notes File - selu moodle
... mountains. Our enzymes can cross the valley, but not climb the mountain. This is why there are calories in potatoes, but not lettuce. 3.3 Nucleic Acids Two main types: DNA and RNA DNA carries the genetic code RNA working nucleic acid – responsible for reading DNA and building proteins Function also ...
... mountains. Our enzymes can cross the valley, but not climb the mountain. This is why there are calories in potatoes, but not lettuce. 3.3 Nucleic Acids Two main types: DNA and RNA DNA carries the genetic code RNA working nucleic acid – responsible for reading DNA and building proteins Function also ...
PPT
... Salt bridges – ionic bonds form between acidic and basic residues Hydrogen bonds – form between polar residues ...
... Salt bridges – ionic bonds form between acidic and basic residues Hydrogen bonds – form between polar residues ...
35 Amino acid breakdown Amino acids comprise one of the three
... Copyright © 2000-2003 Mark Brandt, Ph.D. ...
... Copyright © 2000-2003 Mark Brandt, Ph.D. ...
Biomolecules are organic molecules built and used inside of cells
... • There are ______ different amino acids (AAs) – All have this general structure, with the ______group representing the molecule that makes each AA unique AAs have: • C,H,O, and ____ • An ______ group ...
... • There are ______ different amino acids (AAs) – All have this general structure, with the ______group representing the molecule that makes each AA unique AAs have: • C,H,O, and ____ • An ______ group ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide File
... 8. Describe end-product inhibition. Is this a positive or negative feedback mechanism? ...
... 8. Describe end-product inhibition. Is this a positive or negative feedback mechanism? ...
Chapter 11: Enzyme Catalysis
... G proteins always serve to activate adenylate cyclase. G proteins always serve to inhibit adenylate cyclase. Some G proteins activate adenylate cyclase, while others inhibit it. G proteins do not act on adenylate cyclase at all. ...
... G proteins always serve to activate adenylate cyclase. G proteins always serve to inhibit adenylate cyclase. Some G proteins activate adenylate cyclase, while others inhibit it. G proteins do not act on adenylate cyclase at all. ...
Cell - Thomas A. Stewart Secondary School
... Carbs… Characteristics of Sugars 1) An –OH group is attached to each carbon except one; this carbon is double bonded to an oxygen (carbonyl group Start numbering the carbons of your sugars at the end closest to the carbonyl group!!! ...
... Carbs… Characteristics of Sugars 1) An –OH group is attached to each carbon except one; this carbon is double bonded to an oxygen (carbonyl group Start numbering the carbons of your sugars at the end closest to the carbonyl group!!! ...
macromoleculeppt
... Carbs… Characteristics of Sugars 1) An –OH group is attached to each carbon except one; this carbon is double bonded to an oxygen (carbonyl group Start numbering the carbons of your sugars at the end closest to the carbonyl group!!! ...
... Carbs… Characteristics of Sugars 1) An –OH group is attached to each carbon except one; this carbon is double bonded to an oxygen (carbonyl group Start numbering the carbons of your sugars at the end closest to the carbonyl group!!! ...
Lectures 1-3: Review of forces and elementary statistical
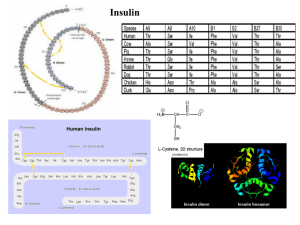
... Insulin: the protein of the 20th century • One of the first proteins crystallized in 1926 (Structural Genomics) • First protein fully sequenced in 1955 (Bioinformatics) • First protein chemically synthesized in 1958 • First human protein manufactured via recombinant in 1979 (Biotechnology) ...
... Insulin: the protein of the 20th century • One of the first proteins crystallized in 1926 (Structural Genomics) • First protein fully sequenced in 1955 (Bioinformatics) • First protein chemically synthesized in 1958 • First human protein manufactured via recombinant in 1979 (Biotechnology) ...
Test your nucleic acid knowledge!
... DNA is often resuspended in molecular-grade water or _______. ...
... DNA is often resuspended in molecular-grade water or _______. ...
