9.1 Catabolic pathways yield energy by oxidizing organic fuels
... 9.6 Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle connect to many other metabolic pathways The catabolism of various molecules from food: “Love the one your with” Any for these 3 macromolecules can be used a fuel source to create ATP. Proteins and Fats just need to be altered first. Proteins- to AA then AA ...
... 9.6 Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle connect to many other metabolic pathways The catabolism of various molecules from food: “Love the one your with” Any for these 3 macromolecules can be used a fuel source to create ATP. Proteins and Fats just need to be altered first. Proteins- to AA then AA ...
2-4 outline cells and energy answers
... Photosynthesis uses light energy and CO2 that is released during cellular respiration to make food energy and release oxygen. When an organism eats plant material, it takes in food energy. An organism’s cells use oxygen released during photosynthesis and convert the food energy into usable energy th ...
... Photosynthesis uses light energy and CO2 that is released during cellular respiration to make food energy and release oxygen. When an organism eats plant material, it takes in food energy. An organism’s cells use oxygen released during photosynthesis and convert the food energy into usable energy th ...
Quick Quiz1
... Discuss delta G (ΔG) and explain how it relates to biochemical reactions (what are the components of ΔG?). Discuss the 3 main parts of glycolysis and the reactions that occur in each part. In a biochemical pathway, explain how a biochemical reaction with a positive ΔG can proceed in a forward direct ...
... Discuss delta G (ΔG) and explain how it relates to biochemical reactions (what are the components of ΔG?). Discuss the 3 main parts of glycolysis and the reactions that occur in each part. In a biochemical pathway, explain how a biochemical reaction with a positive ΔG can proceed in a forward direct ...
A1981LY47200002
... bridge, I had worked on the rat muscle. I hope that it adequately diaphragm assay for insulin and anti-inrepresented and acknowledged the sulin factors in blood plasma. This excontribution of colleagues in other perience convinced me that the route laboratories. The main controversy to an understand ...
... bridge, I had worked on the rat muscle. I hope that it adequately diaphragm assay for insulin and anti-inrepresented and acknowledged the sulin factors in blood plasma. This excontribution of colleagues in other perience convinced me that the route laboratories. The main controversy to an understand ...
PhotosynthesisCalvin Cycle
... (crassulacean acid metabolism). These CAM plants include succulent plants and pineapples. Because of the intense heat and arid conditions, these plants only open up the stomates at night for gas exchange. Plants that use C4 photosynthesis include corn, sugar cane, and sorhum. The CO2 (like C4 photos ...
... (crassulacean acid metabolism). These CAM plants include succulent plants and pineapples. Because of the intense heat and arid conditions, these plants only open up the stomates at night for gas exchange. Plants that use C4 photosynthesis include corn, sugar cane, and sorhum. The CO2 (like C4 photos ...
Cellular Respiration - Cathkin High School
... The electron transport chain is a collection of proteins attached to the folded inner membranes of the mitochondria. NADH and FADH2 release the high-energy electrons to the electron transport chain where they pass along the chain, releasing energy. The energy is used to pump H ions across the ...
... The electron transport chain is a collection of proteins attached to the folded inner membranes of the mitochondria. NADH and FADH2 release the high-energy electrons to the electron transport chain where they pass along the chain, releasing energy. The energy is used to pump H ions across the ...
melgarejo richard
... B. The structure of a water molecule results from its hydrogen bonding. It forms a bent design and has an angle less that 107.5 actually being 105. This is due to that the bonds of the water molecule are polar, meaning that they have one slightly positive atom (H) and one that is slightly negative ( ...
... B. The structure of a water molecule results from its hydrogen bonding. It forms a bent design and has an angle less that 107.5 actually being 105. This is due to that the bonds of the water molecule are polar, meaning that they have one slightly positive atom (H) and one that is slightly negative ( ...
Biochemistry-lab-identifying
... Atoms are pure substances like Hydrogen, Oxygen, Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus. Scientists use the Periodic Table of Elements to organize all pure substances on earth. Elements often join together (or bond) through donating or sharing energy from electrons. When two or more elements join together ...
... Atoms are pure substances like Hydrogen, Oxygen, Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus. Scientists use the Periodic Table of Elements to organize all pure substances on earth. Elements often join together (or bond) through donating or sharing energy from electrons. When two or more elements join together ...
Week 10 notes
... • Metabolism: All the chemical reactions that occur within the cells. • Monomer: Basic subunit used to build larger molecules. Eg. Amino acids • Polymer: Molecules composed of many basic subunits bonded together – Eg. Many amino acids bond together to form ...
... • Metabolism: All the chemical reactions that occur within the cells. • Monomer: Basic subunit used to build larger molecules. Eg. Amino acids • Polymer: Molecules composed of many basic subunits bonded together – Eg. Many amino acids bond together to form ...
Metabolism Stages Figure
... The Three Stages of Catabolism Stage I: Hydrolysis of Macromolecules into Building Blocks ...
... The Three Stages of Catabolism Stage I: Hydrolysis of Macromolecules into Building Blocks ...
Carbonyl Compounds by Dr.Alaa J.Mahrath Medicinal Chemistry
... If the liver glycogen is used up and its quantities run low, our system says it is time to eat again. If we do not eat, the cells start to catabolize (break down) some of the body fats and proteins. Only if we are starving, or eat a series of low-carbohydrate meals, does this begin to have an advers ...
