* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHAPTER 1: BEGINNINGS TO 1763
Province of New York wikipedia , lookup
History of Jamestown, Virginia (1607–99) wikipedia , lookup
Dominion of New England wikipedia , lookup
Colonial period of South Carolina wikipedia , lookup
Province of Massachusetts Bay wikipedia , lookup
Slavery in Canada (New France) wikipedia , lookup
Shipbuilding in the American colonies wikipedia , lookup
Jamestown supply missions wikipedia , lookup
English overseas possessions in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms wikipedia , lookup
Peace of Paris (1783) wikipedia , lookup
Queen Anne's War wikipedia , lookup
Cuisine of the Thirteen Colonies wikipedia , lookup
Thirteen Colonies wikipedia , lookup
Slavery in the colonial United States wikipedia , lookup
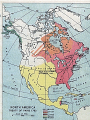
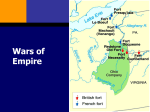
CHAPTER 1,2, and 3: BEGINNINGS TO 1763 EXPLORATION & THE COLONIAL ERA THE AMERICAS, WEST AFRICA, AND EUROPE – 3 Worlds Meet Chapter 1 ► ► ► ► ► Ancient Cultures arrived about 22,000 years ago via a land bridge Earliest settlers were hunters Agriculture thrived starting about 5,000 years ago Some Natives remained Nomadic Maya, Aztec, and Inca societies flourished NATIVE AMERICAS IN 1400S ► Native American societies in North America were as varied as the geography ► Most of the tribes in America had common religious views, trade patterns & values WEST AFRICAN SOCIETIES OF THE 1400S ► ► ► ► Long established, sophisticated societies existed in Western Africa The Kingdom of Songhai controlled trans-Sahara trade Kingdom of Benin and Congo were two famous dynasties Village and family bonds formed the basis of life EUROPEAN SOCIETIES OF THE 1400S ► European villages had a long tradition of social hierarchy – complete with nobles, merchants & peasants ► Christianity played a critical role – religious leaders had power ► The Reformation in the early 1500s led to a split in the church Martin Luther EUROPEAN EXPLORATION ► The countries of Portugal, Spain, France and England explored in the late 1400s for God, Gold, and Glory ► Improved mapmaking, better sailboats, compasses, astrolabes, Prince Henry– all led to better exploration SPANISH NORTH AMERICA – Chapter 2 Columbus crosses the Atlantic in October of 1492 and lands in San Salvador (“Holy Savior”) ► He spent about 3 months exploring Islands in the Bahamas ► Europeans used advanced weapons to force locals into labor: Plantation System ► Disease devastated Native population ► IMPACT OF COLUMBUS On Africans- Before slave trade ended in the 1800s, 10 million Africans taken On Europeans- Biggest voluntary migration in world history On Trade- Columbian Exchange meant new goods & products flowed between continents The Columbian Biological Exchange Old World to New World: Diseases: Smallpox Measles Chicken Pox Malaria Yellow Fever Influenza The Common Cold New World to Old World: Syphilis The Columbian Biological Exchange Animals: Old World to New World: Horses Cattle Pigs Sheep Goats Chickens New World to Old World: Turkeys Llamas Alpacas Guinea Pigs The Columbian Biological Exchange Old World to New World: Plants: Rice Wheat Barley Oats Coffee Sugarcane Bananas Melons Olives Dandelions Daisies Clover Ragweed Kentucky Bluegrass New World to Old World: Corn (Maize) Potatoes (White & Sweet Varieties) Beans (Snap, Kidney, & Lima Varieties) Tobacco Peanuts Squash Peppers Tomatoes Pumpkins Pineapples Cacao (Source of Chocolate) Chicle (Source of Chewing Gum) Papayas Manioc (Tapioca) Guavas Avocados SPAIN CLAIMS A NEW EMPIRE ► ► ► ► Spanish explorers (Conquistadors) seized much of the Americas Cortes conquered the Aztecs in Mexico Pizzaro conquered the Incas in Peru Exploitation of local populations was significant – Encomienda System SPAIN EXPLORES SOUTHWEST AND WESTERN AMERICA ► ► ► ► California Missions Mid-1500s, Spain explored much of what is today the SW & West of the USA New Mexico settled by Spanish priest who converted Natives (Pueblos) What we now