Sample exam 1
... 6. Gastric juice has a pH of 1.5 and is produced by pumping HCl from blood plasma (pH 7.4) into the stomach. a. Calculate the free energy required to concentrate the H+ in 1 L of gastric juice at 37°C. For this problem, you can ignore the effects of the transmembrane electrical potential difference. ...
... 6. Gastric juice has a pH of 1.5 and is produced by pumping HCl from blood plasma (pH 7.4) into the stomach. a. Calculate the free energy required to concentrate the H+ in 1 L of gastric juice at 37°C. For this problem, you can ignore the effects of the transmembrane electrical potential difference. ...
Sample Exam 1
... c. ATP synthesis d. protein synthesis e. protein modification 37. The innermost region of the mitochondria is called the ____________. a. inner mitochondrial membrane b. cytoplasm c. cristae d. matrix e. intermembrane space 38. What is a function of the nucleus of a cell? a. It synthesizes ATP. b. I ...
... c. ATP synthesis d. protein synthesis e. protein modification 37. The innermost region of the mitochondria is called the ____________. a. inner mitochondrial membrane b. cytoplasm c. cristae d. matrix e. intermembrane space 38. What is a function of the nucleus of a cell? a. It synthesizes ATP. b. I ...
IRRN 1998 23 (2) 22-24
... The polyprotein is thought to be cleaved by the virus and/or cell-encoded proteases. The genome also contains two short open reading frames at the 3' end. Recent studies have demonstrated that rice cultivars react differently to RTSV variants. TKM6, resistant to type variant A, is susceptible to the ...
... The polyprotein is thought to be cleaved by the virus and/or cell-encoded proteases. The genome also contains two short open reading frames at the 3' end. Recent studies have demonstrated that rice cultivars react differently to RTSV variants. TKM6, resistant to type variant A, is susceptible to the ...
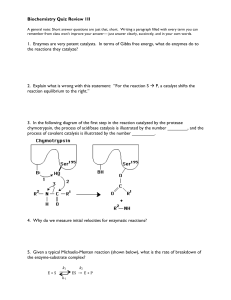
Biochemistry Quiz Review 1II 1. Enzymes are very potent catalysts
... 25. Describe the part of the glycolytic pathway from fructose 6-phosphate to glyceraldehyde 3phosphate. Show structures of intermediates, enzyme names, and indicate where any cofactors participate. ...
... 25. Describe the part of the glycolytic pathway from fructose 6-phosphate to glyceraldehyde 3phosphate. Show structures of intermediates, enzyme names, and indicate where any cofactors participate. ...
The Body`s Essential Building Blocks, Article by Gloria Gilbère, N.D.
... Sources of protein from vegetables contain only incomplete proteins—low in essential amino acids, even in high protein amounts. ...
... Sources of protein from vegetables contain only incomplete proteins—low in essential amino acids, even in high protein amounts. ...
What happens to proteins key
... broken down into amino acids and absorbed into your blood to be used by your cells. A limited supply of amino acids exist in pools in your body, which act as reservoir for the synthesis of protein as needed. Surplus amino acids are broken down, and the carboncontaining remains can be used for glucos ...
... broken down into amino acids and absorbed into your blood to be used by your cells. A limited supply of amino acids exist in pools in your body, which act as reservoir for the synthesis of protein as needed. Surplus amino acids are broken down, and the carboncontaining remains can be used for glucos ...
The Anatomy of Sea Turtles
... The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract or gut) extends from the mouth to the cloaca (Fig. 164). It is demarked by structural and functional divisions. The mouth captures and processes food. The esophagus conveys food to the stomach and expels excess water. It also works with the tongue in swallowing. ...
... The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract or gut) extends from the mouth to the cloaca (Fig. 164). It is demarked by structural and functional divisions. The mouth captures and processes food. The esophagus conveys food to the stomach and expels excess water. It also works with the tongue in swallowing. ...
GI - EPI - Prestige Animal Hospital
... absolutely normal quality of life and normal life expectancy. The pancreas often does not regenerate when it is affected by exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, and treatment is typically required for the life of the pet. Relapses may occur and can be caused by forgetting to give the enzyme supplemen ...
... absolutely normal quality of life and normal life expectancy. The pancreas often does not regenerate when it is affected by exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, and treatment is typically required for the life of the pet. Relapses may occur and can be caused by forgetting to give the enzyme supplemen ...
protein digest.99
... Mucus provides sink for protons • pH of stomach fluid is below 2.0 • negative charges on COO groups of mucus sidechains sop up millions of protons • increases the pH along stomach lining to near 5 ...
