Nutrition
... the body and will make thirst worse. Proteins Protein molecules contain nitrogen, which is essential for building body proteins. After proteins are digested, the resulting amino acids are used by the body to build structures and to make enzymes. Proteins are found in muscles, blood, and other struct ...
... the body and will make thirst worse. Proteins Protein molecules contain nitrogen, which is essential for building body proteins. After proteins are digested, the resulting amino acids are used by the body to build structures and to make enzymes. Proteins are found in muscles, blood, and other struct ...
food nutrients - Queensland Science Teachers
... Examples are sugars, starches (pasta, potatoes, flour) and cellulose (fibre) Contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen with the ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms as 2H : 1O An immediate source of energy for the body In the process of respiration, glucose sugar and oxygen give energy and wast ...
... Examples are sugars, starches (pasta, potatoes, flour) and cellulose (fibre) Contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen with the ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms as 2H : 1O An immediate source of energy for the body In the process of respiration, glucose sugar and oxygen give energy and wast ...
Metabolism of Glycerol
... The fat cells (adipocytes) that make up adipose tissue are capable of storing unlimited quantities of triacylglycerols. Adipose tissue (made of adipocytes) stores 85% of the total energy available in the body. ...
... The fat cells (adipocytes) that make up adipose tissue are capable of storing unlimited quantities of triacylglycerols. Adipose tissue (made of adipocytes) stores 85% of the total energy available in the body. ...
An External Channel for Endoscopy
... During endoscopy, a procedure using an endoscope to look inside the gastrointestinal tract, a surgeon may encounter blockages such as blood clots or partially digested food. Limitations of standard endoscope internal channel sizes may prevent these obstacles from being suctioned. This invention, whi ...
... During endoscopy, a procedure using an endoscope to look inside the gastrointestinal tract, a surgeon may encounter blockages such as blood clots or partially digested food. Limitations of standard endoscope internal channel sizes may prevent these obstacles from being suctioned. This invention, whi ...
Biological effects of GH
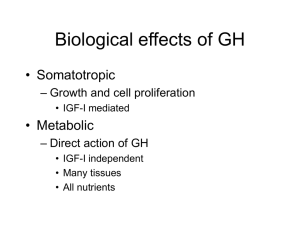
... Biological effects of GH • Somatotropic – Growth and cell proliferation • IGF-I mediated ...
... Biological effects of GH • Somatotropic – Growth and cell proliferation • IGF-I mediated ...
Macromolecules: Building blocks of life
... processes, because molecules and ions must be free to move and interact, which only happens when they are dissolved in water. Water also transports materials in living organisms, such as in blood or sap. ...
... processes, because molecules and ions must be free to move and interact, which only happens when they are dissolved in water. Water also transports materials in living organisms, such as in blood or sap. ...
Terminal Exam Revision - St Micks Science
... • Can work at low pressures • Efficient catalysts • Using pure enzymes are more expensive but they do not use any substrate in their process ...
... • Can work at low pressures • Efficient catalysts • Using pure enzymes are more expensive but they do not use any substrate in their process ...
Slide 1 - helmricht
... Denaturation- the loss of the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures of a protein by chemical or physical agent that leaves the primary structure intact Enzymes lose their catalytic activity and other proteins can’t carry out their biological functions when denatured ...
... Denaturation- the loss of the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures of a protein by chemical or physical agent that leaves the primary structure intact Enzymes lose their catalytic activity and other proteins can’t carry out their biological functions when denatured ...
Unit Topic: Chemistry of Life
... Broad Concept: All life is built out of four essential molecules: proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. Carbon compounds: 1. Organic means made from carbon - CHONPS (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur) 2. Protein, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids 3. Draw ...
... Broad Concept: All life is built out of four essential molecules: proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. Carbon compounds: 1. Organic means made from carbon - CHONPS (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur) 2. Protein, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids 3. Draw ...
Diversity in Nutrition
... muscle it is long and the cow uses it to wrap around long grass and pull it into it’s mouth. The cow has an under developed temporalis muscle; herbivores do not eat other consumers so do not need to hold/pin down other animals using their mouths. Cows do have a very large well developed masseter mus ...
... muscle it is long and the cow uses it to wrap around long grass and pull it into it’s mouth. The cow has an under developed temporalis muscle; herbivores do not eat other consumers so do not need to hold/pin down other animals using their mouths. Cows do have a very large well developed masseter mus ...
Key: Biomolecule Study Guide 1) In animals, excess carbohydrates
... They must fit the molecules that they interact with (Lock and Key) 10) What does it mean to say an enzyme is “denatured”? It has changed its 3-D shape 11) What are 2 ways to denature an enzyme? Change the temperature or pH ...
... They must fit the molecules that they interact with (Lock and Key) 10) What does it mean to say an enzyme is “denatured”? It has changed its 3-D shape 11) What are 2 ways to denature an enzyme? Change the temperature or pH ...
The Necessities of Life
... other necessities. Many animals, including the warbler in Figure 2, will claim a particular space. After claiming a space, they try to keep other animals away. ...
... other necessities. Many animals, including the warbler in Figure 2, will claim a particular space. After claiming a space, they try to keep other animals away. ...
Enzymes - Kevan Kruger
... What is the importance of enzymes in the body? Where are enzymes synthesized? What is their molecular structure and chemical make up? Where are enzymes manufactured? What is the function of enzymes in cells? How do enzymes lower the activation energy of a reaction? Give five specific examples of enz ...
... What is the importance of enzymes in the body? Where are enzymes synthesized? What is their molecular structure and chemical make up? Where are enzymes manufactured? What is the function of enzymes in cells? How do enzymes lower the activation energy of a reaction? Give five specific examples of enz ...