Lecture 15: Translation and Transcription
... Redundancy exists because two or more codons differing only in their third base (e.g., UUU and UUC each code for phenylalanine) ii. Codons only code for one amino acid, therefore there is no ambiguity ...
... Redundancy exists because two or more codons differing only in their third base (e.g., UUU and UUC each code for phenylalanine) ii. Codons only code for one amino acid, therefore there is no ambiguity ...
DNA
... - Sugar & phosphate form backbone - The bases form the “steps” of ladder, held together by Hydrogen bonds • C-G = 3 hydrogen bonds • A-T = 2 hydrogen bonds ...
... - Sugar & phosphate form backbone - The bases form the “steps” of ladder, held together by Hydrogen bonds • C-G = 3 hydrogen bonds • A-T = 2 hydrogen bonds ...
Unit 3: Chapter 6
... iii. ____________________ - The amount of enzyme or substrate can affect the enzyme activity to a point. - As the concentration increases the enzyme activity increases until it “_____________” ...
... iii. ____________________ - The amount of enzyme or substrate can affect the enzyme activity to a point. - As the concentration increases the enzyme activity increases until it “_____________” ...
Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids Chapter 3 MACROMOLECULES
... • Genetic regulatory proteins regulate when, how, and to what extent a gene is expressed. AMINO ACIDS Amino acids have carboxyl and amino groups—so they function as both acid and base. The α carbon atom is asymmetrical. Amino acids exist in two isomeric forms: D-amino acids (dextro, “ right “) L-ami ...
... • Genetic regulatory proteins regulate when, how, and to what extent a gene is expressed. AMINO ACIDS Amino acids have carboxyl and amino groups—so they function as both acid and base. The α carbon atom is asymmetrical. Amino acids exist in two isomeric forms: D-amino acids (dextro, “ right “) L-ami ...
Chapter 14: Carbohydrates
... Proteins Proteins form components of the body such as muscles, hair, and nails Enzymes are proteins that act as tiny “machines” in cellular processes Hemoglobin is a protein that carries oxygen in the blood Proteins can also act as storage molecules. Some hormones are proteins. ...
... Proteins Proteins form components of the body such as muscles, hair, and nails Enzymes are proteins that act as tiny “machines” in cellular processes Hemoglobin is a protein that carries oxygen in the blood Proteins can also act as storage molecules. Some hormones are proteins. ...
Protein Synthesis PPT
... • If the 3 base anticodon of the tRNA complements the 3 base codon of the mRNA, they briefly combine. • The amino acid is left behind when the tRNA leaves. • As each codon is read, the next tRNA brings in a new amino acid and the polypeptide (protein) chain grows. • This requires enzymes and ATP. ...
... • If the 3 base anticodon of the tRNA complements the 3 base codon of the mRNA, they briefly combine. • The amino acid is left behind when the tRNA leaves. • As each codon is read, the next tRNA brings in a new amino acid and the polypeptide (protein) chain grows. • This requires enzymes and ATP. ...
Chapter 3
... – Both of these are covalently bonded to a central carbon atom – Also bonded to the central carbon is a hydrogen atom and some other chemical group symbolized by R ...
... – Both of these are covalently bonded to a central carbon atom – Also bonded to the central carbon is a hydrogen atom and some other chemical group symbolized by R ...
Zoo/Bot 3333
... blot analysis. The probe used in this instance hybridizes to a DNA fragment linked to the disease gene, which shows polymorphism for this restriction enzyme. The autoradiogram of this blot is shown above, aligned with the family pedigree. 5. In the above example, which of the following are likely t ...
... blot analysis. The probe used in this instance hybridizes to a DNA fragment linked to the disease gene, which shows polymorphism for this restriction enzyme. The autoradiogram of this blot is shown above, aligned with the family pedigree. 5. In the above example, which of the following are likely t ...
CH5-Macromolecules
... This diversity comes from various combinations of the 40-50 common monomers and other rarer ones. These monomers can be connected in various combinations like the 26 letters in the alphabet can be used to create a great diversity of words. Biological molecules are even more diverse. ...
... This diversity comes from various combinations of the 40-50 common monomers and other rarer ones. These monomers can be connected in various combinations like the 26 letters in the alphabet can be used to create a great diversity of words. Biological molecules are even more diverse. ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.