A question of taste
... potentially harmful and toxic substances and are thus crucial for survival. There are many sorts of bitter taste receptors, each of which is sensitive to a different bitter substance. ...
... potentially harmful and toxic substances and are thus crucial for survival. There are many sorts of bitter taste receptors, each of which is sensitive to a different bitter substance. ...
Purification and Characterization of Bacteriocin Produced by Lactococcus lactis
... Key word: Bacteriocins, Lactococcus lactis, nisin, bacteriocin purification INTRODUCTION In fermented foods, lactic acid bacteria (LAB) displays numerous antimicrobial activities. This is mainly due to the production of antimicrobial metabolites including organic acids, bacteriocins and antifungal p ...
... Key word: Bacteriocins, Lactococcus lactis, nisin, bacteriocin purification INTRODUCTION In fermented foods, lactic acid bacteria (LAB) displays numerous antimicrobial activities. This is mainly due to the production of antimicrobial metabolites including organic acids, bacteriocins and antifungal p ...
Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension ...
... Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension ...
View/Open - Oregon State University
... undefined media, they are still inappropriate for most biochemical and phenotypic testing. In addition, most biochemical tests are designed for identification of enteric bacteria and do not reveal useful information about free-living bacteria in their natural environment (O’Hara et al., 1992; Torsvi ...
... undefined media, they are still inappropriate for most biochemical and phenotypic testing. In addition, most biochemical tests are designed for identification of enteric bacteria and do not reveal useful information about free-living bacteria in their natural environment (O’Hara et al., 1992; Torsvi ...
Bioinformatics Molecular Genetics
... • Prokaryotes: organisms without a cell nucleus (= karyon), or any other membrane-bound organelles – Archaebacteria The kingdom (or "domain") of single-celled organisms that live under extreme environmental conditions and have distinctive biochemical features. – Bacteria (s: bacterium) A single-cell ...
... • Prokaryotes: organisms without a cell nucleus (= karyon), or any other membrane-bound organelles – Archaebacteria The kingdom (or "domain") of single-celled organisms that live under extreme environmental conditions and have distinctive biochemical features. – Bacteria (s: bacterium) A single-cell ...
overview, inorgs, trace nutrients
... choline • Choline is not a vitamin or a carrier. • It is a source methyl groups and is recommended in the diet. • It has lipotropic effects due to its role in phospholipid metabolism. ...
... choline • Choline is not a vitamin or a carrier. • It is a source methyl groups and is recommended in the diet. • It has lipotropic effects due to its role in phospholipid metabolism. ...
Whole body and tissue protein synthesis in cattle
... protein (nitrogen x 6*25)/d. The cow ate all the ration and her weight at the date of the infusion was the same as that 4 months previously. The two heifers were allowed access ad fib. to the diet between IOO kg to 220 kg live weight and during this period the average weight gains (kg/d) were 0.97 ( ...
... protein (nitrogen x 6*25)/d. The cow ate all the ration and her weight at the date of the infusion was the same as that 4 months previously. The two heifers were allowed access ad fib. to the diet between IOO kg to 220 kg live weight and during this period the average weight gains (kg/d) were 0.97 ( ...
Pepsinogen and Pepsin - The Journal of General Physiology
... m a y be determined and the position of any cross-bonding, as has been obtained for insulin (15) and ribonuclease (2, 3), and will probably be completed for others before long. Useful and important for the total picture as this is, the amino acid sequence of the enzyme is not particularly helpful to ...
... m a y be determined and the position of any cross-bonding, as has been obtained for insulin (15) and ribonuclease (2, 3), and will probably be completed for others before long. Useful and important for the total picture as this is, the amino acid sequence of the enzyme is not particularly helpful to ...
File
... • Phosphates can also be transferred from ATP to reactants in the pathway to make them more ADP ATP reactive e.g. Glucose ------------> Glucose- 6- Phosphate • Often a step in a pathway can only proceed if a reactant becomes phosphorylated ...
... • Phosphates can also be transferred from ATP to reactants in the pathway to make them more ADP ATP reactive e.g. Glucose ------------> Glucose- 6- Phosphate • Often a step in a pathway can only proceed if a reactant becomes phosphorylated ...
Genes affecting starch biosynthesis exert pleiotropic effects on the
... content than wild-type. However, since some mutants had a lower total protein content than wild-type, the relationship between albumin content and total protein (or legumin) content was less clear and this prompted an investigation of the effects of the mutations on other protein fractions. The prop ...
... content than wild-type. However, since some mutants had a lower total protein content than wild-type, the relationship between albumin content and total protein (or legumin) content was less clear and this prompted an investigation of the effects of the mutations on other protein fractions. The prop ...
