Document
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) is the blueprint for construction of a protein. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is the construction site where the protein is made. Transfer RNA (tRNA) is the truck delivering the proper amino acid to the site at the right time. ...
... Messenger RNA (mRNA) is the blueprint for construction of a protein. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is the construction site where the protein is made. Transfer RNA (tRNA) is the truck delivering the proper amino acid to the site at the right time. ...
Metabolism Aerobic Respiration Other Ways of Generating ATP
... – Low energy yield – Acid production affects cell/body pH ...
... – Low energy yield – Acid production affects cell/body pH ...
2.Molecular basis of heredity. Realization of hereditary information
... Lipoproteins -are a combination of lipids and proteins; they are active in transporting fat molecules throughout the body via the bloodstream. They amount to a capsule of protein surrounding a globule of fat. ...
... Lipoproteins -are a combination of lipids and proteins; they are active in transporting fat molecules throughout the body via the bloodstream. They amount to a capsule of protein surrounding a globule of fat. ...
Gluconeogenesis
... number of carbons that have a minute contribution to the synthesis of glucose. Fatty acids contribute to the fasting organism with ATP through β-oxidation and oxidation of ketone bodies in the Krebs cycle. Ketone bodies only partially substitute for glucose and are synthesized by a pathway different ...
... number of carbons that have a minute contribution to the synthesis of glucose. Fatty acids contribute to the fasting organism with ATP through β-oxidation and oxidation of ketone bodies in the Krebs cycle. Ketone bodies only partially substitute for glucose and are synthesized by a pathway different ...
Unit 2 ~ Learning Guide Name
... we store them in adipose (________) cells. They function as a _____________________________________, _______________________________, and ______________________. The three lipids you need to know for this course are the fats, phospholipids and steroids. Lipids such as those shown above typically con ...
... we store them in adipose (________) cells. They function as a _____________________________________, _______________________________, and ______________________. The three lipids you need to know for this course are the fats, phospholipids and steroids. Lipids such as those shown above typically con ...
Microbial Nutrition and Growth
... copper. Sulfur is incorporated into certain amino acids, so is essential to protein formation. Phosphorous is used for the synthesis of phospholipids, nucleic acids and a variety of nucleotide derivatives such as coenzymes (NAD, FAD, NADP), and high energy compounds (ATP, GTP, etc.). Iron and copper ...
... copper. Sulfur is incorporated into certain amino acids, so is essential to protein formation. Phosphorous is used for the synthesis of phospholipids, nucleic acids and a variety of nucleotide derivatives such as coenzymes (NAD, FAD, NADP), and high energy compounds (ATP, GTP, etc.). Iron and copper ...
1 In Class Examples Protein Synthesis a) Enkephalins (penta
... haemoglobin molecule? (It’s a part of a chromosome!) 4. If you go back to the original transfer RNA codes, which codes resemble each other when you compare those of valine to those of glutamic acid? 5. This substitution of valine for glutamic acid creates a hydrophobic(water-avoiding) spot on the ou ...
... haemoglobin molecule? (It’s a part of a chromosome!) 4. If you go back to the original transfer RNA codes, which codes resemble each other when you compare those of valine to those of glutamic acid? 5. This substitution of valine for glutamic acid creates a hydrophobic(water-avoiding) spot on the ou ...
Eicosanoid Synthesis
... derived from a plant source is necessary. • These essential fatty acids give rise to eicosanoic (C20) fatty ...
... derived from a plant source is necessary. • These essential fatty acids give rise to eicosanoic (C20) fatty ...
Pancreatic enzymes basics
... • Bird – No diabetes ! Why • Pancreas becomes more discrete as we move from lower vertebrates up to primates. • Diverse in macroscopic structure! • Controlled by parasympathetic and sympathetic inputs but- not primary controls. ...
... • Bird – No diabetes ! Why • Pancreas becomes more discrete as we move from lower vertebrates up to primates. • Diverse in macroscopic structure! • Controlled by parasympathetic and sympathetic inputs but- not primary controls. ...
Chapter 2 - Water - Technicalsymposium
... Proteins Proteins can be classified as either: 1) globular - spherical; water-soluble molecules with a hydrophobic interior and hydrophobic surface; have mostly functional roles in the cell, e.g. enzymes 2) fibrous - made into threads or cables with repeating units; water-insoluble molecules that pr ...
