SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION STUDY OF PHYSICAL MIXTURE OF CARBAMAZEPINE AND
... carrier out in CO2 free water distilled at a temperature 37 ± 0.5 ºC. Dissolution performed with USP dissolution apparatus II (paddle type) and stirred at a speed of 75 rpm for 60 minutes. Results: Solubility test of carbamazepine and carbamazepine physical mixture of amino acids CBZ-GLY, CBZ-ALA, a ...
... carrier out in CO2 free water distilled at a temperature 37 ± 0.5 ºC. Dissolution performed with USP dissolution apparatus II (paddle type) and stirred at a speed of 75 rpm for 60 minutes. Results: Solubility test of carbamazepine and carbamazepine physical mixture of amino acids CBZ-GLY, CBZ-ALA, a ...
Arabidopsis Contains Nine Long-Chain Acyl
... occupies a critical position in the biosynthetic pathways of nearly all fatty acid-derived molecules. LACS esterifies free fatty acids to acyl-CoAs, a key activation step that is necessary for the utilization of fatty acids by most lipid metabolic enzymes. LACS catalyzes the formation of acyl-CoA by ...
... occupies a critical position in the biosynthetic pathways of nearly all fatty acid-derived molecules. LACS esterifies free fatty acids to acyl-CoAs, a key activation step that is necessary for the utilization of fatty acids by most lipid metabolic enzymes. LACS catalyzes the formation of acyl-CoA by ...
CHM 303 - Unaab.edu.ng
... fat), which serves as a depot or storage site for lipids. Monoacylglycerols and diacylglycerols also exist, but are far less common than the triacylglycerols. Most natural plant and animal fat is composed of mixtures of simple and mixed triacylglycerols. Acylglycerols can be hydrolyzed by heating wi ...
... fat), which serves as a depot or storage site for lipids. Monoacylglycerols and diacylglycerols also exist, but are far less common than the triacylglycerols. Most natural plant and animal fat is composed of mixtures of simple and mixed triacylglycerols. Acylglycerols can be hydrolyzed by heating wi ...
... i) Although the relative position of the TA bases is correct, the diagram contains at least three errors. Identify and correct three of these errors (3 pts). ii) Sketch the phosphate linkage that you would observe linking the T to the next base (2 pts) ii) Indicate the “Watson-Crick’ hydrogen bonds ...
Levy APS - Indiana University Bloomington
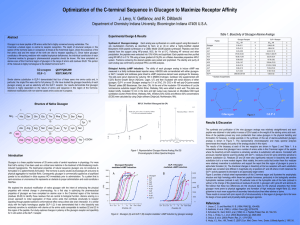
... immediately obvious that glucagon has a number of amino acids in this C-terminal region of the peptide where the bioactivity at both receptors is extremely sensitive to substitution with alanine. Consistent with previously reported alanine scanning studies with GLP-1, residues 22 and 23 were extreme ...
... immediately obvious that glucagon has a number of amino acids in this C-terminal region of the peptide where the bioactivity at both receptors is extremely sensitive to substitution with alanine. Consistent with previously reported alanine scanning studies with GLP-1, residues 22 and 23 were extreme ...
Document
... ligands in trigonal bipyramidal structures. Asymmetric. Lacking all symmetry elements (pointing group C1). All asymmetric molecules are chiral. Asymmetric carbon atom. Traditional term used to describe a carbon with four different ligands attached. Not recommended in modern usage. Atactic. A term de ...
... ligands in trigonal bipyramidal structures. Asymmetric. Lacking all symmetry elements (pointing group C1). All asymmetric molecules are chiral. Asymmetric carbon atom. Traditional term used to describe a carbon with four different ligands attached. Not recommended in modern usage. Atactic. A term de ...
Directions for Use Taq DNA Polymerase, 500U
... Will UNG remove uracil from both ss- and dsDNA with the same efficiency? No, UNG removes uracil from ss-DNA at a rate of 200% compared to dsDNA. Will UNG remove uracil from RNA? Will it work with short oligos (e.g. 25-mer)? UNG does not act on uracil on the ribose sugar backbone. It will work on ura ...
... Will UNG remove uracil from both ss- and dsDNA with the same efficiency? No, UNG removes uracil from ss-DNA at a rate of 200% compared to dsDNA. Will UNG remove uracil from RNA? Will it work with short oligos (e.g. 25-mer)? UNG does not act on uracil on the ribose sugar backbone. It will work on ura ...
L-ASPG86 - Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology
... effects, such as liver dysfunction, pancreatitis, leucopenia, neurological seizures, and coagulation abnormalities [11]. Asparaginase is also used in the food industry during food processing to reduce acrylamide [22]. Acrylamide, which is formed from asparagine when starchy foods such as breads and ...
... effects, such as liver dysfunction, pancreatitis, leucopenia, neurological seizures, and coagulation abnormalities [11]. Asparaginase is also used in the food industry during food processing to reduce acrylamide [22]. Acrylamide, which is formed from asparagine when starchy foods such as breads and ...
Carbon dioxide fixation.
... as well as serving as the starting material for fuel, fiber, animal feed, oil, and other compounds used by people. Collectively, the biochemical processes by which CO2 is assimilated into organic molecules are known as the photosynthetic dark reactions, not because they must occur in darkness but be ...
... as well as serving as the starting material for fuel, fiber, animal feed, oil, and other compounds used by people. Collectively, the biochemical processes by which CO2 is assimilated into organic molecules are known as the photosynthetic dark reactions, not because they must occur in darkness but be ...
Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acids
... The sodium salt of citric acid, sodium citrate, is used in buffers with citric acid to maintain desirable characteristics of foams and gels (jelly, ice cream, candy, whipped cream, etc.) by controlling the pH of the product; also used in medicines and blood for transfusions; also functions as an ant ...
... The sodium salt of citric acid, sodium citrate, is used in buffers with citric acid to maintain desirable characteristics of foams and gels (jelly, ice cream, candy, whipped cream, etc.) by controlling the pH of the product; also used in medicines and blood for transfusions; also functions as an ant ...
... biosynthesis of 2 is of considerable interest both in considerations on the OSC-catalyzed concerted or nonconcerted cyclization mechanism and biological activities.22,23 The first but multiple step chemical synthesis of 2 was developed using titanium(III)-mediated free-radical cyclization of epoxypo ...
Slide 1
... - monomer = monosaccharide (simple sugar) CnH2nOn glucose, galactose, fructose are hexose sugars ribose, ribulose, deoxyribose are pentose sugars - monomers are linked together into polymers using dehydration synthesis - a removal of a water molecule (dehydration) and the synthesis of a bond. This r ...
... - monomer = monosaccharide (simple sugar) CnH2nOn glucose, galactose, fructose are hexose sugars ribose, ribulose, deoxyribose are pentose sugars - monomers are linked together into polymers using dehydration synthesis - a removal of a water molecule (dehydration) and the synthesis of a bond. This r ...
Engineering carbonic anhydrase for highly selective ester hydrolysis Gunnar Höst
... important topic in biochemistry, where a lot of effort is put into structure determination of proteins. Several approaches for exploring the relation between form and function exist. The absolute majority of enzyme engineering work takes advantage of the possibility to clone a gene and incorporate m ...
... important topic in biochemistry, where a lot of effort is put into structure determination of proteins. Several approaches for exploring the relation between form and function exist. The absolute majority of enzyme engineering work takes advantage of the possibility to clone a gene and incorporate m ...
List of Possible Bacteria
... Streptococcus mutans 210007.1 uses all four sugars as well as mannitol. The net reaction observed in the fermentation test is usually the difference between the production of acid from a sugar and the production of alkaline end products, such as ammonia, from peptone. The test result therefore is de ...
... Streptococcus mutans 210007.1 uses all four sugars as well as mannitol. The net reaction observed in the fermentation test is usually the difference between the production of acid from a sugar and the production of alkaline end products, such as ammonia, from peptone. The test result therefore is de ...
Food Science and Nutrition
... If a product is said to be "Sugar Free" it contains how much sugar? Less than 0.5 grams of sugar per serving Less than 10.0 grams ...
... If a product is said to be "Sugar Free" it contains how much sugar? Less than 0.5 grams of sugar per serving Less than 10.0 grams ...
Protein Nutrition For Cattle - Blogging at Oregon State University
... the nitrogen (N) concentration × 6.25. This definition assumes that the average N concentration of a protein molecule is 16 %. Crude protein can be divided into ruminally undegraded protein (RUP) and RDP, which includes the non-protein N. Natural (or true) protein – Protein constituted by amino acid ...
... the nitrogen (N) concentration × 6.25. This definition assumes that the average N concentration of a protein molecule is 16 %. Crude protein can be divided into ruminally undegraded protein (RUP) and RDP, which includes the non-protein N. Natural (or true) protein – Protein constituted by amino acid ...
STRONG AND WEAK HYDROGEN BONDS IN Sm/LSm
... Hydrogen bonding plays a key role in structure and function of proteins including features such as protein folding, ligand recognition, hydration, as well as local architecture, enzymatic activity and molecular dynamics [1,2]. The hydrogen bonds are manifested in a variety of strengths and geometrie ...
... Hydrogen bonding plays a key role in structure and function of proteins including features such as protein folding, ligand recognition, hydration, as well as local architecture, enzymatic activity and molecular dynamics [1,2]. The hydrogen bonds are manifested in a variety of strengths and geometrie ...
to this tutorial as a PDF
... structure. However, by using the Select command, you can specify portions of a molecular structure and change the Display Formats or Display Colors for just that region. The select command on its own will not change the way your molecular structure is displayed. Rather, it simply designates what ato ...
... structure. However, by using the Select command, you can specify portions of a molecular structure and change the Display Formats or Display Colors for just that region. The select command on its own will not change the way your molecular structure is displayed. Rather, it simply designates what ato ...
Metabolic fate and effects of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids in
... been reported to oxidize oleate at significantly lower rates than hepatocytes and to possess a form ofCPT I which is highly sensitive to inhibition by malonyl CoA (6). Fatty acids are also used as structural components within the cell and are incorporated into phospholipids and neutral lipids at rat ...
... been reported to oxidize oleate at significantly lower rates than hepatocytes and to possess a form ofCPT I which is highly sensitive to inhibition by malonyl CoA (6). Fatty acids are also used as structural components within the cell and are incorporated into phospholipids and neutral lipids at rat ...
Solution structure of the Drosha double-stranded RNA-binding domain Open Access
... MicroRNA (miRNA) are small regulatory RNAs derived from longer RNA transcripts called primary miRNA (pri-miRNA) ([1], reviewed recently in [2]). Pri-miRNA are cleaved by an RNase III family enzyme called Drosha to produce hairpin precursor miRNA (pre-miRNA) [3]. Pre-miRNA are transported to the cyto ...
... MicroRNA (miRNA) are small regulatory RNAs derived from longer RNA transcripts called primary miRNA (pri-miRNA) ([1], reviewed recently in [2]). Pri-miRNA are cleaved by an RNase III family enzyme called Drosha to produce hairpin precursor miRNA (pre-miRNA) [3]. Pre-miRNA are transported to the cyto ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.