Bio-Organic Mechanism Game – Simplistic biochemical structures
... reaction mechanisms are used to explain common biochemical transformations. Simplified biochemical molecules are presented first. Many biomolecules have a somewhat complex structure that makes it difficult to write out step by step mechanisms. However, if we simplify those structures to the essentia ...
... reaction mechanisms are used to explain common biochemical transformations. Simplified biochemical molecules are presented first. Many biomolecules have a somewhat complex structure that makes it difficult to write out step by step mechanisms. However, if we simplify those structures to the essentia ...
Nitrogen source governs the patterns of growth and
... fermentation. More generally, several studies have shown that nitrogen assimilation is crucial for the regulation of antibiotic production but the mechanisms involved have not yet been unravelled. In addition, there is experimental evidence for repression of antibiotic production exerted by some nit ...
... fermentation. More generally, several studies have shown that nitrogen assimilation is crucial for the regulation of antibiotic production but the mechanisms involved have not yet been unravelled. In addition, there is experimental evidence for repression of antibiotic production exerted by some nit ...
here - Newtricious
... ischemia, chronic light exposure, oxidative stress, inflammation, cellular signaling mechanisms, and aging. A number of bioactive molecules within the retina affect, and are effected by such conditions. These molecules operate within complex systems and include compounds classified as eicosanoids, ang ...
... ischemia, chronic light exposure, oxidative stress, inflammation, cellular signaling mechanisms, and aging. A number of bioactive molecules within the retina affect, and are effected by such conditions. These molecules operate within complex systems and include compounds classified as eicosanoids, ang ...
BEL β-trefoil: A novel lectin with antineoplastic properties in king
... called lectins (Sharon 2007). In general, ligand binding precedes the fulfillment of an important biological function, which in some cases is still not known. Some members of this family are also called agglutinins because of their ability to agglutinate red blood cells, but this term does not necess ...
... called lectins (Sharon 2007). In general, ligand binding precedes the fulfillment of an important biological function, which in some cases is still not known. Some members of this family are also called agglutinins because of their ability to agglutinate red blood cells, but this term does not necess ...
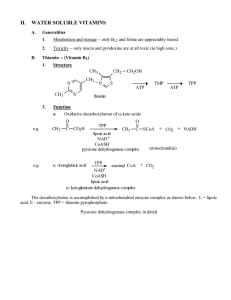
Vitamin B2 -- Riboflavin
... dose is absorbed when taken with meals compared to 15% when taken separately. • Synthetic thyroid medication decreases absorption, but thyroid in general increases the absorption. • It should be noted that gastric acid is responsible for releasing B-2 from non-covalent bonding in foods so that it ma ...
... dose is absorbed when taken with meals compared to 15% when taken separately. • Synthetic thyroid medication decreases absorption, but thyroid in general increases the absorption. • It should be noted that gastric acid is responsible for releasing B-2 from non-covalent bonding in foods so that it ma ...
Biosynthetic Potentials of Metabolites and Their
... Life is based on the ability of cells to convert raw materials into complex chemicals like proteins or DNA. This ability is obtained through the interplay of a large number of enzymes, which are specialized proteins, each facilitating one specific chemical transformation. Since the products of one r ...
... Life is based on the ability of cells to convert raw materials into complex chemicals like proteins or DNA. This ability is obtained through the interplay of a large number of enzymes, which are specialized proteins, each facilitating one specific chemical transformation. Since the products of one r ...
as a PDF
... in complex biological samples (5). The basis for this type of analysis is the production of mostly intact molecular species from a complex mixture by use of a “soft” ionization technique, after which molecular fragments are identified from specific components induced by collisions with neutral gas m ...
... in complex biological samples (5). The basis for this type of analysis is the production of mostly intact molecular species from a complex mixture by use of a “soft” ionization technique, after which molecular fragments are identified from specific components induced by collisions with neutral gas m ...
Controlling reaction specificity in pyridoxal phosphate
... resonance stabilized, carbanionic intermediate. Consequently, the first problem in controlling reaction specificity arises: how does a given enzyme control which of the three labile bonds to Cα is broken to initiate forward reaction from the external aldimine intermediate given that the carbanion form ...
... resonance stabilized, carbanionic intermediate. Consequently, the first problem in controlling reaction specificity arises: how does a given enzyme control which of the three labile bonds to Cα is broken to initiate forward reaction from the external aldimine intermediate given that the carbanion form ...
Sink regulation of photosynthesis
... oxidized plastoquinone signals that PSII is rate-limiting and rapidly initiates the transcription of PSII reaction centre genes and decreases the transcription of genes encoding PSI reaction centre proteins. Reduced plastoquinone signals that PSI is rate-limiting and this initiates the transcription ...
... oxidized plastoquinone signals that PSII is rate-limiting and rapidly initiates the transcription of PSII reaction centre genes and decreases the transcription of genes encoding PSI reaction centre proteins. Reduced plastoquinone signals that PSI is rate-limiting and this initiates the transcription ...
Nonenzymatic, Self-Elimination Degradation
... N-terminal amino group in GSH (Scheme 1), is the most likely possibility. Another possibility for the degradation of GSH is via thiolysis of the free #SH group of Cys with the g-COOH group of Glu followed by thioester bond cleavage. This is not consistent with the data. The products obtained after t ...
... N-terminal amino group in GSH (Scheme 1), is the most likely possibility. Another possibility for the degradation of GSH is via thiolysis of the free #SH group of Cys with the g-COOH group of Glu followed by thioester bond cleavage. This is not consistent with the data. The products obtained after t ...
