biochem 47 A [3-20
... a. Citrate, which diffuses out slightly from the mitochondria i. malonyl CoA increases, signaling CPT-1 to reduce FA oxidation 16. What are 3 situations in which anaerobic glycolysis is especially important to produce ATP in exercise? a. At onset of exercise because phosphocreatine and stored ATP ca ...
... a. Citrate, which diffuses out slightly from the mitochondria i. malonyl CoA increases, signaling CPT-1 to reduce FA oxidation 16. What are 3 situations in which anaerobic glycolysis is especially important to produce ATP in exercise? a. At onset of exercise because phosphocreatine and stored ATP ca ...
Practice Biochem Test
... carbon atoms. e. They are one of several factors that contribute to heart disease. ____ 16. A molecule with the formula C18H54O2 is probably a a. carbohydrate. b. fatty acid. c. protein. d. glycerol e. hydrocarbon. ____ 17. Which of the following statements is false for the class of biological molec ...
... carbon atoms. e. They are one of several factors that contribute to heart disease. ____ 16. A molecule with the formula C18H54O2 is probably a a. carbohydrate. b. fatty acid. c. protein. d. glycerol e. hydrocarbon. ____ 17. Which of the following statements is false for the class of biological molec ...
- Wiley Online Library
... cells (LRCs) and non-LRCs, with the LRC population expressing higher levels of Pax7 and markers of quiescence, and lower levels of Myf5. Finally, in transplantation experiments, the LRC population of SCs showed a greater propensity for self-renewal, providing support for the LRC population containin ...
... cells (LRCs) and non-LRCs, with the LRC population expressing higher levels of Pax7 and markers of quiescence, and lower levels of Myf5. Finally, in transplantation experiments, the LRC population of SCs showed a greater propensity for self-renewal, providing support for the LRC population containin ...
Macromolecule Virtual Lab
... f. A saturated fatty acid has maximum number of _______________ atoms in its chain. g. A molecule of fat has ____(#) fatty acid chains and a phospholipid has ____(#) fatty acid chains. h. How can the main structural backbone of all steroids be described? I. Amino acids are bonded together in differe ...
... f. A saturated fatty acid has maximum number of _______________ atoms in its chain. g. A molecule of fat has ____(#) fatty acid chains and a phospholipid has ____(#) fatty acid chains. h. How can the main structural backbone of all steroids be described? I. Amino acids are bonded together in differe ...
ergogenic aids: boon or bane to mankind?
... Performance-enhancing substances have been used for thousands of years in traditional medicine by societies around the world, with the aim of promoting vitality and strength. Term ‘Ergogenics’ is derived from Greek word - ergon (tending to increase work power).Ergogenic aids means any potential mean ...
... Performance-enhancing substances have been used for thousands of years in traditional medicine by societies around the world, with the aim of promoting vitality and strength. Term ‘Ergogenics’ is derived from Greek word - ergon (tending to increase work power).Ergogenic aids means any potential mean ...
Membrane Lipid Integrity Relies on a Threshold of ATP Production
... instance, changes in membrane lipids have mostly been studied during aging, and have been related to overall lipid unsaturation, lipid degradation, and peroxidation processes (Knowles and Knowles, 1989; Spychalla and Desborough, 1990a, 1990b; Kumar and Knowles, 1993; Dipierro and De Leonardis, 1997) ...
... instance, changes in membrane lipids have mostly been studied during aging, and have been related to overall lipid unsaturation, lipid degradation, and peroxidation processes (Knowles and Knowles, 1989; Spychalla and Desborough, 1990a, 1990b; Kumar and Knowles, 1993; Dipierro and De Leonardis, 1997) ...
The Implausibility of Metabolic Cycles on the
... could be diverted to side products, some or all of which might find use at a later stage of chemical evolution. The cycle could not survive if side reactions funneled off more than half of the cycle components irreversibly, because then the concentration of the cycle components would decline exponent ...
