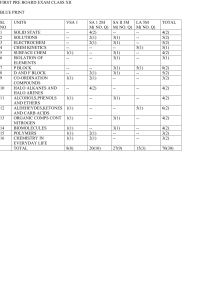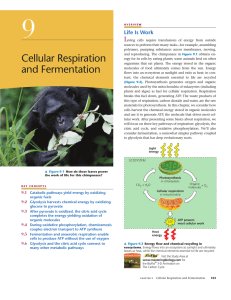
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... atoms. Compounds that can participate in exergonic reactions can act as fuels. With the help of enzymes, a cell systematically degrades complex organic molecules that are rich in potential energy to simpler waste products that have less energy. Some of the energy taken out of chemical storage can be ...
... atoms. Compounds that can participate in exergonic reactions can act as fuels. With the help of enzymes, a cell systematically degrades complex organic molecules that are rich in potential energy to simpler waste products that have less energy. Some of the energy taken out of chemical storage can be ...
N-terminal portion acts as an initiator of the inactivation of pepsin at
... synthesized at the Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology at McMaster University (Hamilton, ON, Canada). The ...
... synthesized at the Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology at McMaster University (Hamilton, ON, Canada). The ...
The Metabolism of Acetate by the Blue-green Algae
... of Dr M. B. Allen through the courtesy of Dr A. A. Horton, Department of Biochemistry, University of Birmingham; Chlorogloea fritschii from Professor G. E. Fogg, Department of Botany, Westfield College, University of London, London. All organisms were maintained on agar (2%) slopes of the mineral sa ...
... of Dr M. B. Allen through the courtesy of Dr A. A. Horton, Department of Biochemistry, University of Birmingham; Chlorogloea fritschii from Professor G. E. Fogg, Department of Botany, Westfield College, University of London, London. All organisms were maintained on agar (2%) slopes of the mineral sa ...
This paper is published in a part-themed issue of Photochemical
... the solutions contained two different compounds: in the cold water solution both were intact, but in the hot water solution, the heat had destroyed one of the components. When the hot solution was cooled and added to the exhausted cold solution it became luminous again because the component that was ...
... the solutions contained two different compounds: in the cold water solution both were intact, but in the hot water solution, the heat had destroyed one of the components. When the hot solution was cooled and added to the exhausted cold solution it became luminous again because the component that was ...
Characterization of NAD Salvage Pathways and their Role in
... (Figure 5A), suggesting that either both proteins can import the molecule, it is modified at the ...
... (Figure 5A), suggesting that either both proteins can import the molecule, it is modified at the ...
File - cpprashanths Chemistry
... C6H6 + CH3 Cl/FeCl3 C6H5—CH3 1M Q17.Explain the structure of natural rubber.Name its monomeric unit. The natural rubber is a linear 1,4-polymer of isopropene. ...
... C6H6 + CH3 Cl/FeCl3 C6H5—CH3 1M Q17.Explain the structure of natural rubber.Name its monomeric unit. The natural rubber is a linear 1,4-polymer of isopropene. ...
Distribution bias analysis of germline and somatic single
... always silent and they are able to cause changes in protein expression, conformation and function15–19. Therefore, we also compare the frequencies of synonymous and non-synonymous mutations on protein functional sites. Since proteins are the foundational and functional blocks of living organisms, ho ...
... always silent and they are able to cause changes in protein expression, conformation and function15–19. Therefore, we also compare the frequencies of synonymous and non-synonymous mutations on protein functional sites. Since proteins are the foundational and functional blocks of living organisms, ho ...
endoglucanase in cellulose biosynthesis is not very clear
... similarity between the bacterial and the plant cellulose synthase genes. Instead, the plant gene was identified by sequencing random cDNAs from a cotton fiber library and analyzing the derived amino acid sequences for presence of the conserved features identified in the bacterial cellulose synthase ...
... similarity between the bacterial and the plant cellulose synthase genes. Instead, the plant gene was identified by sequencing random cDNAs from a cotton fiber library and analyzing the derived amino acid sequences for presence of the conserved features identified in the bacterial cellulose synthase ...
Regulation of Phenylalanine and Tyrosine
... hyperbolic with K , values of 0.31 r n M for chorismate and 0.015 mM for prephenate, respectively. The substrate saturation curve of the complexed prephenate dehydratase I was sigmoid; a Km value of 0-18 mM was calculated for prephenate. Chorismate mutase, prephenate dehydratase and prephenate dehyd ...
... hyperbolic with K , values of 0.31 r n M for chorismate and 0.015 mM for prephenate, respectively. The substrate saturation curve of the complexed prephenate dehydratase I was sigmoid; a Km value of 0-18 mM was calculated for prephenate. Chorismate mutase, prephenate dehydratase and prephenate dehyd ...
lipoprotein metabolism
... Where is VLDL formed? What are the lipids Carried by VLDL? Which lipid is delivered by VLDL? What is the mechanism of FFA release from VLDL? What is the fate of Remnant VLDL? What are the lipids present in excess when VLDL becomes VLDLR? ...
