Whole Food Protein Preventing Muscle Loss
... age, and by 80s, only half the amount of muscles in 20s are left. As the muscle mass shrink, your strength diminishes, and the quality of life decreases. Also, fat replaces muscle and cause lifestyle disease. In order to prevent muscle loss, consuming protein everyday is important. ...
... age, and by 80s, only half the amount of muscles in 20s are left. As the muscle mass shrink, your strength diminishes, and the quality of life decreases. Also, fat replaces muscle and cause lifestyle disease. In order to prevent muscle loss, consuming protein everyday is important. ...
Chapter 1 Review Understanding Concepts
... with its lipoprotein receptor, which has some hydrocarbon side chains of its own (like dissolves like!). The fatty tail also allows the molecule to slip through lipid-rich cell membranes, making the burn more persistent. (c) The perception that peppers are “hot” is not an accident. Capsaicin allows ...
... with its lipoprotein receptor, which has some hydrocarbon side chains of its own (like dissolves like!). The fatty tail also allows the molecule to slip through lipid-rich cell membranes, making the burn more persistent. (c) The perception that peppers are “hot” is not an accident. Capsaicin allows ...
1. Which of the following is not a feature of scientific hypotheses? A
... A) chromoplasts. B) granularplasts. C) chloroplasts. D) potatoplasts. E) leucoplasts. ...
... A) chromoplasts. B) granularplasts. C) chloroplasts. D) potatoplasts. E) leucoplasts. ...
Nutrition
... care, individualization is important. One patient may be experiencing a high level of dental caries, yet professes to have excellent home care. Upon your analysis, you discover that the patient is on a low-fat, high-carbohydrate diet. She thinks she is a healthy eater. After all, we have been taug ...
... care, individualization is important. One patient may be experiencing a high level of dental caries, yet professes to have excellent home care. Upon your analysis, you discover that the patient is on a low-fat, high-carbohydrate diet. She thinks she is a healthy eater. After all, we have been taug ...
03 - summer worksheet
... Most plentiful sugar in nature; transport form of carbohydrates in plants; table sugar; formed from glucose and fructose Five-carbon sugar occurring in DNA. Main energy source for most organisms; precursor of many organic organisms; serve as building blocks for larger carbohydrates Structural materi ...
... Most plentiful sugar in nature; transport form of carbohydrates in plants; table sugar; formed from glucose and fructose Five-carbon sugar occurring in DNA. Main energy source for most organisms; precursor of many organic organisms; serve as building blocks for larger carbohydrates Structural materi ...
plants sample questions
... Pfr is converted by red light to Pr which acts as an inhibitor of flowering. (Total 1 mark) ...
... Pfr is converted by red light to Pr which acts as an inhibitor of flowering. (Total 1 mark) ...
WORD
... Describe the basic structure and function of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids ...
... Describe the basic structure and function of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids ...
4 Classes of Large Biological Molecules Carbohydrates Lipids
... Cholesterol: precursor from which many other steroids are made ...
... Cholesterol: precursor from which many other steroids are made ...
Notes
... inherited inborn error of metabolism. This means that children born with this disorder can’t convert some of the food they eat into energy. In a normal metabolic cycle, carbohydrates are broken down into energy by certain enzymes called the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. These are the molecules tha ...
... inherited inborn error of metabolism. This means that children born with this disorder can’t convert some of the food they eat into energy. In a normal metabolic cycle, carbohydrates are broken down into energy by certain enzymes called the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. These are the molecules tha ...
Topic 2.4 Proteins Study Guide Amino acids are linked together by
... Amino acids are linked together by condensation to form polypeptides. There are 20 different amino acids in polypeptides synthesized on ribosomes. Amino acids can be linked together in any sequence giving a huge range of possible polypeptides. The amino acid sequence of polypeptides is coded for by ...
... Amino acids are linked together by condensation to form polypeptides. There are 20 different amino acids in polypeptides synthesized on ribosomes. Amino acids can be linked together in any sequence giving a huge range of possible polypeptides. The amino acid sequence of polypeptides is coded for by ...
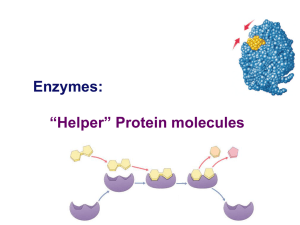
Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... sucrase breaks down sucrose Oh, I get it! They end in -ase ...
... sucrase breaks down sucrose Oh, I get it! They end in -ase ...
Cystic Fibrosis and The Effects on the Kidneys
... • Since no enzymes reach the intestines and these enzymes help digest and absorb fat along with a few other nutrients, Not much fat is absorbed in the body, and other nutrients are not absorbed properly. • That is why people with cystic fibrosis are normally skinny, even with strong healthy diets, t ...
... • Since no enzymes reach the intestines and these enzymes help digest and absorb fat along with a few other nutrients, Not much fat is absorbed in the body, and other nutrients are not absorbed properly. • That is why people with cystic fibrosis are normally skinny, even with strong healthy diets, t ...
biochemistry - Kuliah FTSL
... Living processes contain thousands of chemical pathways. Precise regulation and integration of these pathways are required to maintain life ...
... Living processes contain thousands of chemical pathways. Precise regulation and integration of these pathways are required to maintain life ...
ministry of education and science of the russian federation
... relief." The fourth methodological rule - an assessment of the motor-evacuation function of organs. Knowledge of normal radiological anatomy, semiotics of diseases of the alimentary canal, the ability to choose the right one or the other method of research is a must in modern medicine. Knowledge of ...
