase to work. After undergoing mastication and starch digestion, the food will be in the form of a small, round slurry mass called a bolus. It will then travel down the esophagus and into the stomach by the action of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach starts protein digestion. Gastric juice mainly contains hydrochloric acid and pepsin. As these two chemicals may damage the stomach wall, mucus is secreted by the stomach, providing a slimy layer that acts as a shield against the damaging effects of the chemicals. At the same time protein digestion is occurring, mechanical mixing occurs by peristalsis, which is waves of muscular contractions that move along the stomach wall. This allows the mass of food to further mix with the digestive enzymes.After some time (typically 1–2 hours in humans, 4–6 hours in dogs, 3–4 hours in house cats), the resulting thick liquid is called chyme. When the pyloric sphincter valve opens, chyme enters the duodenum where it mixes with digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile juice from the liver and then passes through the small intestine, in which digestion continues. When the chyme is fully digested, it is absorbed into the blood. 95% of absorption of nutrients occurs in the small intestine. Water and minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood in the colon (large intestine) where the pH is slightly acidic about 5.6 ~ 6.9. Some vitamins, such as biotin and vitamin K (K2MK7) produced by bacteria in the colon are also absorbed into the blood in the colon. Waste material is eliminated from the rectum during defecation.