Chapter 6 - Mr. Hilbert`s History Class
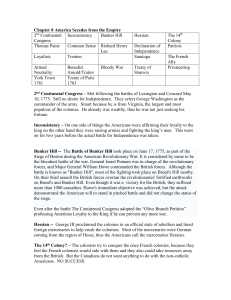
... Austrian Succession and came to be called King George’s War in America. – France allied itself with Spain, but England’s troops captured the reputed impregnable fortress of Cape Breton Island (Fort Louisbourg) in 1748. – However, peace terms of this war gave strategically located Louisbourg, which t ...
... Austrian Succession and came to be called King George’s War in America. – France allied itself with Spain, but England’s troops captured the reputed impregnable fortress of Cape Breton Island (Fort Louisbourg) in 1748. – However, peace terms of this war gave strategically located Louisbourg, which t ...
02.III Northern Explorations and Encounters | WHAT DIFFERENCES
... coastal North American waters of the North Atlantic. The Grand Banks, off the coast of Newfoundland, had abundant cod. It is possible that European fishermen were working those waters before Columbus’s voyages. Certainly by 1500, hundreds of ships and thousands of sailors were sailing annually to th ...
... coastal North American waters of the North Atlantic. The Grand Banks, off the coast of Newfoundland, had abundant cod. It is possible that European fishermen were working those waters before Columbus’s voyages. Certainly by 1500, hundreds of ships and thousands of sailors were sailing annually to th ...
document
... Identify the first main threat to the British colonies-French quest for empire-and the four wars that resulted Recall major leaders and battles of the French and Indian War Outline the causes, course, and consequences of the French and Indian War Discuss the British victory over the French at the Ba ...
... Identify the first main threat to the British colonies-French quest for empire-and the four wars that resulted Recall major leaders and battles of the French and Indian War Outline the causes, course, and consequences of the French and Indian War Discuss the British victory over the French at the Ba ...
CHAPTER 1: BEGINNINGS TO 1763
... world wars for mastery of the N. American Continent take place ...
... world wars for mastery of the N. American Continent take place ...
Unit 1: Chapters 1 and 2 European Expansion
... • King Henry VIII established the Protestant Church of England. • “Bloody Mary” murdered hundreds of Protestants. • ________________encouraged supporters to subdue Irish Catholics to prevent any invasion efforts by Spain. – Brutal, vicious invasion led to conquest of Ireland, setting English pattern ...
... • King Henry VIII established the Protestant Church of England. • “Bloody Mary” murdered hundreds of Protestants. • ________________encouraged supporters to subdue Irish Catholics to prevent any invasion efforts by Spain. – Brutal, vicious invasion led to conquest of Ireland, setting English pattern ...
European Exploration and Settlement
... Eventually the Dutch settlement in Manhattan swelled to over 1,000 people. In 1647, the Dutch West India Company hired Peter Stuyvesant as the colony’s new Governor. He held the position for 17 years. When he arrived, he declared that the settlement would be called New Amsterdam, after the capital c ...
... Eventually the Dutch settlement in Manhattan swelled to over 1,000 people. In 1647, the Dutch West India Company hired Peter Stuyvesant as the colony’s new Governor. He held the position for 17 years. When he arrived, he declared that the settlement would be called New Amsterdam, after the capital c ...
Causes of the American Revolution
... the colonies without paying any of the navigation taxes that were imposed on colonial merchants ● With this, the British company would be underselling the American companies in effect ...
... the colonies without paying any of the navigation taxes that were imposed on colonial merchants ● With this, the British company would be underselling the American companies in effect ...
Exploration and Expansion Section 2
... French, Dutch, and English Colonies in the Americas -Silver and gold from American colonies began to circulate in Europe -Leaders in France, England, and the Netherlands decided that they needed to establish colonies in the Americas. New France • French explorers established colonies in New France o ...
... French, Dutch, and English Colonies in the Americas -Silver and gold from American colonies began to circulate in Europe -Leaders in France, England, and the Netherlands decided that they needed to establish colonies in the Americas. New France • French explorers established colonies in New France o ...
Presentation
... Effects of the War on Americans? ■The 1760s were an affluent & optimistic “post-war” period: –The French & Indian War united the colonists against a common enemy for the 1st time –Most colonists considered themselves proud members of England’s empire with little (if any) thought of independence ...
