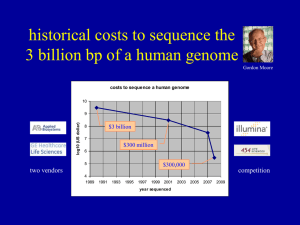
lecture28_Sequencing.. - University of Alberta
... Viral and bacterial cultures; polymerase-chain-reaction assays for known pathogens; viral and ...
... Viral and bacterial cultures; polymerase-chain-reaction assays for known pathogens; viral and ...
Rapid Evolution in the Human Genome
... lineage-specific evolution: a phylogenetic hidden Markov model (phylo-HMM) and a likelihood ratio test (LRT). The phylo-HMM works well for identifying relatively ancient events, while the LRT is much more powerful at the leaves of a phylogeny (e.g. the human lineage). Using this LRT, we identified 2 ...
... lineage-specific evolution: a phylogenetic hidden Markov model (phylo-HMM) and a likelihood ratio test (LRT). The phylo-HMM works well for identifying relatively ancient events, while the LRT is much more powerful at the leaves of a phylogeny (e.g. the human lineage). Using this LRT, we identified 2 ...
2nd problem set
... a) After a genome is sequenced, you know exactly how many genes it contains. b) Genome sequencing requires the artificial synthesis of DNA (synthesis outside of a cell). c) The sequence of a genome tells you the exact sequence of nucleotides for all members of that species. d) Comparing the genomes ...
... a) After a genome is sequenced, you know exactly how many genes it contains. b) Genome sequencing requires the artificial synthesis of DNA (synthesis outside of a cell). c) The sequence of a genome tells you the exact sequence of nucleotides for all members of that species. d) Comparing the genomes ...
Human genome
... Genes encode noncoding RNA or proteins Repeat sequences are > 50% of genome Distinct types of gene organization Combinatorial strategies amplify genetic information and increase diversity Evolution by lateral transfer of genes from one organism to another Males have twofold higher mutation rate than ...
... Genes encode noncoding RNA or proteins Repeat sequences are > 50% of genome Distinct types of gene organization Combinatorial strategies amplify genetic information and increase diversity Evolution by lateral transfer of genes from one organism to another Males have twofold higher mutation rate than ...
Genome Sequencing Machine Learning for Big Data Seminar by Guided by
... The human genome has a surprising tendency to grow, shrink or otherwise rearrange itself. This so-called structural variation is the cause of 'genomic disorders' but also provides the raw material needed by evolution. But in finding out more about how genomic rearrangements occur, scientists are ...
... The human genome has a surprising tendency to grow, shrink or otherwise rearrange itself. This so-called structural variation is the cause of 'genomic disorders' but also provides the raw material needed by evolution. But in finding out more about how genomic rearrangements occur, scientists are ...
A method for paralogy trees reconstruction
... Genes belonging to the same organism are called paralogs when they show a significant similarity in the sequences, even if they have a different biological function. It is an emergent biological paradigm that the families of paralogs derive from a mechanism of gene duplication with modification, rep ...
... Genes belonging to the same organism are called paralogs when they show a significant similarity in the sequences, even if they have a different biological function. It is an emergent biological paradigm that the families of paralogs derive from a mechanism of gene duplication with modification, rep ...
Evolution
... The genes themselves do not change or blend during reproduction If chromosomes and loci of the male and female do not match perfectly, reproduction cannot occur (prevents interbreeding) Offspring will resemble parents because genes must match at each locus, but the offspring will differ from both pa ...
... The genes themselves do not change or blend during reproduction If chromosomes and loci of the male and female do not match perfectly, reproduction cannot occur (prevents interbreeding) Offspring will resemble parents because genes must match at each locus, but the offspring will differ from both pa ...
Genetics - Bill Nye ANSWERS
... Hershey and Chase studied bacteriophage viruses and found that genetic material is located in nucleus and not cytoplasm. DNA is composed of 4 bases. What are they? Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine DNA is a double helix. DNA bases are held together by hydrogen bonds. DNA is responsible for making ...
... Hershey and Chase studied bacteriophage viruses and found that genetic material is located in nucleus and not cytoplasm. DNA is composed of 4 bases. What are they? Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine DNA is a double helix. DNA bases are held together by hydrogen bonds. DNA is responsible for making ...
Document
... having evolved one from another through gene duplication. Paralogs are separated by a gene duplication event. • Each specific gene family member (e.g. a specific gene in human) is an ortholog of the same family member in another species (e.g. mouse). Both evolved from an ancestral globin gene. Ortho ...
... having evolved one from another through gene duplication. Paralogs are separated by a gene duplication event. • Each specific gene family member (e.g. a specific gene in human) is an ortholog of the same family member in another species (e.g. mouse). Both evolved from an ancestral globin gene. Ortho ...
7 Self study questions
... 1. Explain why ORF scanning is a feasible way of identifying genes in a prokaryotic DNA sequence. 2. What modifications are introduced when ORF scanning is applied to a eukaryotic DNA sequence? 3. Describe how homology searching is used to locate genes in a DNA sequence and to assign possible functi ...
... 1. Explain why ORF scanning is a feasible way of identifying genes in a prokaryotic DNA sequence. 2. What modifications are introduced when ORF scanning is applied to a eukaryotic DNA sequence? 3. Describe how homology searching is used to locate genes in a DNA sequence and to assign possible functi ...
PPT Version - OMICS International
... in the last 23 years. Currently, he is a Professor of Pathology and Director of High Throughput Genome Center at University of Pittsburgh. • In the last 13 years, Dr. Luo has been largely focusing on genetic and molecular mechanism of human prostate and hepatocellular carcinomas. In this period, his ...
