Using NMR Metabolomics to Investigate Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
... are regulated by environmental and nutritional signals (2). Accordingly, a major area of interest in microbiology is determining how bacteria “sense” and respond to environmental signals. Given the tremendous diversity of microbial life, it is not surprising that the mechanisms bacteria employ are e ...
... are regulated by environmental and nutritional signals (2). Accordingly, a major area of interest in microbiology is determining how bacteria “sense” and respond to environmental signals. Given the tremendous diversity of microbial life, it is not surprising that the mechanisms bacteria employ are e ...
The Enzymes of Ammonia Assimilation and their
... The activities of GS, NADP-GOGAT and NADP-GDH in extracts of members of the ‘herbicola’, ‘carotovora’ and ‘amylovora’ clusters, grown with different sources of nitrogen, are shown in Table 1. NAD-GOGAT, NAD-GDH and corresponding amidotransferases and dehydrogenases (both NAD- and NADP-linked) able t ...
... The activities of GS, NADP-GOGAT and NADP-GDH in extracts of members of the ‘herbicola’, ‘carotovora’ and ‘amylovora’ clusters, grown with different sources of nitrogen, are shown in Table 1. NAD-GOGAT, NAD-GDH and corresponding amidotransferases and dehydrogenases (both NAD- and NADP-linked) able t ...
File
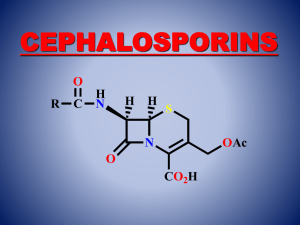
... •Not possible to generate analogues by fermentation •Not possible to generate analogues by a full synthesis •Restricted to semi-synthetic procedure ...
... •Not possible to generate analogues by fermentation •Not possible to generate analogues by a full synthesis •Restricted to semi-synthetic procedure ...
Caprotein by Mt. Capra Premium Goat
... Animal protein, such as that found in natural goat-milk protein, is the only source of vitamins A and D as well as being a complete protein containing all essential amino acids. Sources of protein from vegetables contain only incomplete proteins—low in essential amino acids, even in high protein amo ...
... Animal protein, such as that found in natural goat-milk protein, is the only source of vitamins A and D as well as being a complete protein containing all essential amino acids. Sources of protein from vegetables contain only incomplete proteins—low in essential amino acids, even in high protein amo ...
Growth-limiting Intracellular Metabolites in Yeast Growing Under Diverse Nutrient Limitations.
... medium containing cells directly into cold methanol, followed by isolation of the cells by centrifugation and subsequent extraction of the cell pellet (de Koning and van Dam 1992). The other involved isolation of the cells by vacuum filtration followed by quenching and extraction of the filtertrappe ...
... medium containing cells directly into cold methanol, followed by isolation of the cells by centrifugation and subsequent extraction of the cell pellet (de Koning and van Dam 1992). The other involved isolation of the cells by vacuum filtration followed by quenching and extraction of the filtertrappe ...
Impaired Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Activity in Mouse Livers Lacking
... Animals—Liver-specific PEPCK knock-out mice, pcklox/lox/AlbCre (PEPCK null), and littermate controls, pcklox/lox (control), were generated as described previously (5). 3–5-Month-old mice weighing 25–30 g were maintained on standard laboratory chow. Prior to removal of livers for perfusion, animals w ...
... Animals—Liver-specific PEPCK knock-out mice, pcklox/lox/AlbCre (PEPCK null), and littermate controls, pcklox/lox (control), were generated as described previously (5). 3–5-Month-old mice weighing 25–30 g were maintained on standard laboratory chow. Prior to removal of livers for perfusion, animals w ...
interrelationships among the gut, mitochondrial function, and
... Mitochondria are distinct cellular organelles that generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP) from adenosine diphosphate (ADP) by oxidizing glucose and fatty acids. ATP is the energy carrier in most mammalian cells. In the simplest terms, mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell, generating energy fr ...
... Mitochondria are distinct cellular organelles that generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP) from adenosine diphosphate (ADP) by oxidizing glucose and fatty acids. ATP is the energy carrier in most mammalian cells. In the simplest terms, mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell, generating energy fr ...
Identification of surface proteins in Enterococcus - UiO
... In the past decade, the extracellular proteomes of several Gram-positive bacteria have been analyzed using proteomics approaches. Many of these studies employed some kind of protein extraction methods from culture supernatants and/or cell wall fractions followed by twodimensional electrophoresis and ...
... In the past decade, the extracellular proteomes of several Gram-positive bacteria have been analyzed using proteomics approaches. Many of these studies employed some kind of protein extraction methods from culture supernatants and/or cell wall fractions followed by twodimensional electrophoresis and ...
Redacted for Privacy
... The etiology of the disease is not known, even though an extraordinary amount of research has been directed toward treating and understanding the condition. The events that participate in atheromatous lesion development have been well ...
... The etiology of the disease is not known, even though an extraordinary amount of research has been directed toward treating and understanding the condition. The events that participate in atheromatous lesion development have been well ...
Limonene_Synthase-Plant Physiol.-1999-Turner-879-86
... 1993). However, preliminary immunohistochemistry indicated the presence of an antigen target in only the glandular (not the nonglandular) cells. Further investigations showed dense, specific labeling with the anti-limonene synthase antibodies to the stroma of leucoplasts of the disc cells from secre ...
