BY 330 Summer 2015Mock Exam 2 Ten molecules of
... 12. The sodium-potassium pump is an example of which specific type of transport protein. Antiport carrier 13. What effect does an action potential have on a carrier protein? Voltage-gated channel proteins? None; Will open voltage-gated 14. A membrane-bound vesicle/endosome forms to bring molecules i ...
... 12. The sodium-potassium pump is an example of which specific type of transport protein. Antiport carrier 13. What effect does an action potential have on a carrier protein? Voltage-gated channel proteins? None; Will open voltage-gated 14. A membrane-bound vesicle/endosome forms to bring molecules i ...
STANDARD 1
... This Standard incorporates the provisions of Regulations 237 and 239A of the former New Zealand Food Regulations (1984), in so far as they relate to special purpose foods and amino acid modified foods. It is anticipated that this Standard will be repealed upon the development of Standards regulating ...
... This Standard incorporates the provisions of Regulations 237 and 239A of the former New Zealand Food Regulations (1984), in so far as they relate to special purpose foods and amino acid modified foods. It is anticipated that this Standard will be repealed upon the development of Standards regulating ...
Document
... A condensation reaction chemically bonds monomers to create polymers by the release of a water molecules. A hydrolysis reaction breaks polymers apart into individual monomers by the addition of water. 6. What is the major function of a monosaccharide, such as glucose? To provide immediate energy 7. ...
... A condensation reaction chemically bonds monomers to create polymers by the release of a water molecules. A hydrolysis reaction breaks polymers apart into individual monomers by the addition of water. 6. What is the major function of a monosaccharide, such as glucose? To provide immediate energy 7. ...
Macromolecules Worksheet
... ____________________ 2. This is the name for a compound with many sugar subunits linked together. ____________________ 3. This is the name given to an amino acid added to a dipeptide. ____________________ 4. Of what kind of organic compound are oils, waxes, and fats an example? ____________________ ...
... ____________________ 2. This is the name for a compound with many sugar subunits linked together. ____________________ 3. This is the name given to an amino acid added to a dipeptide. ____________________ 4. Of what kind of organic compound are oils, waxes, and fats an example? ____________________ ...
Proteins are made of subunits called amino acids and are
... _________________________________________________________________________________ How many amino acids are there? ____________ ...
... _________________________________________________________________________________ How many amino acids are there? ____________ ...
2. How we study biology • The scientific method requires controls
... The pancreas secretes hormones that regulate the amount of glucose in the blood and also secretes digestive enzymes. The ducts of the pancreas and liver flow together into the duodenum. Exocrine cells that secrete enzymes dump into the pancreatic duct and from there pass into the duodenum. Its funct ...
... The pancreas secretes hormones that regulate the amount of glucose in the blood and also secretes digestive enzymes. The ducts of the pancreas and liver flow together into the duodenum. Exocrine cells that secrete enzymes dump into the pancreatic duct and from there pass into the duodenum. Its funct ...
Summary and example
... examine different components of the natural world. Biology is the study of life. The smallest unit of life is a cell. Some organisms are multi-cellular and consist of tissues, organs and organ ...
... examine different components of the natural world. Biology is the study of life. The smallest unit of life is a cell. Some organisms are multi-cellular and consist of tissues, organs and organ ...
Organic
... • For each peptide bond formed, a water molecule is lost thru dehydration synthesis. • How that polypeptide folds and takes on a 3-D shape is determined by its R groups and how they interact w/ each other. ...
... • For each peptide bond formed, a water molecule is lost thru dehydration synthesis. • How that polypeptide folds and takes on a 3-D shape is determined by its R groups and how they interact w/ each other. ...
Food Poisonings in Hong Kong—Hazards and Prevention
... the production of lactic acid or alcohol from simple sugars by lactic acid bacteria or yeasts. Examples are production of yogurt and wine. More complex fermentations require degradation of complex carbohydrates such as starch by hydrolases into simple sugars first. Simple sugars are then converted t ...
... the production of lactic acid or alcohol from simple sugars by lactic acid bacteria or yeasts. Examples are production of yogurt and wine. More complex fermentations require degradation of complex carbohydrates such as starch by hydrolases into simple sugars first. Simple sugars are then converted t ...
Syllabus Notes - Southwest High School
... – They MAKE or BREAK stuff generally. – The long chain of amino acids fold into a specific shape. (FYI: Change one amino acid? Primary, secondary, and tertiary structure all change… the function could change too!) – This 3D shape of the enzyme fits its substrate EXACTLY. Just like a lock fits only o ...
... – They MAKE or BREAK stuff generally. – The long chain of amino acids fold into a specific shape. (FYI: Change one amino acid? Primary, secondary, and tertiary structure all change… the function could change too!) – This 3D shape of the enzyme fits its substrate EXACTLY. Just like a lock fits only o ...
waterside dentalcare What is acid erosion of the teeth? What do I eat
... finishing your meal with a little cheese or milk. Try to eat fewer acidic meals or snacks. 2. Avoid all acid food or drinks between meals. Remember, sugar in tea or coffee will also form acids that will damage your teeth. 3. If as a result of ‘Heartburn’ or indigestion for example, acid from your st ...
... finishing your meal with a little cheese or milk. Try to eat fewer acidic meals or snacks. 2. Avoid all acid food or drinks between meals. Remember, sugar in tea or coffee will also form acids that will damage your teeth. 3. If as a result of ‘Heartburn’ or indigestion for example, acid from your st ...
Nutrients note
... SUCROSE = GLUCOSE + FRUCTOSE - table sugar, fruits, vegetables and grains MALTOSE = GLUCOSE + GLUCOSE - produced when starch breaks down (during carbohydrate digestion and fermentation) LACTOSE = GLUCOSE + GALACTOSE - principle carbohydrate of milk ...
