Biochemistry Powerpoint - Glasgow Independent Schools
... • Some water molecules break apart to form hydronium and hydroxide ions. • In pure water, hydronium and hydroxide ions are present in equal numbers. • Acids and bases are compounds that change the balance of these ions. ...
... • Some water molecules break apart to form hydronium and hydroxide ions. • In pure water, hydronium and hydroxide ions are present in equal numbers. • Acids and bases are compounds that change the balance of these ions. ...
Microbial Metabolism
... The energy from the transfer of electrons along thechain transports protons across the membrane and creates an electrochemical gradient. As the accumulating protons follow the electrochemical gradient back across the membrane through an ATP synthase complex, the movement of the protons provides ener ...
... The energy from the transfer of electrons along thechain transports protons across the membrane and creates an electrochemical gradient. As the accumulating protons follow the electrochemical gradient back across the membrane through an ATP synthase complex, the movement of the protons provides ener ...
IB BIOLOGY: Respiration Notes - NatronaBiology-IB2
... NADH +H+, the electron transport chain and the role of oxygen. In aerobic respiration (in mitochondria in eukaryotes), each pyruvate is decarboxylated (CO2 removed). The remaining two-carbon molecule (acetyl group) reacts with reduced coenzyme A, and, at the same time, one NADH + H+ is formed. This ...
... NADH +H+, the electron transport chain and the role of oxygen. In aerobic respiration (in mitochondria in eukaryotes), each pyruvate is decarboxylated (CO2 removed). The remaining two-carbon molecule (acetyl group) reacts with reduced coenzyme A, and, at the same time, one NADH + H+ is formed. This ...
Primary functions Fat-soluble vitamin
... – In type 2 diabetes, the body develops impaired insulin production and increased insulin resistance, which leads to increased fat deposition and elevated fatty acid levels. – Cardiovascular disease affects the heart and can lead to hypertension, heart attack, and ...
... – In type 2 diabetes, the body develops impaired insulin production and increased insulin resistance, which leads to increased fat deposition and elevated fatty acid levels. – Cardiovascular disease affects the heart and can lead to hypertension, heart attack, and ...
detailed lecture outline
... components. Figure 25-1 Cells are chemical factories that break down organic molecules to obtain energy, which can then be used to generate ATP. Reactions within mitochondria provide most of the energy needed by a typical cell. To carry out these metabolic reactions, cells must have a reliable s ...
... components. Figure 25-1 Cells are chemical factories that break down organic molecules to obtain energy, which can then be used to generate ATP. Reactions within mitochondria provide most of the energy needed by a typical cell. To carry out these metabolic reactions, cells must have a reliable s ...
- Riverside Preparatory High School
... Occurs in the folds of the Inner Membrane of the Mitochondria (Cristae) The electrons are passed down a chain of proteins until they reach the final electron acceptor…..oxygen! ...
... Occurs in the folds of the Inner Membrane of the Mitochondria (Cristae) The electrons are passed down a chain of proteins until they reach the final electron acceptor…..oxygen! ...
Slide ()
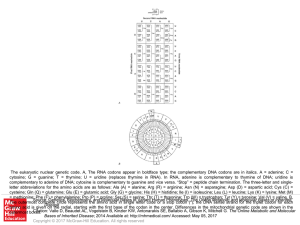
... The eukaryotic nuclear genetic code. A, The RNA codons appear in boldface type; the complementary DNA codons are in italics. A = adenine; C = cytosine; G = guanine; T = thymine; U = uridine (replaces thymine in RNA). In RNA, adenine is complementary to thymine of DNA; uridine is complementary to ade ...
... The eukaryotic nuclear genetic code. A, The RNA codons appear in boldface type; the complementary DNA codons are in italics. A = adenine; C = cytosine; G = guanine; T = thymine; U = uridine (replaces thymine in RNA). In RNA, adenine is complementary to thymine of DNA; uridine is complementary to ade ...
Document
... Fire extinguishers are used for putting out fires. There are different types of fire extinguisher, and it is important always to use the correct sort for a particular fire. Sand or fire blankets can also be used to put out fires. Water is often used to put out fires, because it takes away the heat. ...
... Fire extinguishers are used for putting out fires. There are different types of fire extinguisher, and it is important always to use the correct sort for a particular fire. Sand or fire blankets can also be used to put out fires. Water is often used to put out fires, because it takes away the heat. ...
ENZYMES: THE MAJESTIC MOLECULES OF LIFE Part
... Usually, the enzyme active centre is made up of 12 to 16 amino acid residues of a polypeptide chain; occasionally their number may be larger. The amino acids that constitute the active centre are located at various sites of the polypeptide chain, often at its opposite ends. When folded in space, the ...
... Usually, the enzyme active centre is made up of 12 to 16 amino acid residues of a polypeptide chain; occasionally their number may be larger. The amino acids that constitute the active centre are located at various sites of the polypeptide chain, often at its opposite ends. When folded in space, the ...
Chapter 2
... along with carbon dioxide in the stroma. Goes through the Calvin Cycle and converts them into glucose. ADP (low energy) & NADP+ (low energy) ATP & NADPH are short term high energy molecules ADP & NADP+ are short term low energy molecules Glucose is a long term high energy molecule In summary: ...
... along with carbon dioxide in the stroma. Goes through the Calvin Cycle and converts them into glucose. ADP (low energy) & NADP+ (low energy) ATP & NADPH are short term high energy molecules ADP & NADP+ are short term low energy molecules Glucose is a long term high energy molecule In summary: ...