... Effects of the War on Americans? ■The 1760s were an affluent & optimistic “post-war” period: –The French & Indian War united the colonists against a common enemy for the 1st time –Most colonists considered themselves proud members of England’s empire with little (if any) thought of independence ...
File - Mr. Dunn`s History Class
... make some money and get even. His plan was discovered. Bloody War – The year 1777 was known as the Bloody year on the Frontier. Both sides had Natives as allies. Mohawk chief Joseph Brant thought a victorious Britain would stop American expansion. Brant and the British attacked the back country area ...
... make some money and get even. His plan was discovered. Bloody War – The year 1777 was known as the Bloody year on the Frontier. Both sides had Natives as allies. Mohawk chief Joseph Brant thought a victorious Britain would stop American expansion. Brant and the British attacked the back country area ...
Monday - Munising Public Schools
... Spain and Portugal disagree over who owns Americas Treaty of Tordesillas Pope Portugal gets Brazil and Spain gets the rest Aztecs and Incas overtaken and enslaved, died, and looted English Henry VII sponsor Italian Cabot N.E. North America 90 years later sponsor a colony Netherlands, Britain and Fra ...
... Spain and Portugal disagree over who owns Americas Treaty of Tordesillas Pope Portugal gets Brazil and Spain gets the rest Aztecs and Incas overtaken and enslaved, died, and looted English Henry VII sponsor Italian Cabot N.E. North America 90 years later sponsor a colony Netherlands, Britain and Fra ...
Chapter Themes
... “I have chosen a life more suited to my solitary disposition, which nevertheless does not make me harsh to my people; though joined to a life among savages, it makes me, perhaps, less polished and compliant than the atmosphere of Paris requires.” (Letter to France, 1683) Robert La Salle (1643–1687) ...
... “I have chosen a life more suited to my solitary disposition, which nevertheless does not make me harsh to my people; though joined to a life among savages, it makes me, perhaps, less polished and compliant than the atmosphere of Paris requires.” (Letter to France, 1683) Robert La Salle (1643–1687) ...
File
... Spain & Portugal: ATTITUDE At first, they just wanted to find gold. Later, they began to establish settlements in order to exploit the natural resources of the “New World.” ...
... Spain & Portugal: ATTITUDE At first, they just wanted to find gold. Later, they began to establish settlements in order to exploit the natural resources of the “New World.” ...
Presentation Plus!
... They had strong alliances with the Native Americans. This allowed them to control land from the St. Lawrence River in Canada south to New Orleans. The British colonists had little help from Britain in fighting the French. ...
... They had strong alliances with the Native Americans. This allowed them to control land from the St. Lawrence River in Canada south to New Orleans. The British colonists had little help from Britain in fighting the French. ...
Present - Images
... religious tolerance By 1643 the Great Migration had begun and there were 16,000 colonist in Massachusetts. John Winthrop and others saw it as a opportunity to create a pure society . . . a “city on a hill” . . . that would be an example to the world. ...
... religious tolerance By 1643 the Great Migration had begun and there were 16,000 colonist in Massachusetts. John Winthrop and others saw it as a opportunity to create a pure society . . . a “city on a hill” . . . that would be an example to the world. ...
APUSH Chapter 6 Study guide
... 3. Compare French relations with the Indians to British and Spanish relations. Why did most Indians support France against Britain? 4. If France instead of Britain had won the “duel for North America,” would the thirteen colonies ever have become independent of Britain, or would they have been forc ...
... 3. Compare French relations with the Indians to British and Spanish relations. Why did most Indians support France against Britain? 4. If France instead of Britain had won the “duel for North America,” would the thirteen colonies ever have become independent of Britain, or would they have been forc ...
Settlement Timeline
... English explorers also sailed along the coast of North America, claiming these lands for the ______________________. – They would later establish permanent settlements along the eastern coast naming them _______________ and __________________. ...
... English explorers also sailed along the coast of North America, claiming these lands for the ______________________. – They would later establish permanent settlements along the eastern coast naming them _______________ and __________________. ...
chapter3
... political society Independence influenced military affairs as few felt compelled to serve unless it was in their own interests ...
... political society Independence influenced military affairs as few felt compelled to serve unless it was in their own interests ...
The French-Indian War
... Braddock and his 1500 men were confident they could take the fort, but they were ambushed outside the gates by French soldiers and their Native American allies. During the battle, Braddock and his staff were killed with the exception of Washington. The British defeat at Fort Duquesne was only ...
