Genetics of Humanness
... Genetic change is random/gradual Genetic change is NOT random and often not gradual rates of epigenetic mutations, such as DNA methylation, are much higher than rates of mutations transmitted genetically and are easily reversed ...
... Genetic change is random/gradual Genetic change is NOT random and often not gradual rates of epigenetic mutations, such as DNA methylation, are much higher than rates of mutations transmitted genetically and are easily reversed ...
The Origins of Variation
... the translocation of genetic material between endosymbionts and their hosts or by bacteriophage vectors e.g., mitochondria - endosymbiotic origin, evidence from cell membranes, gene structure, origin of replication, the fact that mitochondrial rRNAs are more similar to endosymbiotic bacterial (Ricke ...
... the translocation of genetic material between endosymbionts and their hosts or by bacteriophage vectors e.g., mitochondria - endosymbiotic origin, evidence from cell membranes, gene structure, origin of replication, the fact that mitochondrial rRNAs are more similar to endosymbiotic bacterial (Ricke ...
TALK
... amount of DNA which serves no useful function for the cell. Introns, inteins, transposons and pesudogenes are examples of "selfish DNA", which persist because their impact on cellular replication efficiency is too small for selection to act directly. This DNA may be eliminated by chance due to a gen ...
... amount of DNA which serves no useful function for the cell. Introns, inteins, transposons and pesudogenes are examples of "selfish DNA", which persist because their impact on cellular replication efficiency is too small for selection to act directly. This DNA may be eliminated by chance due to a gen ...
Hanada_et_all_cover_ml_shs - Shiu Lab
... gene content perspective, plants are distinct from most other eukaryotes in that they contain a higher proportion of recent duplicate genes. This is due to more frequent genome doubling and tandem duplication. Given that gene duplication provides much of the raw material for functional evolution of ...
... gene content perspective, plants are distinct from most other eukaryotes in that they contain a higher proportion of recent duplicate genes. This is due to more frequent genome doubling and tandem duplication. Given that gene duplication provides much of the raw material for functional evolution of ...
Lecture_4
... • In most cases computer annotation will only be able to predict function - NOT assign function. – The biological function of many genes have not been determined, even in model systems. – As genomic characterization of gene function continues - more and more computer generated annotations will be c ...
... • In most cases computer annotation will only be able to predict function - NOT assign function. – The biological function of many genes have not been determined, even in model systems. – As genomic characterization of gene function continues - more and more computer generated annotations will be c ...
Advances in Genetics - Madison County Schools
... Human genes can be inserted into the cells of cows – The cows will produce the protein for which the gene codes in their milk This has been used to produce the blood clotting protein needed by people with hemophilia Genes have also been inserted into plants to help them survive in cold tempera ...
... Human genes can be inserted into the cells of cows – The cows will produce the protein for which the gene codes in their milk This has been used to produce the blood clotting protein needed by people with hemophilia Genes have also been inserted into plants to help them survive in cold tempera ...
What are 3 major limitations of using the chimpanzee genome for
... This exam consists of four sets of questions relating to the four indicated papers that have appeared in the past few months. Each question is worth 5 points, for a total of 100 points. You should write up to a half page for each answer. ...
... This exam consists of four sets of questions relating to the four indicated papers that have appeared in the past few months. Each question is worth 5 points, for a total of 100 points. You should write up to a half page for each answer. ...
BIOL 433 Plant Genetics Term 1, 2005
... http://www.nature.com/nmeth/journal/v5/n1/full/nmeth1156.html ...
... http://www.nature.com/nmeth/journal/v5/n1/full/nmeth1156.html ...
Group presentations guide 10-4
... of the approximately 3 billion DNA base pairs, or letters, that make up the human genome. With its four-letter language, DNA contains the information needed to build the entire human body. A gene traditionally refers to the unit of DNA that carries the instructions for making a specific protein or s ...
... of the approximately 3 billion DNA base pairs, or letters, that make up the human genome. With its four-letter language, DNA contains the information needed to build the entire human body. A gene traditionally refers to the unit of DNA that carries the instructions for making a specific protein or s ...
Open questions: A logic (or lack thereof) of genome organization COMMENT Open Access
... do these motifs impact on the evolution of the protein and gene sequence within which they are embedded [3]? As nucleosome location is important for gene expression, then does selection act on the DNA level to maintain proper positioning? Does this mean that a single point mutation can be disfavored ...
... do these motifs impact on the evolution of the protein and gene sequence within which they are embedded [3]? As nucleosome location is important for gene expression, then does selection act on the DNA level to maintain proper positioning? Does this mean that a single point mutation can be disfavored ...
Complex Evolutionary Dynamics of Massively Expanded
... Genomic organization of Tetranychus urticae GRs and ENaCs. Genomic distribution of CRs by family or clade: (a) clade A TuGRs, (b) clade B TuGRs, and (c) ENaCs. In each case the distribution of CRs along the genome is shown with lengths of vertical line segments corresponding to counts in a gene clus ...
... Genomic organization of Tetranychus urticae GRs and ENaCs. Genomic distribution of CRs by family or clade: (a) clade A TuGRs, (b) clade B TuGRs, and (c) ENaCs. In each case the distribution of CRs along the genome is shown with lengths of vertical line segments corresponding to counts in a gene clus ...