... Proteins Proteins can be classified as either: 1) globular - spherical; water-soluble molecules with a hydrophobic interior and hydrophobic surface; have mostly functional roles in the cell, e.g. enzymes 2) fibrous - made into threads or cables with repeating units; water-insoluble molecules that pr ...
et al
... When you have read Chapter 3, you should be able to: 1. Define the terms ‘transcriptome' and ‘proteome' 2. Draw a diagram illustrating the modern interpretation of the genome expression pathway, indicating the main points at which genome expression is regulated 3. Distinguish between coding and non- ...
... When you have read Chapter 3, you should be able to: 1. Define the terms ‘transcriptome' and ‘proteome' 2. Draw a diagram illustrating the modern interpretation of the genome expression pathway, indicating the main points at which genome expression is regulated 3. Distinguish between coding and non- ...
inhibition of very long chain fatty acid synthesis in barley and wild
... interfere with surface wax formation. We have shown that they have a major effect on the synthesis of very long chain fatty acidswhich are precursors for surface waxes. However, the inhibitory characteristics are such that a metabolite, probably the sulphoxide, rather than the parent compound is the ...
... interfere with surface wax formation. We have shown that they have a major effect on the synthesis of very long chain fatty acidswhich are precursors for surface waxes. However, the inhibitory characteristics are such that a metabolite, probably the sulphoxide, rather than the parent compound is the ...
File
... Dehydrogenase enzymes remove hydrogen ions and electrons which are passed to the coenzymes NAD or FAD to form NADH or FADH2 in glycolysis and citric acid pathways. NADH and FADH2 release the high-energy electrons to the electron transport chain on the mitochondrial membrane and this results in the s ...
... Dehydrogenase enzymes remove hydrogen ions and electrons which are passed to the coenzymes NAD or FAD to form NADH or FADH2 in glycolysis and citric acid pathways. NADH and FADH2 release the high-energy electrons to the electron transport chain on the mitochondrial membrane and this results in the s ...
Isolation of Viable Cells from Mammalian Tissues
... A metabolically more interesting cell type is the fat cell or adipocyte. The mature fat cell has a characteristic signet ring shape in which the storage product, triacylgycerol is surrounded by a thin layer of cytoplasm. Adipocytes can be isolated from fat deposits such as the epidydimal fat pad fou ...
... A metabolically more interesting cell type is the fat cell or adipocyte. The mature fat cell has a characteristic signet ring shape in which the storage product, triacylgycerol is surrounded by a thin layer of cytoplasm. Adipocytes can be isolated from fat deposits such as the epidydimal fat pad fou ...
powerpoint
... End products are acetyl-CoA and Propionyl-CoA Ribose sugar component may be converted to ribose-5-phosphate which is a substrate for PRPP Synthetase Ribose sugar component may be further catabolized in HMP pathway ...
... End products are acetyl-CoA and Propionyl-CoA Ribose sugar component may be converted to ribose-5-phosphate which is a substrate for PRPP Synthetase Ribose sugar component may be further catabolized in HMP pathway ...
The Discovery of C4 Photosynthesis
... ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) to form a six-carbon intermediate which immediately splits to form two C3 molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate. In the latter half of the next decade Marshall Hatch and Roger Slack with, PhD students Hilary Johnson and John Andrews, working at the Brisbane laboratory of the C ...
... ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) to form a six-carbon intermediate which immediately splits to form two C3 molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate. In the latter half of the next decade Marshall Hatch and Roger Slack with, PhD students Hilary Johnson and John Andrews, working at the Brisbane laboratory of the C ...
Amino acid substitution and protein structure
... Proteins classified as homologs by one tend to be classified as homologs by the other (why?) ...
... Proteins classified as homologs by one tend to be classified as homologs by the other (why?) ...
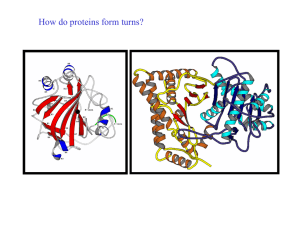
How do proteins form turns? - UF Macromolecular Structure Group
... Helical regions are excluded from this definition (see later) Reverse turns are very abundant in globular proteins and generally occur at the surface of the molecule. It has been suggested that turn regions act as nucleation centres during protein folding ...
... Helical regions are excluded from this definition (see later) Reverse turns are very abundant in globular proteins and generally occur at the surface of the molecule. It has been suggested that turn regions act as nucleation centres during protein folding ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.