... could be diverted to side products, some or all of which might find use at a later stage of chemical evolution. The cycle could not survive if side reactions funneled off more than half of the cycle components irreversibly, because then the concentration of the cycle components would decline exponent ...
Royal Jelly - Centerchem
... microbial attacks, such like skin, intestines and lungs. Up to date, about 500 AMPs from different organisms including humans, plants, invertebrates, amphibians, fishes and microorganisms, have been described (Montaño Pérez, K. & Vargas Albores, F., 2002). AMPs produce their antimicrobial action th ...
... microbial attacks, such like skin, intestines and lungs. Up to date, about 500 AMPs from different organisms including humans, plants, invertebrates, amphibians, fishes and microorganisms, have been described (Montaño Pérez, K. & Vargas Albores, F., 2002). AMPs produce their antimicrobial action th ...
Lecture 15, Feb 26
... A polypeptide chain that is folded into its normal, functional conformation is said to be in its native conformation. A polypeptide that is folded improperly so that it cannot function is said to be to be denatured or in a denatured conformation. ...
... A polypeptide chain that is folded into its normal, functional conformation is said to be in its native conformation. A polypeptide that is folded improperly so that it cannot function is said to be to be denatured or in a denatured conformation. ...
Italian Gelato (artisan ice cream) Gelato is a natural
... • Minerals (needs for natural elements): helps nutrients do their jobs. • Vitamins (vitamin needs): necessary for making best use of nutrients in food. Gelato contains all these elements, essential for complete nutrition. Just think about the significant presence of milk in gelato, milk being the on ...
... • Minerals (needs for natural elements): helps nutrients do their jobs. • Vitamins (vitamin needs): necessary for making best use of nutrients in food. Gelato contains all these elements, essential for complete nutrition. Just think about the significant presence of milk in gelato, milk being the on ...
Inborn errors of metabolism
... 9. Hepatic failure 10. Metabolic acidosis 11. Ketosis 12. Hypoglycemia 13. Hyperlactacidemia 14. Hyperammonemia ...
... 9. Hepatic failure 10. Metabolic acidosis 11. Ketosis 12. Hypoglycemia 13. Hyperlactacidemia 14. Hyperammonemia ...
1 Enzymes – Enzyme Mechanism
... trough between the two transition states • Lifetime > ~10-14 to 10-13 sec ...
... trough between the two transition states • Lifetime > ~10-14 to 10-13 sec ...
Enzymes – Enzyme Mechanism
... • Enzymes properly position substrates for reaction (makes the formation of the transition state more frequent and lowers the energy of activation) (2) Transition state binding • Transition states are bound more tightly than substrates (this also lowers the activation energy) ...
... • Enzymes properly position substrates for reaction (makes the formation of the transition state more frequent and lowers the energy of activation) (2) Transition state binding • Transition states are bound more tightly than substrates (this also lowers the activation energy) ...
Homology among (βα) 8 Barrels: Implications for the Evolution of
... aldolase (Mavridis et al., 1982), and shows signi®cant sequence similarity to other phosphate-binding TIM barrels (Figure 1). Comparison of known structures shows that the Schiff base-forming catalytic lysine residue is found in an exactly equivalent position in type I fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldo ...
... aldolase (Mavridis et al., 1982), and shows signi®cant sequence similarity to other phosphate-binding TIM barrels (Figure 1). Comparison of known structures shows that the Schiff base-forming catalytic lysine residue is found in an exactly equivalent position in type I fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldo ...
15 N- 1 H HSQC spectra as
... One reason for this dispersion is that the side chains of the 20 amino acids are different, and these differences will have some effect on the Ha shift. The table at right shows “typical” values observed for different protons in the 20 amino acids. These were measured in unstructured peptides to mim ...
... One reason for this dispersion is that the side chains of the 20 amino acids are different, and these differences will have some effect on the Ha shift. The table at right shows “typical” values observed for different protons in the 20 amino acids. These were measured in unstructured peptides to mim ...