... Braddock and his 1500 men were confident they could take the fort, but they were ambushed outside the gates by French soldiers and their Native American allies. During the battle, Braddock and his staff were killed with the exception of Washington. The British defeat at Fort Duquesne was only ...
French and Indian War
... • Germany (Prussia), Fredrick the Great won his title of “Great” by repelling French, Austrian, and Russian armies(was outnumbered) • Americans sought for the colonies to unite (strength in numbers) • 1754, 7 of the 13 colonies met for an inter-colonial congress held in Albany, New York, known as Al ...
... • Germany (Prussia), Fredrick the Great won his title of “Great” by repelling French, Austrian, and Russian armies(was outnumbered) • Americans sought for the colonies to unite (strength in numbers) • 1754, 7 of the 13 colonies met for an inter-colonial congress held in Albany, New York, known as Al ...
From Comfort to Discontent
... How were the colonists forced to help pay for war costs and troops? 1.THE SUGAR ACT OF 1764: taxed imported sugar and molasses; $ goes to England 2. QUARTERING ACT OF 1765: The troops sent to enforce the Proclamation of 1763 would now be supported by the colonists; the act forced colonies to provid ...
... How were the colonists forced to help pay for war costs and troops? 1.THE SUGAR ACT OF 1764: taxed imported sugar and molasses; $ goes to England 2. QUARTERING ACT OF 1765: The troops sent to enforce the Proclamation of 1763 would now be supported by the colonists; the act forced colonies to provid ...
The Albany Plan of Union - Grade-8-Social
... The Albany Plan of Union When tensions between the French and English were heating up before the French and Indian War started, representatives from several colonies met in Albany, New York, to discuss a plan about how to handle the French. ...
... The Albany Plan of Union When tensions between the French and English were heating up before the French and Indian War started, representatives from several colonies met in Albany, New York, to discuss a plan about how to handle the French. ...
Student Study Guide for the American Pageant
... though thinly settled empire economically based on the fur trade. During much of the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, Britain and France engaged in a bitter power struggle that frequently erupted into worldwide wars. In North America these wars constituted an extended military duel for imperial ...
... though thinly settled empire economically based on the fur trade. During much of the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, Britain and France engaged in a bitter power struggle that frequently erupted into worldwide wars. In North America these wars constituted an extended military duel for imperial ...
Queen Anne's War
Queen Anne's War (1702–1713), as the North American theater of the War of the Spanish Succession was known in the British colonies, was the second in a series of French and Indian Wars fought between France and England, later Great Britain, in North America for control of the continent. The War of the Spanish Succession was primarily fought in Europe. In addition to the two main combatants, the war also involved numerous Native American tribes allied with each nation, and Spain, which was allied with France. It was also known as the Third Indian War or in French as the Second Intercontinental War.The war was fought on three fronts: Spanish Florida and the English Province of Carolina were each subjected to attacks from the other, and the English engaged the French based at Mobile in what was essentially a proxy war involving primarily allied Native Americans on both sides. The southern war, although it did not result in significant territorial changes, had the effect of nearly wiping out the Native population of Spanish Florida, including parts of present-day southern Georgia, and destroying Spain's network of missions in the area. The English colonies of New England fought with French and Native American forces based in Acadia and Canada. Quebec City was repeatedly targeted (but never successfully reached) by British expeditions, and the Acadian capital Port Royal was taken in 1710. The French and Wabanaki Confederacy sought to thwart New England expansion into Acadia, whose border New France defined as the Kennebec River in southern Maine. Toward this end, they executed raids against targets in Massachusetts (including present-day Maine), most famously raiding Deerfield in 1704. On Newfoundland, English colonists based at St. John's disputed control of the island with the French based at Plaisance. Most of the conflict consisted of economically destructive raids against the other side's settlements. The French successfully captured St. John's in 1709, but the British quickly reoccupied it after the French abandoned it.Following a preliminary peace in 1712, the Treaty of Utrecht ended the war in 1713. It resulted in the French cession of claims to the territories of Hudson Bay, Acadia, and Newfoundland to Britain, while retaining Cape Breton and other islands in the Gulf of St. Lawrence. Some of its terms were ambiguous, and concerns of various Native American tribes were not included in the treaty, setting the stage for future conflicts.