call Texas area had 30 expeditions in 16th century What we call the state of California was site of numerous missions EARLY BRITISH COLONIES – Chapter 2 Section 2 ► ► ► ► Beginning in the early 1600s, the English established colonies along the eastern coast of North America 1607: Jamestown was first to be settled John Smith led this group of settlers Colony struggled at first, then was saved by Tobacco crop England has “Surplus Population” Virginia Joint Stock Company of London receives charter from King James - Gold ? Passage to the Indies? Wanted to get rich quick >>>>Long Term???? Charter= “overseas settlers guaranteed same rights as home” Chesapeake bay May 24, 1607 - 100 English Settle “Jamestown” - disease - malnutrition - starvation Had to eat… - dogs, cats, rats,mice - one man ate his wife By 1625 1,200 survivors of 8,000 Jamestown Virginia saved by John Smith Don’t eat = don’t work 1608 Before “in charge” of Jamestown… Captured by Indian Chief Powhatan ► Powhatan’s daughter Pocahontas saves him (puts her head between the clubs about to beat him) ► Creates Symbolism for peaceful relations Peaceful Relations? ► Anglo-Powhatan War I (1610) John Rolfe and Pocahontas marriage marks the end of Anglo-Powhatan War I ► Anglo-Powhatan War II (1644) Banished Chesapeake Indians from ancestral lands Separates Indian/White areas ►Origins of reservation system Natives Becoming Extinct? Disease Disorganization Disposability King Nicotine “King Nicotine” was hard on soil Tobacco was “labor intensive” To farm it you needed fresh labor Creates the plantation system Fresh labor; Mostly white indentured servants working for a specific time period earning their freedom First African slaves 1619 (about 20) Another Notable 1st for Virginia ► Representative Self Government was born in Virginia in 1619 ► The Joint stockholders authorized the settlers to summon an assembly ► Known as the Houses of Burgesses ► A momentous precedent is established ► The 16th century Reformation caused a split in the Christian Church; Catholics and Protestants ► Some extreme Protestant reformers – sought to cleanse their religion and Separate from the church and left England Mayflower 1620 ► ► ► ► ½ not members (but looking for opportunity) They were Separatists Set up in Plymouth Mayflower Compact Agreement to form Gov. Signed by who? ► Protected by God? ► Fur Fish Lumber Bible William Bradford- Governor 30 times! Massachusetts Bay Colony ► Another group arrives in 1629 but they are ► Non-Separatist Puritans They officially said they did not want to Separate Church of England…only it’s impurities ► 1630’s Great Migration 70,000 leave England 11,000 to Massachusetts ► John Winthrop it’s 1st Governor Skills and resources “Churched” Men ► “Visible Saints” were able to enforce “God’s law” ► Bible Commonwealth/religion called the shots ► Trouble in the Bible Commonwealth Anne Hutchinson ► 14 Children/Challenges Predestination ► “Antinomianism” Holy life didn’t = saved and saved don’t need to obey law of God or Man Banned/moved to NY/RI area and was eventually killed by “Indians” ► Pious John Winthrop saw “God’s Hand” New England New England Colonies by 1650 COLONISTS MEET RESISTANCE ► New England Colonists soon conflicted with the Native Americans over land & religion ► King Philip’s War was fought in 1675 between the Natives and New Englanders ending a year later with many dead and the Natives retreating Pilgrims and Indians ► Massasoit the Chief Squanto, Wampanoag, 1st Thanksgiving ► King Phillips War Slows English Settlement Massasoit’s son, Metacom, “called King Phillip” ►Formed alliances Population in Colonies SETTLING THE MIDDLE COLONIES ► Dominated by Dutch and Quaker settlers, the Middle Colonies were founded in the mid-1600s ► William Penn led Quakers as they colonized Pennsylvania and Delaware Pennsylvania William Penn’s Holy Experiment ► He Was a Quaker ► Deep Conviction =they shaked ► Quakers = religious society of Friends ► Penn = Quaker Advertises Treats Indians Well ► Non Quakers Immigrate