Chapter 12 - North Mac Schools
... Genes that control this differentiation early in development Mutations involving hox genes can have HUGE effect on outcome of organism ...
... Genes that control this differentiation early in development Mutations involving hox genes can have HUGE effect on outcome of organism ...
The Nature of Matter
... Macromolecules are formed in a process called polymerization “Poly” means “many”. Monomers are smaller units that join together to form polymers, which are macromolecules. ...
... Macromolecules are formed in a process called polymerization “Poly” means “many”. Monomers are smaller units that join together to form polymers, which are macromolecules. ...
Pipecleaner Proteins Lab
... of three charges – positive, negative, or neutral. Like opposite sides of a magnet, positively and negatively charged amino acids try to move toward each other; similarly-charged amino acids will repel each other. ...
... of three charges – positive, negative, or neutral. Like opposite sides of a magnet, positively and negatively charged amino acids try to move toward each other; similarly-charged amino acids will repel each other. ...
DNA - Royal Society of Chemistry
... expected to share. However the award is not made posthumously and by 1958 Rosalind Franklin’s short but productive life was over. Nucleotides Just as proteins are polymers made of amino acids, nucleic acids (such as DNA and RNA) are polymers made from individual building blocks called ...
... expected to share. However the award is not made posthumously and by 1958 Rosalind Franklin’s short but productive life was over. Nucleotides Just as proteins are polymers made of amino acids, nucleic acids (such as DNA and RNA) are polymers made from individual building blocks called ...
Review Problems for amino acids, carbohydrates, glycolysis and the
... Consider the following explanation (from Web MD) of lactic acidosis, a condition that arises during vigorous anaerobic exercise. “Lactic acidosis occurs naturally when lactic acid, a byproduct of metabolism, builds up in muscles and blood during vigorous exercise. Lactic acidosis due to exercise lea ...
... Consider the following explanation (from Web MD) of lactic acidosis, a condition that arises during vigorous anaerobic exercise. “Lactic acidosis occurs naturally when lactic acid, a byproduct of metabolism, builds up in muscles and blood during vigorous exercise. Lactic acidosis due to exercise lea ...
Introduction to Biochemistry
... Correct Answer: 2) kinked • Unsaturated fatty acid: 1 or more double bonds in hydrocarbon chain • This is an example of a monounsaturated fatty acid, because it has only 1 double bond in the hydrocarbon chain ...
... Correct Answer: 2) kinked • Unsaturated fatty acid: 1 or more double bonds in hydrocarbon chain • This is an example of a monounsaturated fatty acid, because it has only 1 double bond in the hydrocarbon chain ...
et al
... When you have read Chapter 3, you should be able to: 1. Define the terms ‘transcriptome' and ‘proteome' 2. Draw a diagram illustrating the modern interpretation of the genome expression pathway, indicating the main points at which genome expression is regulated 3. Distinguish between coding and non- ...
... When you have read Chapter 3, you should be able to: 1. Define the terms ‘transcriptome' and ‘proteome' 2. Draw a diagram illustrating the modern interpretation of the genome expression pathway, indicating the main points at which genome expression is regulated 3. Distinguish between coding and non- ...
Biochemistry of Cells
... Fats in Organisms Most plants oils tend to be low in saturated fatty acids & exist as liquids at room temperature (oils) Fats Dietary fat consists largely of the molecule triglyceride composed of glycerol and three fatty acid chains Steroids The carbon skeleton of steroids is bent to form 4 fused ri ...
... Fats in Organisms Most plants oils tend to be low in saturated fatty acids & exist as liquids at room temperature (oils) Fats Dietary fat consists largely of the molecule triglyceride composed of glycerol and three fatty acid chains Steroids The carbon skeleton of steroids is bent to form 4 fused ri ...
md 2 bbq
... has no other malformations and is otherwise healthy. He has no family history of birth defects. His parents are not related. Which of the following genetic mechanisms is most likely to have caused these congenital abnormalities? • Autosomal dominant inheritance • Autosomal recessive inheritance • Ch ...
... has no other malformations and is otherwise healthy. He has no family history of birth defects. His parents are not related. Which of the following genetic mechanisms is most likely to have caused these congenital abnormalities? • Autosomal dominant inheritance • Autosomal recessive inheritance • Ch ...
BiochemLecture03
... • Role in function: Unlike the very similar Phenylalanine, Tyrosine contains a reactive hydroxyl group, thus making it much more likely to be involved in interactions with non protein atoms. Like other aromatic amino acids, Tyrosine can be involved in interactions with non-protein ligands that thems ...
... • Role in function: Unlike the very similar Phenylalanine, Tyrosine contains a reactive hydroxyl group, thus making it much more likely to be involved in interactions with non protein atoms. Like other aromatic amino acids, Tyrosine can be involved in interactions with non-protein ligands that thems ...
powerpoint
... Detection: refractive index, circular dichroism, (MS/MS) vs. derivitization for UV or fluorescence or MS ...
... Detection: refractive index, circular dichroism, (MS/MS) vs. derivitization for UV or fluorescence or MS ...
Macromolecules and the Molecules of Life
... Macromolecules • Macromolecules • Made of CHNOP • Large molecules formed by joining polymers • Monomers • The basic units that bond together to form molecules essential to life • Bond via condensation reaction • Monomer + monomer = polymer + water • Polymers • Several monomers joined together • Sep ...
... Macromolecules • Macromolecules • Made of CHNOP • Large molecules formed by joining polymers • Monomers • The basic units that bond together to form molecules essential to life • Bond via condensation reaction • Monomer + monomer = polymer + water • Polymers • Several monomers joined together • Sep ...
handout
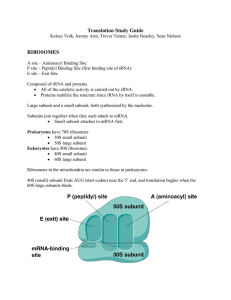
... 2. The bond attaching the amino acid chain to the tRNA in the P site is broken and a peptide bond is formed to the new tRNA amino acid in the A site moving the growing chain from the P site to the A site. 3. The large subunit of the ribosome shifts one codon, moving the tRNA with the growing amino ...
... 2. The bond attaching the amino acid chain to the tRNA in the P site is broken and a peptide bond is formed to the new tRNA amino acid in the A site moving the growing chain from the P site to the A site. 3. The large subunit of the ribosome shifts one codon, moving the tRNA with the growing amino ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.