Biochemical Characterization of 2-Nitropropane Dioxygenase from
... Table 2.4. Apparent steady state second order rate constants, kcat/KM, for alkyl nitronates as substrates for H. mrakii 2-nitropropane dioxygenase in 50 mM potassium phosphate pH 6 and 30 oC…………………………………………………………………………………55 Table 3.1. Oxygen consumption and nitrite production during 2-nitropropane d ...
... Table 2.4. Apparent steady state second order rate constants, kcat/KM, for alkyl nitronates as substrates for H. mrakii 2-nitropropane dioxygenase in 50 mM potassium phosphate pH 6 and 30 oC…………………………………………………………………………………55 Table 3.1. Oxygen consumption and nitrite production during 2-nitropropane d ...
as a PDF
... count in the carbon dioxide. For every mole of citrate recycled, 3 moles of carbon dioxide are evolved, 2 moles of which have half the activity of carboxyl 1, the 3rd mole being unlabeled. The last column of Table III shows the labeling of carboxyls 2 and 3 that would result from the amount of recyc ...
... count in the carbon dioxide. For every mole of citrate recycled, 3 moles of carbon dioxide are evolved, 2 moles of which have half the activity of carboxyl 1, the 3rd mole being unlabeled. The last column of Table III shows the labeling of carboxyls 2 and 3 that would result from the amount of recyc ...
Formation of Monoterpenes in Antirrhinum majus
... Gershenzon, 2002). Monoterpenes also are often released from vegetative tissues, where they function as toxic agents in direct defense against microbes and animals or help to indirectly protect the plant by attracting predators of the attacking herbivores (Langenheim, 1994; Gershenzon and Kreis, 199 ...
... Gershenzon, 2002). Monoterpenes also are often released from vegetative tissues, where they function as toxic agents in direct defense against microbes and animals or help to indirectly protect the plant by attracting predators of the attacking herbivores (Langenheim, 1994; Gershenzon and Kreis, 199 ...
The KIebsieIIa pneumoniae cytochrome bd
... conditions the high-affinity cytochrome bd’ predominates (Smith et al., 1990; Tseng et al., 1996); the latter conditions are those that permit diazotrophy in K . pneumoniae (Smith et al., 1990). In A. vinelandii, by contrast, conditions of high 0, input lead to enhanced synthesis of the cytochrome b ...
... conditions the high-affinity cytochrome bd’ predominates (Smith et al., 1990; Tseng et al., 1996); the latter conditions are those that permit diazotrophy in K . pneumoniae (Smith et al., 1990). In A. vinelandii, by contrast, conditions of high 0, input lead to enhanced synthesis of the cytochrome b ...
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle-Dependent Regulation of Staphylococcus
... adhesin (PIA) is an important mediator of biofilm formation and pathogenesis. Synthesis of PIA is regulated by at least three DNA binding proteins (IcaR, SarA, and B) and several environmental and nutritional conditions. Previously, we observed the environmental conditions that increased PIA synthe ...
... adhesin (PIA) is an important mediator of biofilm formation and pathogenesis. Synthesis of PIA is regulated by at least three DNA binding proteins (IcaR, SarA, and B) and several environmental and nutritional conditions. Previously, we observed the environmental conditions that increased PIA synthe ...
A tribute to sulfur - Wiley Online Library
... of molybdopterin, while lipoic acid biosynthesis is thought to proceed in a way similar to that of biotin. In addition, we have learned from studies on microbes and eukaryotic cellular systems that there seems to be continuous synthesis, disassembly and rebuilding of Fe±S clusters in proteins; in eu ...
... of molybdopterin, while lipoic acid biosynthesis is thought to proceed in a way similar to that of biotin. In addition, we have learned from studies on microbes and eukaryotic cellular systems that there seems to be continuous synthesis, disassembly and rebuilding of Fe±S clusters in proteins; in eu ...
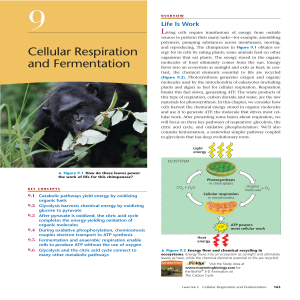
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... respiration. During glycolysis, each glucose molecule is broken down into two molecules of the compound pyruvate. In eukaryotic cells, as shown here, the pyruvate enters the mitochondrion. There it is oxidized to acetyl CoA, which is further oxidized to CO2 in the citric acid cycle. NADH and a simil ...
... respiration. During glycolysis, each glucose molecule is broken down into two molecules of the compound pyruvate. In eukaryotic cells, as shown here, the pyruvate enters the mitochondrion. There it is oxidized to acetyl CoA, which is further oxidized to CO2 in the citric acid cycle. NADH and a simil ...
A new natural product-based hybrid
... frequently reported is the framework combination strategy. In this approach, two separate pharmacophores that inhibit different targets are synthetically linked or merged into a single molecule (7, 8). The major complexity that is involved in the design of multiple ligands lies in balancing both dru ...
... frequently reported is the framework combination strategy. In this approach, two separate pharmacophores that inhibit different targets are synthetically linked or merged into a single molecule (7, 8). The major complexity that is involved in the design of multiple ligands lies in balancing both dru ...