too Civil and Religious Liberty Penn’s Treaty with the Native Americans Other Colonies Founded Maryland = Founded by Catholics Lord Baltimore Tobacco Indentured servants Toleration of all Christians Death to atheist/Jews Southern States The Carolina’s ► Carolina developed close economic ties to the West Indies. Many Carolinian settlers were originally from the West Indies. They used local Savannah Indians to enslave other Indians [ 1707 Savannah Indians decided to migrate to PA. PA promised better relations with whites. Rice: Crop of the Carolinas ► The primary export. ► Rice was still an exotic food in England. Was grown in Africa, so planters imported West African slaves. These slaves had a genetic trait that made them immune to malaria. ► By 1710 black slaves were a majority in Carolina. Georgia: The Last Colony ► Founded in 1733. ► Last of the 13 colonies. ► Named in honor of King George II. ► Great Founded by James Oglethorpe. ► Unhealthy Climate ► Spanish Attacks ENGLAND’S COLONIES PROSPER ► Throughout the 1600s and 1700s, more British Colonies were established ► There was a great deal of Salutary Neglect King George III MERCANTILISM: AN ECONOMIC SYSTEM IN WHICH NATIONS SEEK TO INCREASE THEIR WEALTH BY OBTAINING GOLD & SILVER AND WITH A FAVORABLE BALANCE OF TRADE MERCANTILISM NAVIGATION ACTS ► ► ► ► ► 1651- England’s Parliament passed a series of laws known as the Navigation Acts These laws restricted the colonies shipping & trade Ships, destinations, crews, goods: All strictly regulated by the English The colonies were developing a spirit of self-determination that England had encouraged with their Salutary Neglect Therefore, they were NOT happy with these restrictions THE COLONIES COME OF AGE – Chapter 3 ► ► ► New England, Middle Colonies, and the South – all developed distinct economies and societies In the South, rural Plantations with a single cash crop were common Small Southern farmers (Germans, Scots-Irish) and African slaves made up the majority of people Southern Plantation Though better than early Colonists; life was still very very hard ► In the Chesapeake (Virginia area) ► Nasty, Malaria, Cut 10 years of life off of newcomers ► 50% did not get to 20 ► Most perished after arrival ► Almost no one knew grandparents Virginia Tobacco ► Planted Tobacco before corn ► Enormous production = prices down ► More labor Indians died Africans cost too much English became indentured servants for a few years in exchange for land But what happens when land runs out? ► The Headright System paid for servants to get 50 acres of land ► Companies sometimes paid people to come to America just to get property ► Fortunes were made in real estate by business groups that worked together to buy large portions of land. Bacon’s Rebellion ► ► ► ► ► Landless Knockabouts Land scarcer which resulted in no land for “freemen” in deal Started by 29 year old planter, Nathaniel Bacon There were Indian attacks on frontier settlements Virginia’s Governor, William Berkeley “refused to retaliate” ► ► ► Bacon and followers murdered Indians, plundered and pilfered Bacon dies of disease Result = plantation owners search for less troublesome laborers Less Troublesome Labors=Slaves ► ► ► ► Most slaves arrived after 1700 because whites in England start earning better wages Enterprising Americans, especially from “the sewer” rush to cash in on the 1698 Royal African Company loss of slave monopoly without a Monopoly what happens to the price of a slave? West Coast of Africa Middle passage Slave vs. servant = early treated same Based on race ► “slave codes” Crime to teach reading or writing to slaves Racial discrimination a norm Molds the American Slave system THE MIDDLE PASSAGE ► During the 17th century, Africans endured a transatlantic crossing from Africa to the North American Colonies ► Cruelty characterized the months long journey – 13% died on route AFRICANS MAINTAIN PARTS OF THEIR CULTURE Despite enslavement, Africans coped with the horrors of slavery via music, dance, and storytelling ► Slaves also resisted their position of subservience by faking illness, breaking tools, or work slowdowns ► Others were more radical and tried escape & revolt ► Africans in America ► Deep south = severe ► Chesapeake = less severe/ grows on its own ► Gullah = Black slave language combining English/African ► Goober = peanut ► Voodoo = witchcraft ► Banjo and Bongo Southern Society ► Planters Then farmers Landless whites Indentured Black Slaves NORTHERN COLONIES COMMERCE THRIVES LIBERTY BELL ► ► ► The development of cities, expansion of trade, and diverse economies gradually made the North radically different from the South Philly was the 2nd largest British port Farming differed from the South: smaller, more diverse crops in North Northern Soil not as fertile ► Families Fertile ► 1 woman had 27 children But Women fear birthing Soil not as Fertile as the women THE ENLIGHTENMENT AND THE GREAT AWAKENING ► ► ► 1700s: An intellectual movement known as the Enlightenment began in Europe and a religious movement to fight it known as the Great Awakening started in the Colonies The Enlightenment emphasized reason, science, and observation and led to the discovery of natural laws Copernicus, Galileo, Franklin and Newton were key figures Original 13 or 32+ ► In actuality, Britain ruled thirty-two colonies in North America, including Canada, the Floridas, and various island in the Caribbean. The Melting Pot ► Dutch (German) ► Scots-Irish ► French Huguenots ► Jews ► Swedes ► Welsh ► Dutch ► Africans ► Salt and pepper Michel-Guillaume de Crevecoeur ► French Settler ► In a famous essay he writes ? “What is an American?” ► He knew we were different he says… “a strange mixture of blood, which you will find in no other country” Colonial Social Hierarchy 1775 RELIGIOUS REVIVAL: THE GREAT AWAKENING ► ► ► ► A series of religious revivals aimed at restoring religious devotion & piety swept through the colonies in the mid-1700s Jonathan Edwards was a Puritan priest from New England who was instrumental in the movement Fire & Brimstone style of worship; large, emotionally charged crowds Like the Enlightenment the movement stressed the importance of the individual When the Great Awakening Ends ► After 1750’s and up to the Revolution ► Clergy less influential ► Most people did not belong to an “established church” Anglican –grown out of the Church of England Congregational Church- grown out of Puritanism ► Lawyers no longer seen as “wind bags”… ► they may have some use in the coming decades Triangular Trade…becoming lopsided Leave New England with rum to Africa Barter liquor for slaves, sail to west Indies Exchange survivors for Molasses distilled into rum Trade Imbalance ► Colonies growing, England not Poorly enforced NAVIGATION ACTS ► Back in 1651- England’s Parliament passed a series of laws known as the Navigation Acts ► These laws restricted the colonies shipping & trade to only England ► Ships, destinations, crews, goods: All strictly regulated by the English ► But Colonial Merchants found that money could be made in other places (Smuggling) The Tavern ► The Cradle of Democracy ► Food, drink, entertainment ► Exchanged and debated political ideas ► “Complained about their developing situation” France finds a foothold in Canada ► France gets late colonial start due to Religious conflicts ► French Huguenots Vs. Catholics ► Edict of Nantes (1598) allowed official Huguenot toleration… France prospers ► 1608 Quebec settled by Samuel de Champlain ► Champlain helps Huron Indians fight their foes the Iroquois 3 Iroquois are killed…forever will they hate the French ► White “lightening Sticks” cause death. ► French penetration into Ohio Valley hampered by Iroquois who serve as allies to the British in the prolonged struggle for the continent New France ► Grows at a slow pace ► Even French peasants own land at home so why move? ► BUT THERE WAS ONE VALUABLE RESOURCE ► The Beaver Coureurs de bois ► “Runners of the woods” ► French fur trappers ► Voyageurs ► 2 fisted drinkers ► Free lovers ► Free