Proteinler - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... • Protein fractionation (several steps) • Determination of purity ...
... • Protein fractionation (several steps) • Determination of purity ...
Lecture#20
... size. In this case the editing site precludes the larger ileu from binding and allows the valine to bind where it can be hydrolyzed. In active site, coarse sieve selects sterically against bigger structure Isoleucine is bigger than valine, but this will help select against larger amino acids Fine si ...
... size. In this case the editing site precludes the larger ileu from binding and allows the valine to bind where it can be hydrolyzed. In active site, coarse sieve selects sterically against bigger structure Isoleucine is bigger than valine, but this will help select against larger amino acids Fine si ...
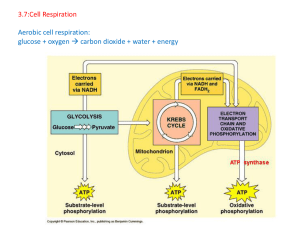
3.7:Cell Respiration Aerobic cell respiration: glucose
... anaerobic/fermentation in plants produces alcohol / anaerobic in animals produces lactic acid neither produced in aerobic respiration; glucose can be the substrate for both; glucose can be the substrate for both; anaerobic entirely in cytoplasm whereas aerobic requires mitochondria/specialized regio ...
... anaerobic/fermentation in plants produces alcohol / anaerobic in animals produces lactic acid neither produced in aerobic respiration; glucose can be the substrate for both; glucose can be the substrate for both; anaerobic entirely in cytoplasm whereas aerobic requires mitochondria/specialized regio ...
EXAM 2012
... Glycolysis takes place inside the mitochondria. Glucose is reduced to pyruvate. NAD+ is an electron donor. Water is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain. Most of the ATP produced is from oxidative phosphorylation. ...
... Glycolysis takes place inside the mitochondria. Glucose is reduced to pyruvate. NAD+ is an electron donor. Water is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain. Most of the ATP produced is from oxidative phosphorylation. ...
Chem Reactions (and Balancing Equations)
... Symbols used in equations (s) after the formula –solid Cu(s) (g) after the formula –gas H2 (g) (l) after the formula -liquid H2O(l) (aq) after the formula - dissolved in water, an aqueous solution. CaCl2 (aq) • used after a product indicates a gas (same as (g)) O2 • used after a product indic ...
... Symbols used in equations (s) after the formula –solid Cu(s) (g) after the formula –gas H2 (g) (l) after the formula -liquid H2O(l) (aq) after the formula - dissolved in water, an aqueous solution. CaCl2 (aq) • used after a product indicates a gas (same as (g)) O2 • used after a product indic ...
Amino acid catabolism I
... Scource of ammonia in different tissues: 1. degradation of amino acids transdeamination (transamination+GDH) minor patways 2. deamination of other compounds N-containing side chains of nucleotides neurotransmitters 3. ammonia production in the large intestine by bacteria portal vein, direct transpor ...
... Scource of ammonia in different tissues: 1. degradation of amino acids transdeamination (transamination+GDH) minor patways 2. deamination of other compounds N-containing side chains of nucleotides neurotransmitters 3. ammonia production in the large intestine by bacteria portal vein, direct transpor ...
Document
... • For each glucose molecule that enters cellular respiration, chemiosmosis produces up to 38 ATP molecules Cytoplasmic fluid ...
... • For each glucose molecule that enters cellular respiration, chemiosmosis produces up to 38 ATP molecules Cytoplasmic fluid ...
Topic 7 - FSU Biology
... 1. Understand the concepts of kinetic vs. potential energy. 2. Understand the concepts of free energy and entropy; use these concepts and thermodynamic principles to show whether a particular reaction is going be spontaneous or not. 3. Be able to define equilibrium constant and how this relates to d ...
... 1. Understand the concepts of kinetic vs. potential energy. 2. Understand the concepts of free energy and entropy; use these concepts and thermodynamic principles to show whether a particular reaction is going be spontaneous or not. 3. Be able to define equilibrium constant and how this relates to d ...
Topic 7: METABOLISM: THERMODYNAMICS, CHEMICAL
... by a process known as cellular energy metabolism (energy metabolism = catabolism of organic molecules yielding ATP [and other useful forms of chemical energy]). Fig. 6.10- the ATP hydrolysis/regeneration cycle in cells Rates of reactions. For a chemical reaction like A à B the rate of the reaction ...
... by a process known as cellular energy metabolism (energy metabolism = catabolism of organic molecules yielding ATP [and other useful forms of chemical energy]). Fig. 6.10- the ATP hydrolysis/regeneration cycle in cells Rates of reactions. For a chemical reaction like A à B the rate of the reaction ...
cell respiration
... acetyl groups and used in the Krebs or citric acid cycle. **Proteins = amino acids The amino acids are sent to the liver where the liver removes the amine group. The left over acid is then used at some point in the Krebs cycle. ...
... acetyl groups and used in the Krebs or citric acid cycle. **Proteins = amino acids The amino acids are sent to the liver where the liver removes the amine group. The left over acid is then used at some point in the Krebs cycle. ...
do not - wwphs
... How do enzymes work? 1) Enzymes act upon a substance called a substrate 2) The enzyme has an indent in it called the active site where the substrate can fit into, kind of like a lock and a key ...