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Phosphatase Deficiency
... sium phosphate, 1.1 m M EDTA, 2.8 m M MgCI,, 1.6% bovine after preincubation with ATP. which is known to inactivate serum albumin (fatty acid free). 1.2 niM dithiothreitol. 0.3 m M pyruvate dehydrogenase by increasing the activity of the controling pyruvate labeled with 0.12 pCi [l-'4C]pyruvate/ml a ...
... sium phosphate, 1.1 m M EDTA, 2.8 m M MgCI,, 1.6% bovine after preincubation with ATP. which is known to inactivate serum albumin (fatty acid free). 1.2 niM dithiothreitol. 0.3 m M pyruvate dehydrogenase by increasing the activity of the controling pyruvate labeled with 0.12 pCi [l-'4C]pyruvate/ml a ...
Stereochemistry, Conformation and Configuration
... that the molecule has to assume a particular specific conformation in the agonist-receptor complex in order for complexation to lead to drug action. Conformational changes in the receptor are also thought to occur. It has been postulated that acetylcholine in the drugreceptor complex could adopt dif ...
... that the molecule has to assume a particular specific conformation in the agonist-receptor complex in order for complexation to lead to drug action. Conformational changes in the receptor are also thought to occur. It has been postulated that acetylcholine in the drugreceptor complex could adopt dif ...
energy supply components - The Company of Biologists
... important metabolic sequences; its main metabolic fate is reconversion to the phosphagenform. (Again, arginine may be an exception, seeHochachkaef a/. 19836.) P;, however, is another matter. It is a highly reactive metabolite involved in numerous enzyme reactions in intermediary metabolism. Just as ...
... important metabolic sequences; its main metabolic fate is reconversion to the phosphagenform. (Again, arginine may be an exception, seeHochachkaef a/. 19836.) P;, however, is another matter. It is a highly reactive metabolite involved in numerous enzyme reactions in intermediary metabolism. Just as ...
NAGS - BMC Biochemistry
... glutamine, bicarbonate and ATP as substrates [53]. Nacetylglutamate (NAG), which is formed enzymatically by N-acetylglutamate synthase (NAGS; EC 2.3.1.1) from glutamate and acetyl coenzyme A (Figure 1), is an essential allosteric activator of CPSI, and deficiency of NAG results in a block in ureagen ...
... glutamine, bicarbonate and ATP as substrates [53]. Nacetylglutamate (NAG), which is formed enzymatically by N-acetylglutamate synthase (NAGS; EC 2.3.1.1) from glutamate and acetyl coenzyme A (Figure 1), is an essential allosteric activator of CPSI, and deficiency of NAG results in a block in ureagen ...
Methylobacterium extorquens AM1
... multicarbon growth conditions (i.e., succinate as sole source of carbon and energy). These investigations include transcriptomic [15], proteomic [16,17], and metabolomic studies [18,19]. The core of the central metabolism of M. extorquens AM1 was described to encompass 85 biochemical reactions that ...
... multicarbon growth conditions (i.e., succinate as sole source of carbon and energy). These investigations include transcriptomic [15], proteomic [16,17], and metabolomic studies [18,19]. The core of the central metabolism of M. extorquens AM1 was described to encompass 85 biochemical reactions that ...
Editing Multiple Alignments
... Conserved glycine or proline suggests a β-turn… Residues with hydrophobic properties conserved at i, i+2, i+4 (etc) separated by unconserved or hydrophilic residues suggests a surface β-strand… ...
... Conserved glycine or proline suggests a β-turn… Residues with hydrophobic properties conserved at i, i+2, i+4 (etc) separated by unconserved or hydrophilic residues suggests a surface β-strand… ...
Trans Fatty Acid Derived Phospholipids Show Increased Membrane
... phospholipid composition due to the differential interactions of phospholipids with cholesterol (25-29). The composition of membrane phospholipids also influences the physical properties and function of membrane proteins (30, 31). However, it is not known whether the presence of TFAderived phospholi ...
... phospholipid composition due to the differential interactions of phospholipids with cholesterol (25-29). The composition of membrane phospholipids also influences the physical properties and function of membrane proteins (30, 31). However, it is not known whether the presence of TFAderived phospholi ...
Respiratory enzyme activity and regulation of respiration pathway in
... 82.6% of the control and adventitious root-retained seedlings. The restored level of SDH activities was 94.6% of the control level, and changes in CCO activity exhibited the same trend. In addition, the lowest activity of MDH was observed in the adventitious root-removed seedlings during the experim ...
... 82.6% of the control and adventitious root-retained seedlings. The restored level of SDH activities was 94.6% of the control level, and changes in CCO activity exhibited the same trend. In addition, the lowest activity of MDH was observed in the adventitious root-removed seedlings during the experim ...
Compartmentation of the Metabolism of Lactose
... by using bromocresol green reagent (Lugg & Overell, 1948), amino acids with ninhydrin and sugars with AgNO, (Smith, 1960). The experiment was done four times with bacteria in Werent states of induction for the lac and gal operons. In bacteria in which neither of these operons were induced the amount ...
... by using bromocresol green reagent (Lugg & Overell, 1948), amino acids with ninhydrin and sugars with AgNO, (Smith, 1960). The experiment was done four times with bacteria in Werent states of induction for the lac and gal operons. In bacteria in which neither of these operons were induced the amount ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.