spenders French Catholic Missionaries “The Jesuits” tried to “SAVE” the natives for Christ and From the Fur trappers ways They didn’t convert many…but they played a vital role as explorers and geographers Other Explorers ► Antoine Cadillac ► Founded Detroit (1701) ► “the city of straits” ► Robert de La Salle floated down the Mississippi and claimed “Louisiana” ► To honor the Sovereign Louis XIV A Clash Of Empires ► England ► France ► Spain ► 1688 to 1763 four world wars for mastery of the N. American Continent take place ► The first two: King Williams War Queen Anne’s War Pitted British Colonians Vs. French Coureurs de bois Neither Nations considered America worth committing “real” troops Spain allies with France ► English Colonials fail miserably … ► Except in large tracts around the Hudson Bay George Washington inaugurates war with France ► The Ohio country was also hotly contested The French erect forts in the area ► Virginia’s Governor sends Washington to survey Virginian’s claims on this 500,000 acres …French say it’s theirs ► He had 150 Virginia Militiamen ► Washington’s men fire first…start a new war ► The French soon surround Washington’s men in a hastily constructed “Fort Necessity” Global war ► George Washington’s Mishap touches off the ► Seven Years War ► or the French and Indian War ► It is fought in Europe, West Indies, the Philippines, Africa, and on the Ocean Join or Die ► In previous clashes Americans had showed an astonishing lack of unity ► Benjamin Franklin’s cartoon in the Pennsylvania Gazette stressed the need for a better joint effort amongst colonials ► A common defense ► Many agreed in spirit…but couldn’t iron out the details FRENCH AND INDIAN WAR ► Competition in North America led to a war (1754-1763) between old rivals France and England ► The French in North America were tradesmen (furs) not long-term inhabitants ► Ohio River valley was the site of the conflict FRENCH INDIAN WAR BY NAT YOUNGBLOOD General Edward Braddock ► Haughty and Bullheaded British General steeped in European Warfare… ► But this is not Europe … ► Opening Clashes of the French and Indian War were bad for English Colonials ► The French and Indians took it to the Colonials ► Braddock killed ► Geo Wash his aide had two horses shot out from under him BRITAIN DEFEATS AN OLD ENEMY ► ► ► ► ► WILLIAM PITT ON A COIN British then select William Pitt led by Pitt they eventually defeated the French Treaty of Paris ends the war in 1763 Brits claim most of North America including Florida (from French ally Spain) & Canada Native Americans also realized a French loss was a Native American loss Why the French and Indian War Matters to US ► Bolsters colonial self esteem ► Though they fought alongside British Military= they saw the British as regular men, sometimes fleeing into the wilderness instead of fighting ► Animosity also rises between arrogant English officers and the raw colonial amateurs ► Soldiers and statesmen shared a common language and ideals Pontiac’s Uprising ► Ottawa Chief led several tribes who had been loyal to the French in a brief but violent campaign to drive the British from the Ohio Valley ► Catching the Brits napping thousands of colonists die ► Whites retaliated… ► Killing Indians and moving into the Appalachians whites settle the area ► One British commander ordered blankets infected with smallpox to be distributed among the Indians PROCLAMATION LINE OF 1763 ► ► To avoid further costly conflicts with Native Americans, the British government prohibited colonists from settling west of the Appalachian Mountains The Proclamation established a line along the Appalachian that colonists could not cross (They did anyway) The Proclamation of 1763 ► Hastily drawn document that the London Government issued in order to prohibit settlement beyond the Appalachians ► It was geared to “protect” the colonials from another Pontiac like uprising… ► However the colonists see the land beyond the Mountains as their birthright ► The Colonists now had a new vision in their destiny