ERT320 BIOSEPARATION ENGINEERING
... Final Purification (Polishing). Necessitated by the extremely high purity required of many bioproducts, particularly pharmaceuticals and therapeutics. After primary purification the product is nearly pure but may not be in the proper form. Partially pure solids may still contain discolored materia ...
... Final Purification (Polishing). Necessitated by the extremely high purity required of many bioproducts, particularly pharmaceuticals and therapeutics. After primary purification the product is nearly pure but may not be in the proper form. Partially pure solids may still contain discolored materia ...
Fundamentals of Biochemistry 2/e
... Glycolysis converts to two C3 units. The free energy released in this process is harvested to synthesize ATP from ADP and Pi ...
... Glycolysis converts to two C3 units. The free energy released in this process is harvested to synthesize ATP from ADP and Pi ...
Chapter 25
... biological work. • There are three major metabolic destinations for the principle nutrients. They will be used for energy for active processes, synthesized into structural or functional molecules, or synthesized as fat or glycogen for later use as energy. ...
... biological work. • There are three major metabolic destinations for the principle nutrients. They will be used for energy for active processes, synthesized into structural or functional molecules, or synthesized as fat or glycogen for later use as energy. ...
A1988N971500002
... residue in AlP. Thus primed with the omnipresence and general importance of activated groups in biochemical processes, it seemed only natural that my interest turned to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) as a form of activated ADP-ribose. Use of this pyridine nucleotide as a substrate of ADP-ri ...
... residue in AlP. Thus primed with the omnipresence and general importance of activated groups in biochemical processes, it seemed only natural that my interest turned to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) as a form of activated ADP-ribose. Use of this pyridine nucleotide as a substrate of ADP-ri ...
Chapter 6 Power Point
... Form an ETC along which electrons are passed Enzyme at the end of the chain combines e- from ETC, H+ ions from fluid inside the cell, and O2 to form H2O Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in respiration Is essential for obtaining energy from both NADH and FADH2 ...
... Form an ETC along which electrons are passed Enzyme at the end of the chain combines e- from ETC, H+ ions from fluid inside the cell, and O2 to form H2O Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in respiration Is essential for obtaining energy from both NADH and FADH2 ...
Answers to Exam 1 multiple choice, TF and short answer questions
... 13. Which of the following statements is(are) FALSE? a. Peptide bonds are the covalent bonds that link together two amino acids in proteins. b. The polypeptide backbone is free to rotate about each peptide bond. c. Nonpolar amino acids tend to be found in the interior of cytosolic proteins. d. The s ...
... 13. Which of the following statements is(are) FALSE? a. Peptide bonds are the covalent bonds that link together two amino acids in proteins. b. The polypeptide backbone is free to rotate about each peptide bond. c. Nonpolar amino acids tend to be found in the interior of cytosolic proteins. d. The s ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... Some organisms, such as yeast and some bacteria, do not require oxygen and can survive on a less efficient way of getting energy Other organisms that generally require oxygen sometimes don’t have enough for all their cells to do aerobic respiration so they can use a less effiecent way of breaking do ...
... Some organisms, such as yeast and some bacteria, do not require oxygen and can survive on a less efficient way of getting energy Other organisms that generally require oxygen sometimes don’t have enough for all their cells to do aerobic respiration so they can use a less effiecent way of breaking do ...
Tutorial Kit (Biochemistry-300 L)
... non-consumable substances that reduce the activation energy necessary for a chemical reaction to occur. Enzymes are highly specific to the reactions they catalyze. They are of vital importance for life because most chemical reactions of the cells and tissues are catalyzed by enzymes. Without enzymat ...
... non-consumable substances that reduce the activation energy necessary for a chemical reaction to occur. Enzymes are highly specific to the reactions they catalyze. They are of vital importance for life because most chemical reactions of the cells and tissues are catalyzed by enzymes. Without enzymat ...
Unit 1 Objectives: Biochemistry
... 1. In nucleic acids, biological information is encoded in sequences of nucleotide monomers. Each nucleotide has structural components: a five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose or ribose), a phosphate and a nitrogen base (adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine or uracil). DNA and RNA differ in function and diff ...
... 1. In nucleic acids, biological information is encoded in sequences of nucleotide monomers. Each nucleotide has structural components: a five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose or ribose), a phosphate and a nitrogen base (adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine or uracil). DNA and RNA differ in function and diff ...
Aerobic Respiration
... Reduced NAD and reduced FAD donate hydrogen atoms. The carriers become re oxidised in the process (due to loss of hydrogen) and return to glycolysis, link reaction or the krebs cycle to collect more hydrogen The hydrogen atoms split into protons (H+) and electrons. (occurs in the matrix) The electro ...
... Reduced NAD and reduced FAD donate hydrogen atoms. The carriers become re oxidised in the process (due to loss of hydrogen) and return to glycolysis, link reaction or the krebs cycle to collect more hydrogen The hydrogen atoms split into protons (H+) and electrons. (occurs in the matrix) The electro ...
moluceular lab 1
... 1-Modern field of science 2-To understand the basic of living organisms’ chemical reactions necessary to build cell’s nutrients and to perform biological functions. Structural organic order is as follows: Organism–System–Organs–Tissues–Cells–Organelles– Molecules-Atoms The body of Living organisms c ...
... 1-Modern field of science 2-To understand the basic of living organisms’ chemical reactions necessary to build cell’s nutrients and to perform biological functions. Structural organic order is as follows: Organism–System–Organs–Tissues–Cells–Organelles– Molecules-Atoms The body of Living organisms c ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.