Metabolic implications of methionine excess. Effects of
... a continuous « flow » of pyruvate coming from methionine degradation in adapted animals (Daniel and Waisman, 1969 ; Simpson and Freedland, 1975). In this hypothesis, the pyruvate formed would participate, via acetyl-CoA, in the Krebs cycle and/or lipogenesis, whose activity would be maintained. Only ...
... a continuous « flow » of pyruvate coming from methionine degradation in adapted animals (Daniel and Waisman, 1969 ; Simpson and Freedland, 1975). In this hypothesis, the pyruvate formed would participate, via acetyl-CoA, in the Krebs cycle and/or lipogenesis, whose activity would be maintained. Only ...
32 Introduction to Protein Structure Proteins are large
... A Ψ angle of 180° results in an alignment of the Namide with the carbonyl oxygen from the same residue. This is allowed, although not especially favored. A Ψ angle of 0° places the Namide from one residue very close to the Namide from the previous residue; this results in a steric clash (as well as ...
... A Ψ angle of 180° results in an alignment of the Namide with the carbonyl oxygen from the same residue. This is allowed, although not especially favored. A Ψ angle of 0° places the Namide from one residue very close to the Namide from the previous residue; this results in a steric clash (as well as ...
Analysis of a Controlling-Element Mutation at the Adh Locus of Maize
... such qustions, we have selected for controlling-element mutations at the Adh locus, which specifies alcohol dehydrogenase, an enzyme readily amenable to biochemical analyses and characterization (SCHWARTZ 1971, 1973). This paper deals with the analysis of one such Adh mutation. It is stable in the a ...
... such qustions, we have selected for controlling-element mutations at the Adh locus, which specifies alcohol dehydrogenase, an enzyme readily amenable to biochemical analyses and characterization (SCHWARTZ 1971, 1973). This paper deals with the analysis of one such Adh mutation. It is stable in the a ...
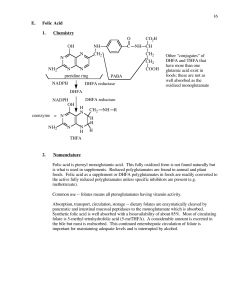
16 E. Folic Acid 1. Chemistry coenzyme DHFA DHFA reductase
... cycle scheme). This is because 5-MeTHFA is not converted back to THFA in the absence of B12. Megabloblastic anemia therefore results from a deficiency of B12. Also, in a B12 deficiency, neurological damage is observed due to lack of B12 (see B12 discussion) which is hard to detect. Therefore high do ...
... cycle scheme). This is because 5-MeTHFA is not converted back to THFA in the absence of B12. Megabloblastic anemia therefore results from a deficiency of B12. Also, in a B12 deficiency, neurological damage is observed due to lack of B12 (see B12 discussion) which is hard to detect. Therefore high do ...
1 - WordPress.com
... reacts with glucose to form lactose, a-Lactalbumin is a protein that serves as the modifier of galactosyl transferase, which catalyzes this reaction. 28. The pentose phosphate pathway generates each of the following products EXCEPT (A) NADPH, which may be used for fatty acid synthesis (B) ribose 5-p ...
... reacts with glucose to form lactose, a-Lactalbumin is a protein that serves as the modifier of galactosyl transferase, which catalyzes this reaction. 28. The pentose phosphate pathway generates each of the following products EXCEPT (A) NADPH, which may be used for fatty acid synthesis (B) ribose 5-p ...
Macromolecule Virtual Lab
... f. A saturated fatty acid has maximum number of _______________ atoms in its chain. g. A molecule of fat has ____(#) fatty acid chains and a phospholipid has ____(#) fatty acid chains. h. How can the main structural backbone of all steroids be described? I. Amino acids are bonded together in differe ...
... f. A saturated fatty acid has maximum number of _______________ atoms in its chain. g. A molecule of fat has ____(#) fatty acid chains and a phospholipid has ____(#) fatty acid chains. h. How can the main structural backbone of all steroids be described? I. Amino acids are bonded together in differe ...
Cellular Respiration Part II: Glycolysis
... Glycolysis harvests chemical energy by oxidizing glucose to pyruvate • Glycolysis (“splitting of sugar”) breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate • Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm and has two major phases – Energy investment phase – Energy payoff phase ...
... Glycolysis harvests chemical energy by oxidizing glucose to pyruvate • Glycolysis (“splitting of sugar”) breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate • Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm and has two major phases – Energy investment phase – Energy payoff phase ...
Distributed Atomic Polarizabilities of Amino Acids and their
... levels of approximation. We used the glycine molecule and three hydrogen bonded dimers as references in order to test various basis set expansions and to compare results from different DFT functionals against those from configuration interaction (CI) or perturbation methods (secondorder Møller-Pless ...
... levels of approximation. We used the glycine molecule and three hydrogen bonded dimers as references in order to test various basis set expansions and to compare results from different DFT functionals against those from configuration interaction (CI) or perturbation methods (secondorder Møller-Pless ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.