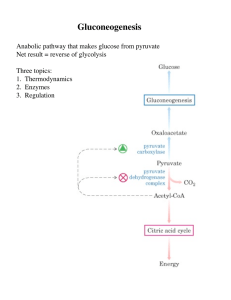
Gluconeogenesis - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... Glucagon (liver, via F 2,6-BP): -lysis OFF, -genesis ON Insulin (muscle, fat): increases [glc] and thus -lysis ON, -genesis OFF ...
... Glucagon (liver, via F 2,6-BP): -lysis OFF, -genesis ON Insulin (muscle, fat): increases [glc] and thus -lysis ON, -genesis OFF ...
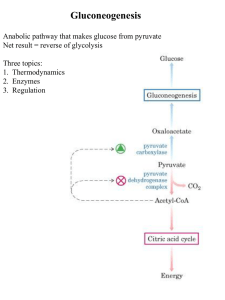
No Slide Title
... Glucagon (liver, via F 2,6-BP): -lysis OFF, -genesis ON Insulin (muscle, fat): increases [glc] and thus -lysis ON, -genesis OFF ...
... Glucagon (liver, via F 2,6-BP): -lysis OFF, -genesis ON Insulin (muscle, fat): increases [glc] and thus -lysis ON, -genesis OFF ...
Sample questions from old exam I BCHS 3304 – Dr. Yeo T
... BCHS 3304 – Dr. Yeo I. True or False (#1 to 5)? ...
... BCHS 3304 – Dr. Yeo I. True or False (#1 to 5)? ...
Tertiary structure
... polypeptide chain is called a "subunit." The way these chains fit together or associate with one another is referred to as the "quaternary structure." • The quarternary structure of the protein refers to the way multiple subunits of a protein interact. This is the arrangement of the individual subun ...
... polypeptide chain is called a "subunit." The way these chains fit together or associate with one another is referred to as the "quaternary structure." • The quarternary structure of the protein refers to the way multiple subunits of a protein interact. This is the arrangement of the individual subun ...
Origins and Evolution of Pathways of Anaerobic Metabolism in the
... SYNOPSIS. Energetic characteristics and functional roles define two main types of anaerobic pathways in the animal kingdom: high efficiency/low rates of energy production pathways geared to anoxia survival (aspartate-succinate and glucose-succinate pathways), and low efficiency/high rates of energy ...
... SYNOPSIS. Energetic characteristics and functional roles define two main types of anaerobic pathways in the animal kingdom: high efficiency/low rates of energy production pathways geared to anoxia survival (aspartate-succinate and glucose-succinate pathways), and low efficiency/high rates of energy ...
Pyropheophytin a accompanies pheophytin a in darkened light
... Agmatine Ureo: Hydrolase Location of Several Enzymes of L-Arginine Catabolism in E v e r n i a p r u n a s t r i Thallus (N) . . . Ajuga Iridoids in Some Teucrium and A j u g a Species . Alanine: Aldehyde Aminotransferase Properties and Subcellular Localization of L-Alanine: Aldehyde Aminotransferas ...
... Agmatine Ureo: Hydrolase Location of Several Enzymes of L-Arginine Catabolism in E v e r n i a p r u n a s t r i Thallus (N) . . . Ajuga Iridoids in Some Teucrium and A j u g a Species . Alanine: Aldehyde Aminotransferase Properties and Subcellular Localization of L-Alanine: Aldehyde Aminotransferas ...
A macrokinetic and regulator model for myeloma cell culture based
... However, it is found that the real glucose uptake rate is much lower than rglc,M at the beginning of cultivation, even though the glucose concentration is the highest. Such discrepancy exists for most Monod type models because the Monod model does not take the induction of the enzyme pool involved i ...
... However, it is found that the real glucose uptake rate is much lower than rglc,M at the beginning of cultivation, even though the glucose concentration is the highest. Such discrepancy exists for most Monod type models because the Monod model does not take the induction of the enzyme pool involved i ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.