The Biochemical Machinery of Plastid Envelope
... leaves is the assimilation of CO2 by chloroplasts, root plastids are mainly involved in the assimilation of inorganic nitrogen. Amyloplasts, which contain large starch grains, behave as storage reservoirs in stems, roots, and tubers. Chromoplasts synthesize large amounts of carotenoids and are prese ...
... leaves is the assimilation of CO2 by chloroplasts, root plastids are mainly involved in the assimilation of inorganic nitrogen. Amyloplasts, which contain large starch grains, behave as storage reservoirs in stems, roots, and tubers. Chromoplasts synthesize large amounts of carotenoids and are prese ...
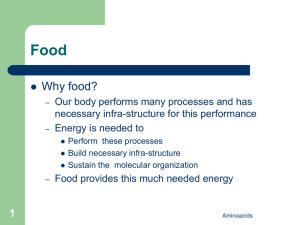
aminoacids
... from specific proteins (tissue /species specific) These proteins then perform various but important functions of the cell/body Aminoacids ...
... from specific proteins (tissue /species specific) These proteins then perform various but important functions of the cell/body Aminoacids ...
The Case Against a Darwinian Origin of Protein Folds
... to stabilize these contacts between proteins therefore adds to their size, over and above the need to stabilize the structures of the individual folded chains. Beyond these general principles, we have specific understanding of the need for structural complexity with respect to many particular protei ...
... to stabilize these contacts between proteins therefore adds to their size, over and above the need to stabilize the structures of the individual folded chains. Beyond these general principles, we have specific understanding of the need for structural complexity with respect to many particular protei ...
Role of Water Mediated Interactions in Protein
... might think that two proteins, complementary with each other in shape and electrostatics, approach as rigid bodies and dock into the native protein complex. This is the celebrated “lock-and-key” paradigm of protein association, hypothesized by Fischer more than 100 years ago.9,10 The simplicity of t ...
... might think that two proteins, complementary with each other in shape and electrostatics, approach as rigid bodies and dock into the native protein complex. This is the celebrated “lock-and-key” paradigm of protein association, hypothesized by Fischer more than 100 years ago.9,10 The simplicity of t ...
Absorption, hepatic metabolism and mammary
... List of tables Table 1. Apparent total tract digestibility of 77 foodstuffs in dry sows ............................................................... 7 Table 2. Range of digestibility of nutrients in ileum and total tract of sows fed low-fiber, high-fiber and highfiber............................ ...
... List of tables Table 1. Apparent total tract digestibility of 77 foodstuffs in dry sows ............................................................... 7 Table 2. Range of digestibility of nutrients in ileum and total tract of sows fed low-fiber, high-fiber and highfiber............................ ...
Characterization and Cloning of the Chlorophyll
... a. Two types of enzymes that catalyze alternative reactions in the formation of PyroPheid a were found (Shioi et al., 1996b; Watanabe et al., 1999; Doi et al., 2001; Suzuki et al., 2002). As shown in Figure 1, one route consists of two reactions: first, enzymatic conversion of Pheid a to a precursor ...
... a. Two types of enzymes that catalyze alternative reactions in the formation of PyroPheid a were found (Shioi et al., 1996b; Watanabe et al., 1999; Doi et al., 2001; Suzuki et al., 2002). As shown in Figure 1, one route consists of two reactions: first, enzymatic conversion of Pheid a to a precursor ...
Slides 2.1
... • Chemicals that can regulate pH change Figure 2.11 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... • Chemicals that can regulate pH change Figure 2.11 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
cholesterol and lipo..
... Endogenous: synthesized in all cells of the body from acetyl CoA. e.g. in liver (mainly), intestine, adrenal cortex, ovaries, testes and skin. Digestion and absorption: mainly in intestine ...
... Endogenous: synthesized in all cells of the body from acetyl CoA. e.g. in liver (mainly), intestine, adrenal cortex, ovaries, testes and skin. Digestion and absorption: mainly in intestine ...
B-Right - LuckyVitamin
... cardiovascular health in the United States.* In addition, folic acid has been shown to play a critical role in protecting against some serious birth defects, including neural tube defects, when taken by women of childbearing age both before and during pregnancy. Biotin (B7) containing enzymes are in ...
... cardiovascular health in the United States.* In addition, folic acid has been shown to play a critical role in protecting against some serious birth defects, including neural tube defects, when taken by women of childbearing age both before and during pregnancy. Biotin (B7) containing enzymes are in ...
Sports Nutrition Manual
... need (RMR + daily activity + exercise expenditure). This is effectively measured in the tables provided elsewhere in this manual. At this 500 calories/day decrease, one should lose bodyweight at a rate of 1 pound per week (7x500=3,500). A diet any lower may result in unacceptable lean tissue loss. C ...
... need (RMR + daily activity + exercise expenditure). This is effectively measured in the tables provided elsewhere in this manual. At this 500 calories/day decrease, one should lose bodyweight at a rate of 1 pound per week (7x500=3,500). A diet any lower may result in unacceptable lean tissue loss. C ...
Hydroxy carboxylic acids
... Citric acid exists in a variety of fruits and vegetables, most notably citrus fruits. Lemons and limes have particularly high concentrations of the acid; it can constitute as much as 8% of the dry weight of these fruits (1.44 and 1.38 grams per ounce of the juices, respectively). The concentrations ...
... Citric acid exists in a variety of fruits and vegetables, most notably citrus fruits. Lemons and limes have particularly high concentrations of the acid; it can constitute as much as 8% of the dry weight of these fruits (1.44 and 1.38 grams per ounce of the juices, respectively). The concentrations ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.