... in the last 23 years. Currently, he is a Professor of Pathology and Director of High Throughput Genome Center at University of Pittsburgh. • In the last 13 years, Dr. Luo has been largely focusing on genetic and molecular mechanism of human prostate and hepatocellular carcinomas. In this period, his ...
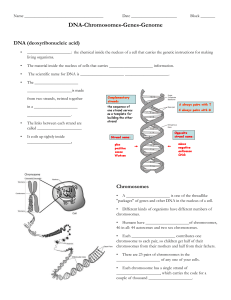
DNA-Chromosomes-Genes-Genome student notesheet
... chromosomes from their mothers and half from their fathers. • There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in the _____________________ of any one of your cells. • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
... chromosomes from their mothers and half from their fathers. • There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in the _____________________ of any one of your cells. • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
Higher Biology Unit 1: DNA and the Genome 5
... of DNA found in two species differs by four bases (as shown below) and we know that this entire length of DNA changes at a rate of approximately one base per 25 million years. That means that the two DNA versions differ by 100 million years of evolution and that their common ancestor lived 50 millio ...
... of DNA found in two species differs by four bases (as shown below) and we know that this entire length of DNA changes at a rate of approximately one base per 25 million years. That means that the two DNA versions differ by 100 million years of evolution and that their common ancestor lived 50 millio ...
Genetica per Scienze Naturali aa 05
... The 16 centromere regions of S. cerevisiae form eight pairs, indicating that an ancestor with eight chromosomes underwent complete doubling. Gene arrangements in Kluyveromyces lactis and four other species agree quantitatively with what would be expected if they diverged from S. cerevisiae before it ...
... The 16 centromere regions of S. cerevisiae form eight pairs, indicating that an ancestor with eight chromosomes underwent complete doubling. Gene arrangements in Kluyveromyces lactis and four other species agree quantitatively with what would be expected if they diverged from S. cerevisiae before it ...
reference-genomes_rchisholm
... coordinate the work at the MOD where they reside. They will also spend some time involved in assessing or annotating human genes when annotating orthologs in their organism • Provide outreach and training to non-reference genomes ...
... coordinate the work at the MOD where they reside. They will also spend some time involved in assessing or annotating human genes when annotating orthologs in their organism • Provide outreach and training to non-reference genomes ...
seminar
... – Lack of introns (but ~20% of real genes lack introns) – Not being the best place in genome an mRNA aligns (be careful not to filter out real paralogs) – Being inserted from another chromosome since dog/human common ancestor (breaking synteny). – High rate of mutation (Ka/Ks ratio). • Robert Baerts ...
... – Lack of introns (but ~20% of real genes lack introns) – Not being the best place in genome an mRNA aligns (be careful not to filter out real paralogs) – Being inserted from another chromosome since dog/human common ancestor (breaking synteny). – High rate of mutation (Ka/Ks ratio). • Robert Baerts ...
doc Genetics 03-22
... of the organism or with the number of genes. – Table of various organisms and genome size (protein-coding genes) and the number of predicted genes. Number of genes and size hard to argue it correlates well with complexity of organism What does correlate is that the larger genomes full of transpo ...
... of the organism or with the number of genes. – Table of various organisms and genome size (protein-coding genes) and the number of predicted genes. Number of genes and size hard to argue it correlates well with complexity of organism What does correlate is that the larger genomes full of transpo ...
Complete genomes comparison based on the taxonomic
... collection of > 100,000 predicted coding sequences. Examining the differences between protein sequences of various organisms gives insight into the origin of genes and the relationship between species. A new tool for the comparison of microbial genomes, called TaxPlot, provides a genome-wide approac ...
... collection of > 100,000 predicted coding sequences. Examining the differences between protein sequences of various organisms gives insight into the origin of genes and the relationship between species. A new tool for the comparison of microbial genomes, called TaxPlot, provides a genome-wide approac ...
Analysis of Differential Gene Expression in a Myotonic Dystrophy
... Visualization of differential gene expression log10 (FPKM + 1) of genes at each dosage that are associated the p53 network. FPKM: fragments per kilobase of exon model per million mapped fragments ...
... Visualization of differential gene expression log10 (FPKM + 1) of genes at each dosage that are associated the p53 network. FPKM: fragments per kilobase of exon model per million mapped fragments ...
Ancestral reconstruction and investigations of - GdR BIM
... Future work The proposal work is ongoing regarding the design of ancestral reconstruction of chloroplastic genomes: ...
... Future work The proposal work is ongoing regarding the design of ancestral reconstruction of chloroplastic genomes: ...
The debate over precision genome engineering by Dr. David L
... comprised of long strands of molecules called nucleotides that come in four flavors: A, T, G, and C. Traditional genetic engineering approaches involve cutting and pasting these strands to create new sequences. The basic approach involves so-called “restriction enzymes” that are able to recognize sp ...
... comprised of long strands of molecules called nucleotides that come in four flavors: A, T, G, and C. Traditional genetic engineering approaches involve cutting and pasting these strands to create new sequences. The basic approach involves so-called “restriction enzymes” that are able to recognize sp ...
Review of relevant topics prior to “Linkage” lectures
... DNA as it exists in the cell- normally vs. metaphase; w/ respect to chromosomes ...
... DNA as it exists in the cell- normally vs. metaphase; w/ respect to chromosomes ...
Genome evolution

Genome evolution is the process by which a genome changes in structure (sequence) or size over time. The study of genome evolution involves multiple fields such as structural analysis of the genome, the study of genomic parasites, gene and ancient genome duplications, polyploidy, and comparative genomics. Genome evolution is a constantly changing and evolving field due to the steadily growing number of sequenced genomes, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, available to the scientific community and the public at large.