... Where is VLDL formed? What are the lipids Carried by VLDL? Which lipid is delivered by VLDL? What is the mechanism of FFA release from VLDL? What is the fate of Remnant VLDL? What are the lipids present in excess when VLDL becomes VLDLR? ...
Predicting the sidechain dihedral angle distributions
... steric, electrostatic, and the attractive component of van der Waals interactions, determine the structure of proteins in general and the conformations of amino acid side chains in particular. However, the relative contributions of the different types of interactions are not known. For example, the ...
... steric, electrostatic, and the attractive component of van der Waals interactions, determine the structure of proteins in general and the conformations of amino acid side chains in particular. However, the relative contributions of the different types of interactions are not known. For example, the ...
Regulation of intermediary metabolism by protein acetylation
... suggest renaming them as lysine-acetyltransferases (KATs) to reflect their broad function in regulating a great number of nonhistone proteins [54], including many metabolic enzymes discussed herein. Intermediary metabolism: often referred to simply as metabolism, includes all steps between extracell ...
... suggest renaming them as lysine-acetyltransferases (KATs) to reflect their broad function in regulating a great number of nonhistone proteins [54], including many metabolic enzymes discussed herein. Intermediary metabolism: often referred to simply as metabolism, includes all steps between extracell ...
Chapter 27 Amino acid
... Conversion to L-tyrosine is one of the major metabolic pathways of L-phenylalanine. Individuals who lack the enzymes necessary to convert L-phenylalanine to L-tyrosine can suffer from PKU disease. In PKU disease, Lphenylalanine is diverted to a pathway leading to phenylpyruvic acid, which is toxic. ...
... Conversion to L-tyrosine is one of the major metabolic pathways of L-phenylalanine. Individuals who lack the enzymes necessary to convert L-phenylalanine to L-tyrosine can suffer from PKU disease. In PKU disease, Lphenylalanine is diverted to a pathway leading to phenylpyruvic acid, which is toxic. ...
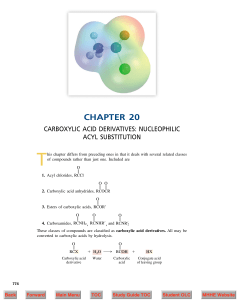
Organic Chemistry/Fourth Edition: e-Text
... The negatively charged oxygen substituent is a powerful electron donor to the carbonyl group. Resonance in carboxylate anions is more effective than resonance in carboxylic acids, acyl chlorides, anhydrides, esters, and amides. Table 20.1 summarizes the stabilizing effects of substituents on carbony ...
... The negatively charged oxygen substituent is a powerful electron donor to the carbonyl group. Resonance in carboxylate anions is more effective than resonance in carboxylic acids, acyl chlorides, anhydrides, esters, and amides. Table 20.1 summarizes the stabilizing effects of substituents on carbony ...
Contribution of 13C-NMR spectroscopy to the elucidation of
... is grown together with D. propionicus in the absence of sulfate. Desulfobulbus is able to convert acetate, CO2 and H2 to propionate (Laanbroek et al. 1982). It is known that homoacetogens have a poor affinity for hydrogen (Cord-Ruwisch et al. 1988). This would enable the sulfate reducer to consume t ...
... is grown together with D. propionicus in the absence of sulfate. Desulfobulbus is able to convert acetate, CO2 and H2 to propionate (Laanbroek et al. 1982). It is known that homoacetogens have a poor affinity for hydrogen (Cord-Ruwisch et al. 1988). This would enable the sulfate reducer to consume t ...
Analysis of structural robustness of metabolic
... mutants of micro-organisms are still able to grow, some with almost the same growth rate as the wild type. This has been shown, for example, by a systematic study on single knockout mutants of virtually all genes in baker’s yeast [1, 2]. In many cells, there are parallel and thus redundant metabolic ...
... mutants of micro-organisms are still able to grow, some with almost the same growth rate as the wild type. This has been shown, for example, by a systematic study on single knockout mutants of virtually all genes in baker’s yeast [1, 2]. In many cells, there are parallel and thus redundant metabolic ...
Metabolism
... When glycogen is hydrolyzed, the product is glucose 1phosphate. This is easily converted to glucose 6-phosphate (these are molecules with the phosphate group attached to different carbon atoms on the glucose). Glucose 6-phosphate is the first product in the glycolysis pathway and its formation from ...
... When glycogen is hydrolyzed, the product is glucose 1phosphate. This is easily converted to glucose 6-phosphate (these are molecules with the phosphate group attached to different carbon atoms on the glucose). Glucose 6-phosphate is the first product in the glycolysis pathway and its formation from ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.