Organic Molecules: The Molecules of Life
... lipids in general contain lots of energy fats in animal bodies function as a long term energy storage fatty tissue also covers our organs and protects them from injury lipids do not dissolve in water It is possible for us to digest fats because we emulsify them. Bile from our gall bladder is secrete ...
... lipids in general contain lots of energy fats in animal bodies function as a long term energy storage fatty tissue also covers our organs and protects them from injury lipids do not dissolve in water It is possible for us to digest fats because we emulsify them. Bile from our gall bladder is secrete ...
PASMODIN DROPS/SUSPENSION
... Dicyclomine relieves smooth muscle spam of gastrointestinal tract via a dual mechanism: Has direct smooth muscle relaxant action in addition to weak anti-cholinergic actions. As a result tone and amplitude of contractions of stomach and intestine are reduced…spam may be relieved. Simethicone is used ...
... Dicyclomine relieves smooth muscle spam of gastrointestinal tract via a dual mechanism: Has direct smooth muscle relaxant action in addition to weak anti-cholinergic actions. As a result tone and amplitude of contractions of stomach and intestine are reduced…spam may be relieved. Simethicone is used ...
Or Is It? Section 1: Characteristics of Living Things (pg 4-7)
... Molecules found in living things are usually made of different combinations of six elements: carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorous, and sulfur. These elements combine to form proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, ATP, and nucleic acids. ...
... Molecules found in living things are usually made of different combinations of six elements: carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorous, and sulfur. These elements combine to form proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, ATP, and nucleic acids. ...
Organic compounds
... A chemical reaction in which water is used to break the bonds of certain substances. In living organisms, these substances are ...
... A chemical reaction in which water is used to break the bonds of certain substances. In living organisms, these substances are ...
Choosing Healthful Foods
... • Two types of fiber: soluble and insoluble • Soluble fiber: binds with cholesterol in the bloodstream to prevent it from building up in artery walls creating heart attacks and heart ...
... • Two types of fiber: soluble and insoluble • Soluble fiber: binds with cholesterol in the bloodstream to prevent it from building up in artery walls creating heart attacks and heart ...
Biomolecules
... bonded together. (cannot be longer or shorter) Polysaccharides – are greater than 2 simple sugars joined together. ...
... bonded together. (cannot be longer or shorter) Polysaccharides – are greater than 2 simple sugars joined together. ...
49. enzyme review - Khan Usman Ghani
... substrate as a result substrate is converted to product. Substrate binds on active site of enzymes that is specific for substrate (Hansen et al., 1990). Enzymes increases or decreases rate of reaction by increasing or decreasing the energy of activation (Amyes et al., 2001). Protein part of enzymes ...
... substrate as a result substrate is converted to product. Substrate binds on active site of enzymes that is specific for substrate (Hansen et al., 1990). Enzymes increases or decreases rate of reaction by increasing or decreasing the energy of activation (Amyes et al., 2001). Protein part of enzymes ...
The Synthesis and Expression of Peptide CbnY Thomas Doerksen
... The King’s University ORAL Collaboration Bacteriocins are small antimicrobial peptides produced by bacteria, and have great potential in the food industry as an alternative to antibiotics. The two-component bacteriocins, produced by various strains of lactic acid bacteria, display optimal activity w ...
... The King’s University ORAL Collaboration Bacteriocins are small antimicrobial peptides produced by bacteria, and have great potential in the food industry as an alternative to antibiotics. The two-component bacteriocins, produced by various strains of lactic acid bacteria, display optimal activity w ...
Digestion

Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into small water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the watery blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into the blood stream. Digestion is a form of catabolism that is often divided into two processes based on how food is broken down: mechanical and chemical digestion. The term mechanical digestion refers to the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces which can subsequently be accessed by digestive enzymes. In chemical digestion, enzymes break down food into the small molecules the body can use.In the human digestive system, food enters the mouth and mechanical digestion of the food starts by the action of mastication (chewing), a form of mechanical digestion, and the wetting contact of saliva. Saliva, a liquid secreted by the salivary glands, contains salivary amylase, an enzyme which starts the digestion of starch in the food; the saliva also contains mucus, which lubricates the food, and hydrogen carbonate, which provides the ideal conditions of pH (alkaline) for amylase to work. After undergoing mastication and starch digestion, the food will be in the form of a small, round slurry mass called a bolus. It will then travel down the esophagus and into the stomach by the action of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach starts protein digestion. Gastric juice mainly contains hydrochloric acid and pepsin. As these two chemicals may damage the stomach wall, mucus is secreted by the stomach, providing a slimy layer that acts as a shield against the damaging effects of the chemicals. At the same time protein digestion is occurring, mechanical mixing occurs by peristalsis, which is waves of muscular contractions that move along the stomach wall. This allows the mass of food to further mix with the digestive enzymes.After some time (typically 1–2 hours in humans, 4–6 hours in dogs, 3–4 hours in house cats), the resulting thick liquid is called chyme. When the pyloric sphincter valve opens, chyme enters the duodenum where it mixes with digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile juice from the liver and then passes through the small intestine, in which digestion continues. When the chyme is fully digested, it is absorbed into the blood. 95% of absorption of nutrients occurs in the small intestine. Water and minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood in the colon (large intestine) where the pH is slightly acidic about 5.6 ~ 6.9. Some vitamins, such as biotin and vitamin K (K2MK7) produced by bacteria in the colon are also absorbed into the blood in the colon. Waste material is eliminated from the rectum during defecation.