... How do enzymes work? 1) Enzymes act upon a substance called a substrate 2) The enzyme has an indent in it called the active site where the substrate can fit into, kind of like a lock and a key ...
Model Description Sheet
... Antibiotic-resistant bacteria are common and hard to treat. There is potential to create synthetic antibiotics based on natural products like enduracidin and mannopeptimycin to fight drug resistant bacteria like MRSA. MppP, an enzyme from Streptomyces wadayamensis, is required for the biosynthesis o ...
... Antibiotic-resistant bacteria are common and hard to treat. There is potential to create synthetic antibiotics based on natural products like enduracidin and mannopeptimycin to fight drug resistant bacteria like MRSA. MppP, an enzyme from Streptomyces wadayamensis, is required for the biosynthesis o ...
Constructing a Model of Protein Synthesis
... Genes are the biological units that determine inherited characteristics, such as hair color and blood type. Genes are short segments of DNA that have the instructions for making the proteins that our cells need to make. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in pro ...
... Genes are the biological units that determine inherited characteristics, such as hair color and blood type. Genes are short segments of DNA that have the instructions for making the proteins that our cells need to make. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in pro ...
Protein synthesis
... long, linear chain of amino acids, which folds in a particular fashion to produce a three-dimensional product. Many enzymes can be unfolded or inactivated by heating, which destroys the three-dimensional structure of the protein. Most enzymes are larger than the substrates they act on and only a ver ...
... long, linear chain of amino acids, which folds in a particular fashion to produce a three-dimensional product. Many enzymes can be unfolded or inactivated by heating, which destroys the three-dimensional structure of the protein. Most enzymes are larger than the substrates they act on and only a ver ...
CH 6: Proteins and Amino Acids
... Amino Acids • Diet must provide all 9 of the essential a.a. on a regular/daily basis for proteins to be made – Need all 20 a.a. to make most proteins – Animal sources of proteins contain all 9 essential ...
... Amino Acids • Diet must provide all 9 of the essential a.a. on a regular/daily basis for proteins to be made – Need all 20 a.a. to make most proteins – Animal sources of proteins contain all 9 essential ...
CATABOLISM OF PROTEINS AND AMINO ACIDS1.36 MB
... subsequent NAD+-dependent oxidation of malate in the mitochondrion forms oxaloacetate (malate dehydrogenase) • Each NADH molecule can generate up to 2.5 ATP during mitochondrial respiration, greatly reducing the overall energetic cost of urea synthesis. ...
... subsequent NAD+-dependent oxidation of malate in the mitochondrion forms oxaloacetate (malate dehydrogenase) • Each NADH molecule can generate up to 2.5 ATP during mitochondrial respiration, greatly reducing the overall energetic cost of urea synthesis. ...
9.3 student notes
... • Proteins and nucleic acids can also be used to make ATP, but they are usually used for building important cell parts. ...
... • Proteins and nucleic acids can also be used to make ATP, but they are usually used for building important cell parts. ...
Lipids WORD 1000 KB - Science Learning Hub
... 3 (omega 3) and 6 (omega 6). These acids are required for the construction of cell membranes and as precursors for the production of hormones. It has been discovered that eating a relatively low fat diet in which much of the fat comes from polyunsaturated sources such as olive oil and oily fish ...
... 3 (omega 3) and 6 (omega 6). These acids are required for the construction of cell membranes and as precursors for the production of hormones. It has been discovered that eating a relatively low fat diet in which much of the fat comes from polyunsaturated sources such as olive oil and oily fish ...
Lipid rafts
... Biologically active lipophilic substances that activate cannabinoid receptors Derivatives of arachidonic acid, which are generated from membrane phospholipids in response to stimuli Two best-characterized: ...
... Biologically active lipophilic substances that activate cannabinoid receptors Derivatives of arachidonic acid, which are generated from membrane phospholipids in response to stimuli Two best-characterized: ...
Exam IV answers
... The uptake of dietary amino acids by enterocytes is coupled to potassium export by these cells. Sodium Non-essential amino acids are ones that in a healthy young adult are not needed for protein synthesis. Can be synthesized in sufficient amounts to maintain homeostasis The transamination of lysine ...
... The uptake of dietary amino acids by enterocytes is coupled to potassium export by these cells. Sodium Non-essential amino acids are ones that in a healthy young adult are not needed for protein synthesis. Can be synthesized in sufficient amounts to maintain homeostasis The transamination of lysine ...
Muscle Juice 2544 - Ultimate Nutrition
... also enhances muscle recovery after exercise and workouts. In it you get the most optimal source of amino acids (the major building blocks of muscle); critical for the repair and growth of muscle tissue. Whey protein boosts immune function by increasing levels of glutathione (the most potent antioxi ...
... also enhances muscle recovery after exercise and workouts. In it you get the most optimal source of amino acids (the major building blocks of muscle); critical for the repair and growth of muscle tissue. Whey protein boosts immune function by increasing levels of glutathione (the most potent antioxi ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.