Jumping Genes - University of South Alabama
... (transcription), and the RNA is copied into DNA by reverse transcriptase and inserted back into the genome. ...
... (transcription), and the RNA is copied into DNA by reverse transcriptase and inserted back into the genome. ...
DNA Replication
... Genome = All of the genetic material (DNA) in a cell. Prokaryotic cell has only one genome located in the nuclear area. Eukaryotic cell has 2 genomes Nuclear genome Mitochondrial genome If not specified, “genome” usually refers to the nuclear genome. ...
... Genome = All of the genetic material (DNA) in a cell. Prokaryotic cell has only one genome located in the nuclear area. Eukaryotic cell has 2 genomes Nuclear genome Mitochondrial genome If not specified, “genome” usually refers to the nuclear genome. ...
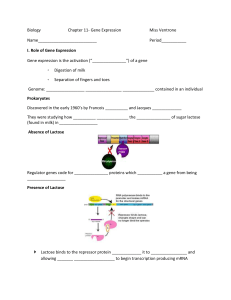
Biology Chapter 11- Gene Expression Miss Ventrone
... Genome: _________________ ________________ ______________ contained in an individual Prokaryotes Discovered in the early 1960’s by Francois __________ and Jacques _____________ They were studying how __________ ______________ the _______________ of sugar lactose (found in milk) in _________________ ...
... Genome: _________________ ________________ ______________ contained in an individual Prokaryotes Discovered in the early 1960’s by Francois __________ and Jacques _____________ They were studying how __________ ______________ the _______________ of sugar lactose (found in milk) in _________________ ...
Short title: create species named Phormidium phage Pf
... The overall genome organization and core genes of this phage are distantly related to the Autographivirinae. The GC content of Pf-WMP3 genome is 46.49%. Based on the results of BLAST searches and modified by visual inspection, 41 potential ORFs were identified on the Pf-WMP3 genome, occupying 89.2% ...
... The overall genome organization and core genes of this phage are distantly related to the Autographivirinae. The GC content of Pf-WMP3 genome is 46.49%. Based on the results of BLAST searches and modified by visual inspection, 41 potential ORFs were identified on the Pf-WMP3 genome, occupying 89.2% ...
Term: SPRING 2000 - Washington University in St. Louis
... focus of the tutorial is to train lower division undergraduates to discover (annotation) and understand gene structure in eukaryotes. Content: Students will be involved in a ‘dry bench’ laboratory where they explore the structure of eukaryotic genomes. Student teams will be assigned ‘chunks’ of DNA ...
... focus of the tutorial is to train lower division undergraduates to discover (annotation) and understand gene structure in eukaryotes. Content: Students will be involved in a ‘dry bench’ laboratory where they explore the structure of eukaryotic genomes. Student teams will be assigned ‘chunks’ of DNA ...
Topic 4 Genetics
... relationship between DNA and the proteins.] DNA is very long, in order to manage it within a cell, it is wound around histones to consolidate it. The term supercoiled, refers to the DNA tightly coiled up prior to mitosis or meiosis. This is when chromosomes are visible. 4.1.2 Define gene, allele, an ...
... relationship between DNA and the proteins.] DNA is very long, in order to manage it within a cell, it is wound around histones to consolidate it. The term supercoiled, refers to the DNA tightly coiled up prior to mitosis or meiosis. This is when chromosomes are visible. 4.1.2 Define gene, allele, an ...
Aim: How do scientists use biotechnology to manipulate genomes?
... 1)Comparing human sequences with those from other species provide evolutionary insight into _____________ ...
... 1)Comparing human sequences with those from other species provide evolutionary insight into _____________ ...
Mutation - WordPress.com
... interspersed nuclear elements) that sweep up DNA and mRNA (then retrotransposed) for insertion into genome ...
... interspersed nuclear elements) that sweep up DNA and mRNA (then retrotransposed) for insertion into genome ...
VII. DNA/ GENES/ AND GENETICS • Describe the relationship
... What mechanism do cells use to turn genes on and off? Give examples of emerging biotechnologies. What modern technologies are currently being implemented to determine evolutionary relationships among species? How are viruses used to treat disease? How can over exposure to sunlight cause skin cancer? ...
... What mechanism do cells use to turn genes on and off? Give examples of emerging biotechnologies. What modern technologies are currently being implemented to determine evolutionary relationships among species? How are viruses used to treat disease? How can over exposure to sunlight cause skin cancer? ...
Bioinformatics Needs for the post
... • We are developing models of gene participation in biological processes. Such models are developed from microarray-based gene expressions and background knowledge, e.g. as provided by the socalled Gene Ontology. The GRID Test Bed will be an excellent computational environment for finding molecular ...
... • We are developing models of gene participation in biological processes. Such models are developed from microarray-based gene expressions and background knowledge, e.g. as provided by the socalled Gene Ontology. The GRID Test Bed will be an excellent computational environment for finding molecular ...
Genome evolution

Genome evolution is the process by which a genome changes in structure (sequence) or size over time. The study of genome evolution involves multiple fields such as structural analysis of the genome, the study of genomic parasites, gene and ancient genome duplications, polyploidy, and comparative genomics. Genome evolution is a constantly changing and evolving field due to the steadily growing number of sequenced genomes, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, available to the scientific community and the public at large.