... 1993). However, preliminary immunohistochemistry indicated the presence of an antigen target in only the glandular (not the nonglandular) cells. Further investigations showed dense, specific labeling with the anti-limonene synthase antibodies to the stroma of leucoplasts of the disc cells from secre ...
Alice and Lewis Carroll
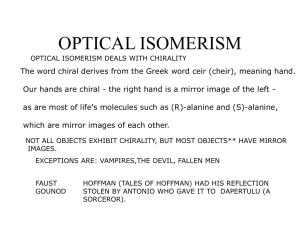
... React a racemic mixture with a chiral compound to form diastereomers, which can be separated. ...
... React a racemic mixture with a chiral compound to form diastereomers, which can be separated. ...
24.5 Nucleic Acids
... 24.5 Nucleic Acids > Gene Mutations • Suppose a string of letters of the alphabet ...
... 24.5 Nucleic Acids > Gene Mutations • Suppose a string of letters of the alphabet ...
"Genetic Methods of Polymer Synthesis". In: Encyclopedia of
... Recombinant DNA methods have been traditionally used in site-directed mutagenesis studies designed to probe protein folding or enzymatic activity. The ease with which genetic sequences can be constructed has, however, led to the increased use of these methods for the synthesis of proteins with repet ...
... Recombinant DNA methods have been traditionally used in site-directed mutagenesis studies designed to probe protein folding or enzymatic activity. The ease with which genetic sequences can be constructed has, however, led to the increased use of these methods for the synthesis of proteins with repet ...
1 Professor D.Sci. Judit Kosáry Nutritional biochemistry of the
... The vitamins are a disparate group of organic compounds whose only common feature is that they are essential (cannot be synthesized inside) and required in small amount for the normal functioning of higher animals and the human body, therefore they must be provided in nutrition. These compounds can ...
... The vitamins are a disparate group of organic compounds whose only common feature is that they are essential (cannot be synthesized inside) and required in small amount for the normal functioning of higher animals and the human body, therefore they must be provided in nutrition. These compounds can ...
aldehyde, ketones and carboxylic acids
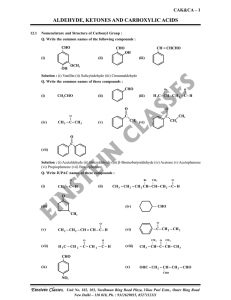
... Q. Why Aldehydes are more reactive than Ketones ? Solution : There are two reasons for this, they are as follows : 1. Steric Factor 2. Electronic factor 1. Steric Factor : With one group being the small hydrogen atom, the central carbon of the tetrahedral product formed from the aldehyde is less cro ...
... Q. Why Aldehydes are more reactive than Ketones ? Solution : There are two reasons for this, they are as follows : 1. Steric Factor 2. Electronic factor 1. Steric Factor : With one group being the small hydrogen atom, the central carbon of the tetrahedral product formed from the aldehyde is less cro ...
02 Cholesterol Metabolism2012-03-18 01:50617 KB
... transcription is suppressed and vice versa • Sterol Regulatory Element (SRE) is a recognition sequence in the DNA • SREBP (SRE binding protein) binding to SRE is essential for transcription of this gene • SREBP cleavage-activating protein (SCAP) is an intracellular cholesterol sensor ...
... transcription is suppressed and vice versa • Sterol Regulatory Element (SRE) is a recognition sequence in the DNA • SREBP (SRE binding protein) binding to SRE is essential for transcription of this gene • SREBP cleavage-activating protein (SCAP) is an intracellular cholesterol sensor ...
On the optimality of the genetic code, with the
... of changes at the three codon positions on mistranslation, a new fitness function was proposed which more accurately modeled the probability of translational errors (Freeland and Hurst, 1998). With the improved ϕ function the fraction of random genetic codes that are better than the natural one decr ...
... of changes at the three codon positions on mistranslation, a new fitness function was proposed which more accurately modeled the probability of translational errors (Freeland and Hurst, 1998). With the improved ϕ function the fraction of random genetic codes that are better than the natural one decr ...
... isolated from the culture broth of S. avidinii by ammonium sulfate precipitation, ion-exchange chromatography, and crystallization. Alternatively, iminobiotin colurnns can be used directly with the bacterial broth. The streptavidin gene has recently been cloned and sequenced (22). From the complete ...
ARTICLE Functional analysis of mutations in SLC7A9, and genotype
... the 12-transmembrane (TM)-domain model of bo,+AT protein is shown in Figure 2. The 18 missense mutations found localize within the putative TM domains I–VII, IX and X (15 mutations) or within the putative intracellular loops 1, 3 and 4 (three mutations). The two single amino acid residue deletions l ...
... the 12-transmembrane (TM)-domain model of bo,+AT protein is shown in Figure 2. The 18 missense mutations found localize within the putative TM domains I–VII, IX and X (15 mutations) or within the putative intracellular loops 1, 3 and 4 (three mutations). The two single amino acid residue deletions l ...
Effect of diet composition and ration size on key enzyme activities of
... intermediary metabolism were studied in the liver of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Highcarbohydrate, low-protein diets stimulated 6-phosphofructo 1-kinase (EC 2.7.1.11), pyruvate kinase (EC 2.7.1.40), glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.49) and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1. ...
... intermediary metabolism were studied in the liver of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Highcarbohydrate, low-protein diets stimulated 6-phosphofructo 1-kinase (EC 2.7.1.11), pyruvate kinase (EC 2.7.1.40), glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.49) and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1. ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.