... relief." The fourth methodological rule - an assessment of the motor-evacuation function of organs. Knowledge of normal radiological anatomy, semiotics of diseases of the alimentary canal, the ability to choose the right one or the other method of research is a must in modern medicine. Knowledge of ...
Summary for Chapter 7 – Metabolism: Transformations
... Summary for Chapter 7 – Metabolism: Transformations and Interactions During digestion the energy-yielding nutrients—carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins—are broken down to glucose (and other monosaccharides), glycerol, fatty acids, and amino acids. Aided by enzymes and coenzymes, the cells use these ...
... Summary for Chapter 7 – Metabolism: Transformations and Interactions During digestion the energy-yielding nutrients—carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins—are broken down to glucose (and other monosaccharides), glycerol, fatty acids, and amino acids. Aided by enzymes and coenzymes, the cells use these ...
1. Amino Acids,Peptides, Proteins
... 16. The Pentose Phosphate Pathway and Other Pathways of Hexose Metabolism Ch. 20. The Pentose Phosphate Pathway & Other Pathways of Hexose Metabolism - without the metabolism of aminosugars 17. Overview of Glucose Metabolism. Control of the Blood Glucose Ch. 19. Gluconeogenesis & the Control of Bloo ...
... 16. The Pentose Phosphate Pathway and Other Pathways of Hexose Metabolism Ch. 20. The Pentose Phosphate Pathway & Other Pathways of Hexose Metabolism - without the metabolism of aminosugars 17. Overview of Glucose Metabolism. Control of the Blood Glucose Ch. 19. Gluconeogenesis & the Control of Bloo ...
What are enzymes?
... the gallbladder. Bile makes fats water-soluble and helps you to get the fat soluble vitamins out of your food. The liver processes cholesterol, carbs and proteins and detoxes other substances you don’t want. By the time the food gets to the large intestine, most of the big enzyme work is done, but t ...
... the gallbladder. Bile makes fats water-soluble and helps you to get the fat soluble vitamins out of your food. The liver processes cholesterol, carbs and proteins and detoxes other substances you don’t want. By the time the food gets to the large intestine, most of the big enzyme work is done, but t ...
Jeopardy - POTOSI SCHOOL DISTRICT
... form of a question. • Select a question by clicking on it. • After reading the question click on the word “answer” on the bottom of the screen. • After seeing the answer, click on the picture of the cell to return to the question board. ...
... form of a question. • Select a question by clicking on it. • After reading the question click on the word “answer” on the bottom of the screen. • After seeing the answer, click on the picture of the cell to return to the question board. ...
Anaerobic Digestion Basics and Microbiology
... Engulf cellulose Exoenzymes produced by a bacteria inside them Cellulases are end product Trichonympha is a species of Metamonad ...
... Engulf cellulose Exoenzymes produced by a bacteria inside them Cellulases are end product Trichonympha is a species of Metamonad ...
Why does a drop of food coloring diffuse more rapidly in
... and must be synthesized within the cell are enzymatically converted to nonpolar forms before crossing the membrane cross membranes by interacting with membrane transport proteins pass between the hydrophobic heads and dissolve through the hydrophilic tails of the phospholipid ...
... and must be synthesized within the cell are enzymatically converted to nonpolar forms before crossing the membrane cross membranes by interacting with membrane transport proteins pass between the hydrophobic heads and dissolve through the hydrophilic tails of the phospholipid ...
1101Lecture 16 powerpoint
... -charge on certain proteins affects pH -channels e.g.-move ions into and out of cells ...
... -charge on certain proteins affects pH -channels e.g.-move ions into and out of cells ...
1101Lecture 24 powerpoint
... -charge on certain proteins affects pH -channels e.g.-move ions into and out of cells ...
... -charge on certain proteins affects pH -channels e.g.-move ions into and out of cells ...
Digestion

Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into small water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the watery blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into the blood stream. Digestion is a form of catabolism that is often divided into two processes based on how food is broken down: mechanical and chemical digestion. The term mechanical digestion refers to the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces which can subsequently be accessed by digestive enzymes. In chemical digestion, enzymes break down food into the small molecules the body can use.In the human digestive system, food enters the mouth and mechanical digestion of the food starts by the action of mastication (chewing), a form of mechanical digestion, and the wetting contact of saliva. Saliva, a liquid secreted by the salivary glands, contains salivary amylase, an enzyme which starts the digestion of starch in the food; the saliva also contains mucus, which lubricates the food, and hydrogen carbonate, which provides the ideal conditions of pH (alkaline) for amylase to work. After undergoing mastication and starch digestion, the food will be in the form of a small, round slurry mass called a bolus. It will then travel down the esophagus and into the stomach by the action of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach starts protein digestion. Gastric juice mainly contains hydrochloric acid and pepsin. As these two chemicals may damage the stomach wall, mucus is secreted by the stomach, providing a slimy layer that acts as a shield against the damaging effects of the chemicals. At the same time protein digestion is occurring, mechanical mixing occurs by peristalsis, which is waves of muscular contractions that move along the stomach wall. This allows the mass of food to further mix with the digestive enzymes.After some time (typically 1–2 hours in humans, 4–6 hours in dogs, 3–4 hours in house cats), the resulting thick liquid is called chyme. When the pyloric sphincter valve opens, chyme enters the duodenum where it mixes with digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile juice from the liver and then passes through the small intestine, in which digestion continues. When the chyme is fully digested, it is absorbed into the blood. 95% of absorption of nutrients occurs in the small intestine. Water and minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood in the colon (large intestine) where the pH is slightly acidic about 5.6 ~ 6.9. Some vitamins, such as biotin and vitamin K (K2MK7) produced by bacteria in the colon are also absorbed into the blood in the colon. Waste material is eliminated from the rectum during defecation.