DISCLAIMER: This lecture outline is intended to help you take notes
... - amino acid catabolism - production of anabolic starting materials - must replace intermediates - anaplerotic reactions - pyruvate carboxylase - allosteric - acetyl-CoA activates ...
... - amino acid catabolism - production of anabolic starting materials - must replace intermediates - anaplerotic reactions - pyruvate carboxylase - allosteric - acetyl-CoA activates ...
Chapter 21: Molecules of Life - Follow “Ironmtn.wordpress.com”
... Twenty represents the number of distinct amino acids available for each protein building block in living systems. Each block in the amino acid chain can be one of twenty amino acids. There are more than three million options in a chain formed from even five amino acid blocks. Typical proteins in liv ...
... Twenty represents the number of distinct amino acids available for each protein building block in living systems. Each block in the amino acid chain can be one of twenty amino acids. There are more than three million options in a chain formed from even five amino acid blocks. Typical proteins in liv ...
A structural determinant in the uracil DNA glycosylase superfamily
... Based on a structural comparison of E. coli MUG and UNG enzymes, we identified Lys-68 as a potential structural element located outside of motifs 1 and 2 that can determine the UDG activity on A/U base pairs. Mutational analysis presented here demonstrates that a K68N substitution not only allows E. ...
... Based on a structural comparison of E. coli MUG and UNG enzymes, we identified Lys-68 as a potential structural element located outside of motifs 1 and 2 that can determine the UDG activity on A/U base pairs. Mutational analysis presented here demonstrates that a K68N substitution not only allows E. ...
6. Protein Folding
... Kinetic factors are important for folding “Calculation for searching all possible conformation in a random fashion to get the lowest energy is impossible!” Assuming each peptide has only three (α,β,L) conformation and time scale is one pico-second (10-12) (for a polypeptide chain of 150 amino acid ...
... Kinetic factors are important for folding “Calculation for searching all possible conformation in a random fashion to get the lowest energy is impossible!” Assuming each peptide has only three (α,β,L) conformation and time scale is one pico-second (10-12) (for a polypeptide chain of 150 amino acid ...
Introduction to Molecular Systematics
... • Linear array of units called nucleotides – Phosphate – Sugar: deoxyribose – One of four bases ...
... • Linear array of units called nucleotides – Phosphate – Sugar: deoxyribose – One of four bases ...
Standard for the presentation of nucleotide and amino acid
... alphabet, it shall also be indicated in characters of the Latin alphabet either as a mere transliteration or through translation into English. The data elements, except those under numeric identifiers <110>, <120> and <160>, shall be repeated for each sequence included in the sequence listing. Only ...
... alphabet, it shall also be indicated in characters of the Latin alphabet either as a mere transliteration or through translation into English. The data elements, except those under numeric identifiers <110>, <120> and <160>, shall be repeated for each sequence included in the sequence listing. Only ...
Chapter 3: Bioenergetics
... – A molecule that loses a hydrogen also loses an electron, and therefore is oxidized ...
... – A molecule that loses a hydrogen also loses an electron, and therefore is oxidized ...
Sialic Acid Production by Metabolically Engineered Escherichia coli
... Limited supply of sialic acid analogs has hindered advancement in basic research, diagnostic development and therapeutic production ...
... Limited supply of sialic acid analogs has hindered advancement in basic research, diagnostic development and therapeutic production ...
Malate Dehydrogenase
... acetyl-CoA using a special H2 02-producing enzyme. The acetyl-CoA produced can be transported via the cytosol to the mitochondria to feed the citric acid cycle, or it can be used for biosynthetic reactions elsewhere. Two very different types of peroxisomes have been extensively studied in plants. On ...
... acetyl-CoA using a special H2 02-producing enzyme. The acetyl-CoA produced can be transported via the cytosol to the mitochondria to feed the citric acid cycle, or it can be used for biosynthetic reactions elsewhere. Two very different types of peroxisomes have been extensively studied in plants. On ...
Chemistry 30 - SharpSchool
... an acid/base reaction is a chemical reaction in which _____________ is transferred from an _________ to a ___________ forming a ________________________ and a _______________________ ...
... an acid/base reaction is a chemical reaction in which _____________ is transferred from an _________ to a ___________ forming a ________________________ and a _______________________ ...
Electromagnetic Properties of Biomolecules
... energies of the same order and nature as the electromagnetic irradiation of light. Protein interactions can be considered as resonant energy transfer between the interacting molecules. This energy can be transferred through oscillations of a physical field, possibly electromagnetic in nature [13,14] ...
... energies of the same order and nature as the electromagnetic irradiation of light. Protein interactions can be considered as resonant energy transfer between the interacting molecules. This energy can be transferred through oscillations of a physical field, possibly electromagnetic in nature [13,14] ...
Computational Studies on Conformations and Properties of Peptide
... functional molecules can wrap around the nanotubes without losing their activity. Therefore, the functional molecules can be selected using the CNTs, as the different adsorbed complexes have different binding energies. In chapter 4, we investigated the adsorptions of three aromatic amino acids (phen ...
... functional molecules can wrap around the nanotubes without losing their activity. Therefore, the functional molecules can be selected using the CNTs, as the different adsorbed complexes have different binding energies. In chapter 4, we investigated the adsorptions of three aromatic amino acids (phen ...
Cellular Respiration - Cathedral High School
... Substrate-level phosphorylation Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Substrate-level phosphorylation Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Chapter 3
... Phospholipids are major components of cell membranes Two fatty acids attached to glycerol and a phosphate group. ...
... Phospholipids are major components of cell membranes Two fatty acids attached to glycerol and a phosphate group. ...
A History of Results
... Glucosamine, MSM and other active ingredients that have been proven beneficial for dogs requiring joint support. Significantly, it is the only clinically researched, Perna-based joint support product available. • Perna canaliculus, commonly known as the New Zealand green-lipped mussel, is a natural ...
... Glucosamine, MSM and other active ingredients that have been proven beneficial for dogs requiring joint support. Significantly, it is the only clinically researched, Perna-based joint support product available. • Perna canaliculus, commonly known as the New Zealand green-lipped mussel, is a natural ...
Chemistry 100 Second Homework
... b. Identify the amine group, the acid group, and the side chain in the amino acid you drew. 11. A dipeptide is a molecule made by attaching two amino acids via a peptide bond. Draw the two different ways a glycine molecule and an alanine molecule can combine to form a dipeptide. The side chain of gl ...
... b. Identify the amine group, the acid group, and the side chain in the amino acid you drew. 11. A dipeptide is a molecule made by attaching two amino acids via a peptide bond. Draw the two different ways a glycine molecule and an alanine molecule can combine to form a dipeptide. The side chain of gl ...
Cellular Respiration
... cytoplasm to two molecules of pyruvate, some ATP formed Transition reaction – pyruvate is oxidized, NADH is formed, and waste CO2 removed Citric acid cycle – NADH and FADH2, release of CO2, and production of additional ATP Electron transport chain – produces 32/34 molecules of ATP, extracts energy f ...
... cytoplasm to two molecules of pyruvate, some ATP formed Transition reaction – pyruvate is oxidized, NADH is formed, and waste CO2 removed Citric acid cycle – NADH and FADH2, release of CO2, and production of additional ATP Electron transport chain – produces 32/34 molecules of ATP, extracts energy f ...
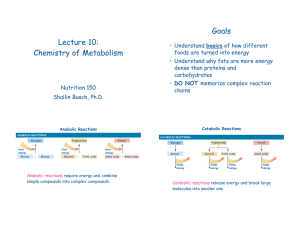
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.