... SUCROSE = GLUCOSE + FRUCTOSE - table sugar, fruits, vegetables and grains MALTOSE = GLUCOSE + GLUCOSE - produced when starch breaks down (during carbohydrate digestion and fermentation) LACTOSE = GLUCOSE + GALACTOSE - principle carbohydrate of milk ...
1 Food intake regulation
... With respect to regulation, a general distinction is made between homeostatic (metabolite input) and hedonic regulation (reward input) ...
... With respect to regulation, a general distinction is made between homeostatic (metabolite input) and hedonic regulation (reward input) ...
Fibrous proteins are especially abundant outside the cell, where
... There was one feature of feedback inhibition that was initially puzzling to those who discovered it: the regulatory molecule often has shape that is totally different from the shape of the enzyme’s preferred substrate. This type of regulation was named as allostery. These types of enzymes must have ...
... There was one feature of feedback inhibition that was initially puzzling to those who discovered it: the regulatory molecule often has shape that is totally different from the shape of the enzyme’s preferred substrate. This type of regulation was named as allostery. These types of enzymes must have ...
syllabus - Wofford
... We didn’t have much time to consider lipid metabolism in B214, but we will be able to concentrate on them in this course. You will need to know the structures of several major lipid compounds. We will emphasize the effects of fat and cholesterol metabolism on health. Week of ...
... We didn’t have much time to consider lipid metabolism in B214, but we will be able to concentrate on them in this course. You will need to know the structures of several major lipid compounds. We will emphasize the effects of fat and cholesterol metabolism on health. Week of ...
ILSI Health and Environmental Sciences Institute
... B. Clinical manifestations C. Risks from conventional food supply ...
... B. Clinical manifestations C. Risks from conventional food supply ...
Document
... functions of the four major categories of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids). 1.3 Explain the role of enzymes as catalysts that lower the activation energy of biochemical reactions. Identify factors, such as pH and temperature, which have an effect on enzymes. ...
... functions of the four major categories of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids). 1.3 Explain the role of enzymes as catalysts that lower the activation energy of biochemical reactions. Identify factors, such as pH and temperature, which have an effect on enzymes. ...
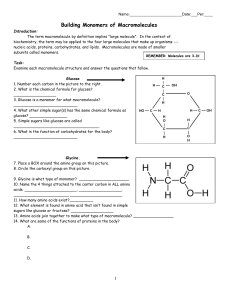
Building Monomers of Macromolecules
... Building Monomers of Macromolecules Introduction: The term macromolecule by definition implies "large molecule". In the context of biochemistry, the term may be applied to the four large molecules that make up organisms --nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Macromolecules are made of ...
... Building Monomers of Macromolecules Introduction: The term macromolecule by definition implies "large molecule". In the context of biochemistry, the term may be applied to the four large molecules that make up organisms --nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Macromolecules are made of ...
Cellular Functions PP
... The protons then diffuse through a special proton channels called ATP synthase, down the concentration gradient back into the matrix of the mitochondria, creating ATP in the process. Chemiosmosis is the coupling of the protonmotive force and ATP synthesis. The final electron acceptor is Oxygen which ...
... The protons then diffuse through a special proton channels called ATP synthase, down the concentration gradient back into the matrix of the mitochondria, creating ATP in the process. Chemiosmosis is the coupling of the protonmotive force and ATP synthesis. The final electron acceptor is Oxygen which ...
THE MOLECULES OF LIFE
... As a protein is made, it folds into a particular shape. o The shape of a protein is important in the job it does o The way a protein folds is determined by o ...
... As a protein is made, it folds into a particular shape. o The shape of a protein is important in the job it does o The way a protein folds is determined by o ...
Digestion

Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into small water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the watery blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into the blood stream. Digestion is a form of catabolism that is often divided into two processes based on how food is broken down: mechanical and chemical digestion. The term mechanical digestion refers to the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces which can subsequently be accessed by digestive enzymes. In chemical digestion, enzymes break down food into the small molecules the body can use.In the human digestive system, food enters the mouth and mechanical digestion of the food starts by the action of mastication (chewing), a form of mechanical digestion, and the wetting contact of saliva. Saliva, a liquid secreted by the salivary glands, contains salivary amylase, an enzyme which starts the digestion of starch in the food; the saliva also contains mucus, which lubricates the food, and hydrogen carbonate, which provides the ideal conditions of pH (alkaline) for amylase to work. After undergoing mastication and starch digestion, the food will be in the form of a small, round slurry mass called a bolus. It will then travel down the esophagus and into the stomach by the action of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach starts protein digestion. Gastric juice mainly contains hydrochloric acid and pepsin. As these two chemicals may damage the stomach wall, mucus is secreted by the stomach, providing a slimy layer that acts as a shield against the damaging effects of the chemicals. At the same time protein digestion is occurring, mechanical mixing occurs by peristalsis, which is waves of muscular contractions that move along the stomach wall. This allows the mass of food to further mix with the digestive enzymes.After some time (typically 1–2 hours in humans, 4–6 hours in dogs, 3–4 hours in house cats), the resulting thick liquid is called chyme. When the pyloric sphincter valve opens, chyme enters the duodenum where it mixes with digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile juice from the liver and then passes through the small intestine, in which digestion continues. When the chyme is fully digested, it is absorbed into the blood. 95% of absorption of nutrients occurs in the small intestine. Water and minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood in the colon (large intestine) where the pH is slightly acidic about 5.6 ~ 6.9. Some vitamins, such as biotin and vitamin K (K2MK7) produced by bacteria in the colon are also absorbed into the blood in the colon. Waste material is eliminated from the rectum during defecation.