... Mucus provides sink for protons • pH of stomach fluid is below 2.0 • negative charges on COO groups of mucus sidechains sop up millions of protons • increases the pH along stomach lining to near 5 ...
213lec3
... 3. They can also be used for energy if other sources of energy are low or energy demands are high. V. How are minerals, vitamins, and water absorbed and transported in the body? A. These nutrients do not have to be broken into smaller units. B. Digestion does help to release these nutrients from the ...
... 3. They can also be used for energy if other sources of energy are low or energy demands are high. V. How are minerals, vitamins, and water absorbed and transported in the body? A. These nutrients do not have to be broken into smaller units. B. Digestion does help to release these nutrients from the ...
Chapter 16 – Food Additives
... It is important to be informed about food additives because of allergy and sensitivities to particular ingredients or chemicals, or for other health and personal reasons. 4) Why does Canada set rules for fortification? Food fortification or enrichment means adding one or more vitamins or minerals to ...
... It is important to be informed about food additives because of allergy and sensitivities to particular ingredients or chemicals, or for other health and personal reasons. 4) Why does Canada set rules for fortification? Food fortification or enrichment means adding one or more vitamins or minerals to ...
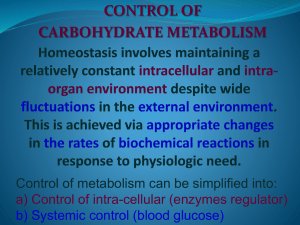
Control of intra-cellular (enzyme regulator)
... interconvert common products may take place in specific sub cellular compartments. ...
... interconvert common products may take place in specific sub cellular compartments. ...
macromolecule webquest
... Click on biochemistry Click on lipids 6. What are the two main parts of a lipid? 7. Explain what makes a fat saturated or unsaturated? 8. How does the basic structure of a steroid differ from other macromolecules such as carbohydrates? 9. What is the role of waxes? 10. Compare the energy values of a ...
... Click on biochemistry Click on lipids 6. What are the two main parts of a lipid? 7. Explain what makes a fat saturated or unsaturated? 8. How does the basic structure of a steroid differ from other macromolecules such as carbohydrates? 9. What is the role of waxes? 10. Compare the energy values of a ...
Bacteria Powerpoint - Nashua School District
... What do they look like? • Three basic shapes – Rod shaped called bacilli (buh-sill-eye) – Round shaped called cocci (cox-eye) – Spiral shaped called spirilla ...
... What do they look like? • Three basic shapes – Rod shaped called bacilli (buh-sill-eye) – Round shaped called cocci (cox-eye) – Spiral shaped called spirilla ...
Power Point CH 26 A
... • Organs that are completely surrounded by visceral peritoneum are called intraperitoneal organs. They include the stomach and most of the small intestines. • Organs that lie in direct contact with the posterior abdominal and pelvic walls and are only covered on their anterolateral surfaces with vis ...
... • Organs that are completely surrounded by visceral peritoneum are called intraperitoneal organs. They include the stomach and most of the small intestines. • Organs that lie in direct contact with the posterior abdominal and pelvic walls and are only covered on their anterolateral surfaces with vis ...
Gastric hormones handout text
... GUT HORMONES IN THE CONTROL OF APPETITE AND FEEDING In addition to the feedback effects from taste, stomach distension etc by the sensory nerves of the alimentary tract, it is now clear that gastrointestinal hormones affect feeding by an action on the hypothalamus and brain stem (via the blood). The ...
... GUT HORMONES IN THE CONTROL OF APPETITE AND FEEDING In addition to the feedback effects from taste, stomach distension etc by the sensory nerves of the alimentary tract, it is now clear that gastrointestinal hormones affect feeding by an action on the hypothalamus and brain stem (via the blood). The ...
Macromolecules - Georgetown ISD
... 2. ______________________ are large organic molecules. 3. Carbon has how many electrons in its outer energy shell? 4. Carbon can form up to ______ covalent bonds with other atoms (elements) 5. Elements that carbon usually bonds with: _____, _____, _____, or _____. Example: ___________________ 6. Mac ...
... 2. ______________________ are large organic molecules. 3. Carbon has how many electrons in its outer energy shell? 4. Carbon can form up to ______ covalent bonds with other atoms (elements) 5. Elements that carbon usually bonds with: _____, _____, _____, or _____. Example: ___________________ 6. Mac ...
Plant Pretest
... 5. Many vegetables (ex. Carrots and beets) store glucose made during photosynthesis. Since this type of storage is underground, they are unable to photosynthesize. When glucose is transported to the site of storage by phloem, which two systems are working together? A. B. C. D. ...