... If the liver glycogen is used up and its quantities run low, our system says it is time to eat again. If we do not eat, the cells start to catabolize (break down) some of the body fats and proteins. Only if we are starving, or eat a series of low-carbohydrate meals, does this begin to have an advers ...
Limits of Human Performance
... • Complete oxidation of palmitate (16C fatty acid) – C16H32O2 + 23O2 → 16CO2 + 16H2O + 129 ATP – And there are 3 fatty acids per molecule of fat (so, 387 ATP) ...
... • Complete oxidation of palmitate (16C fatty acid) – C16H32O2 + 23O2 → 16CO2 + 16H2O + 129 ATP – And there are 3 fatty acids per molecule of fat (so, 387 ATP) ...
Metabolism and Glycolysis
... 4) Regulatory enzymes. (Metabolic conditions that stimulate or inhibit the pathway). 5) Organization of the pathway and the formulas of the compounds involved. (The map of the pathway). 6) Relationship with other pathways. (Shared metabolites, enzymes and regulations). 7) Later, you will have to vis ...
... 4) Regulatory enzymes. (Metabolic conditions that stimulate or inhibit the pathway). 5) Organization of the pathway and the formulas of the compounds involved. (The map of the pathway). 6) Relationship with other pathways. (Shared metabolites, enzymes and regulations). 7) Later, you will have to vis ...
Document
... Catabolism = the breaking down of complex molecules into simple molecules with the release of energy Anabolism = the synthesis of complex molecules from simple molecules with the use of energy ...
... Catabolism = the breaking down of complex molecules into simple molecules with the release of energy Anabolism = the synthesis of complex molecules from simple molecules with the use of energy ...
SADDLEBACK COLLEGE BIOLOGY 20 EXAMINATION 2 STUDY
... • Citric Acid cycle (Krebs cycle) – where does this occur? mitochondrial matrix & produce energy. Succinic acid dehydrogenase/succinic acid from the hamburger lab. • Electron Transport Chain (ETC) & oxidative phosphorylation – where is the ETC located. Know that the majority of ATP is produced here. ...
... • Citric Acid cycle (Krebs cycle) – where does this occur? mitochondrial matrix & produce energy. Succinic acid dehydrogenase/succinic acid from the hamburger lab. • Electron Transport Chain (ETC) & oxidative phosphorylation – where is the ETC located. Know that the majority of ATP is produced here. ...
presentation source
... Chemiosmosis in mitochondria • Energy from electrons is harnessed by – NADH dehydrogenase complex – cytochrome c reductase complex – cytochrome c oxidase complex • the complexes pump protons against their gradient from the matrix into the inner membrane space • a strong diffusion gradient is set up ...
... Chemiosmosis in mitochondria • Energy from electrons is harnessed by – NADH dehydrogenase complex – cytochrome c reductase complex – cytochrome c oxidase complex • the complexes pump protons against their gradient from the matrix into the inner membrane space • a strong diffusion gradient is set up ...
hydrogen bonds - Orientamento In Rete
... together, water is released as the carboxyl end of one amino acid bonds to the amine end of the adjacent one forming a peptide bond, as illustrated at the left. Because water is lost, the process is called: Condensation synthesis, or… ...
... together, water is released as the carboxyl end of one amino acid bonds to the amine end of the adjacent one forming a peptide bond, as illustrated at the left. Because water is lost, the process is called: Condensation synthesis, or… ...
UG Curriculum
... 1. Need not know the structure of cholesterol. Should know why it cannot be carried free in plasma. 2. Mutarotation should not be taught. Student should know why amylase will not hydrolyse cellulose. 3. Need not know the details of alpha - helix and beta – pleats in proteins. 4. Need not know mechan ...
... 1. Need not know the structure of cholesterol. Should know why it cannot be carried free in plasma. 2. Mutarotation should not be taught. Student should know why amylase will not hydrolyse cellulose. 3. Need not know the details of alpha - helix and beta – pleats in proteins. 4. Need not know mechan ...
Biology Name_____________________________________
... b. Two molecules of pyruvic acid are produced. c. An ADP is transformed into an ATP d. An ATP is used to provide energy. e. NAD+ is transformed into NADH 9. What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration? What processes are involved in each type of respiration? ...
... b. Two molecules of pyruvic acid are produced. c. An ADP is transformed into an ATP d. An ATP is used to provide energy. e. NAD+ is transformed into NADH 9. What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration? What processes are involved in each type of respiration? ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • These are the polymers of sugars – the true macromolecules of the carbohydrates. – Serve as storage material that is hydrolyzed as needed in the body or as structural units that support bodies of organisms. ...
... • These are the polymers of sugars – the true macromolecules of the carbohydrates. – Serve as storage material that is hydrolyzed as needed in the body or as structural units that support bodies of organisms. ...
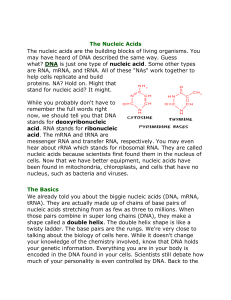
Introduction to Nucleic Acids
... There are five easy parts of nucleic acids. All nucleic acids are made up of the same building blocks (monomers). Chemists call the monomers "nucleotides." The five pieces are uracil, cytosine, thymine,a denine, and guanine. No matter what science class you are in, you will always hear about ATCG wh ...
... There are five easy parts of nucleic acids. All nucleic acids are made up of the same building blocks (monomers). Chemists call the monomers "nucleotides." The five pieces are uracil, cytosine, thymine,a denine, and guanine. No matter what science class you are in, you will always hear about ATCG wh ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.