... 5. Many vegetables (ex. Carrots and beets) store glucose made during photosynthesis. Since this type of storage is underground, they are unable to photosynthesize. When glucose is transported to the site of storage by phloem, which two systems are working together? A. B. C. D. ...
HTR - Wsfcs
... Compare calorie to another source of energy used by a non-human. How many calories does the average person need? If a person consumes 2,000 calories a day, will he or she gain weight or lose weight? What factors play a role beside calorie intake? How do you find out how many calories a food has? Lis ...
... Compare calorie to another source of energy used by a non-human. How many calories does the average person need? If a person consumes 2,000 calories a day, will he or she gain weight or lose weight? What factors play a role beside calorie intake? How do you find out how many calories a food has? Lis ...
“Are we really what we eat?” “Where does the `stuff` that makes us
... Recap: Proteins like enzymes, hemoglobin, and hormones help control reactions and create muscle. These proteins are made up of smaller units called amino acids, and can be found in foods such as meats and nuts. ...
... Recap: Proteins like enzymes, hemoglobin, and hormones help control reactions and create muscle. These proteins are made up of smaller units called amino acids, and can be found in foods such as meats and nuts. ...
Contractile Proteins
... Contractile Proteins - are responsible for movement. Examples include actin and myosin. These proteins are involved in muscle contraction and movement. Enzymes - are proteins that facilitate biochemical reactions. They are often referred to as catalysts because they speed up chemical reactions. Exam ...
... Contractile Proteins - are responsible for movement. Examples include actin and myosin. These proteins are involved in muscle contraction and movement. Enzymes - are proteins that facilitate biochemical reactions. They are often referred to as catalysts because they speed up chemical reactions. Exam ...
SURFIN` THROUGH STAAR
... a. composed of building blocks called amino acids b. insoluble in water and are used by the body for energy storage and insulation c. complex biomolecules that store genetic information d. organic compounds used by cells to store and release energy ...
... a. composed of building blocks called amino acids b. insoluble in water and are used by the body for energy storage and insulation c. complex biomolecules that store genetic information d. organic compounds used by cells to store and release energy ...
Biology - secondary
... molecule than aerobic cellular respiration 107-110 • Building big muscles is an example of catabolic metabolism 119 • 109-Cellular formation is the breakdown of food without O2 • The RNA molecule that contains the code for a polypeptide chain of amino acids is called transfer RNA ...
... molecule than aerobic cellular respiration 107-110 • Building big muscles is an example of catabolic metabolism 119 • 109-Cellular formation is the breakdown of food without O2 • The RNA molecule that contains the code for a polypeptide chain of amino acids is called transfer RNA ...
Digestion

Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into small water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the watery blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into the blood stream. Digestion is a form of catabolism that is often divided into two processes based on how food is broken down: mechanical and chemical digestion. The term mechanical digestion refers to the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces which can subsequently be accessed by digestive enzymes. In chemical digestion, enzymes break down food into the small molecules the body can use.In the human digestive system, food enters the mouth and mechanical digestion of the food starts by the action of mastication (chewing), a form of mechanical digestion, and the wetting contact of saliva. Saliva, a liquid secreted by the salivary glands, contains salivary amylase, an enzyme which starts the digestion of starch in the food; the saliva also contains mucus, which lubricates the food, and hydrogen carbonate, which provides the ideal conditions of pH (alkaline) for amylase to work. After undergoing mastication and starch digestion, the food will be in the form of a small, round slurry mass called a bolus. It will then travel down the esophagus and into the stomach by the action of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach starts protein digestion. Gastric juice mainly contains hydrochloric acid and pepsin. As these two chemicals may damage the stomach wall, mucus is secreted by the stomach, providing a slimy layer that acts as a shield against the damaging effects of the chemicals. At the same time protein digestion is occurring, mechanical mixing occurs by peristalsis, which is waves of muscular contractions that move along the stomach wall. This allows the mass of food to further mix with the digestive enzymes.After some time (typically 1–2 hours in humans, 4–6 hours in dogs, 3–4 hours in house cats), the resulting thick liquid is called chyme. When the pyloric sphincter valve opens, chyme enters the duodenum where it mixes with digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile juice from the liver and then passes through the small intestine, in which digestion continues. When the chyme is fully digested, it is absorbed into the blood. 95% of absorption of nutrients occurs in the small intestine. Water and minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood in the colon (large intestine) where the pH is slightly acidic about 5.6 ~ 6.9. Some vitamins, such as biotin and vitamin K (K2MK7) produced by bacteria in the colon are also absorbed into the blood in the colon. Waste material is eliminated from the rectum during defecation.