Things to Cover for Exam 1
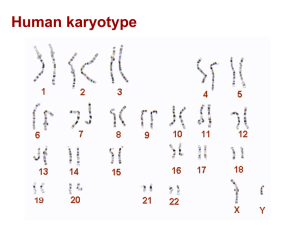
... o **All sexually reproducing living organisms obtain half of their genetic information from each parent. Each parent contributes one of the two homologous chromosomes. What type of cells result from Meiosis? Sex cells or somatic (body) cells? Diploid (2n) cells or haploid (n) cells? Genetically id ...
... o **All sexually reproducing living organisms obtain half of their genetic information from each parent. Each parent contributes one of the two homologous chromosomes. What type of cells result from Meiosis? Sex cells or somatic (body) cells? Diploid (2n) cells or haploid (n) cells? Genetically id ...
Name:
... Goals/uses of transformation & genetic engineering: o significance of plasmids, restriction enzymes & ligase, “sticky ends” GMOs: production, uses, controversy Animal cloning: process, controversy DNA technology o PCR o Electrophoresis: How does it work? What can it be used for? Regulation ...
... Goals/uses of transformation & genetic engineering: o significance of plasmids, restriction enzymes & ligase, “sticky ends” GMOs: production, uses, controversy Animal cloning: process, controversy DNA technology o PCR o Electrophoresis: How does it work? What can it be used for? Regulation ...
Genetic Technology
... Dog breeders wanted to breed a dog that would run fast but also be born with long, shiny fur, looking for the best characteristics from the parents. ...
... Dog breeders wanted to breed a dog that would run fast but also be born with long, shiny fur, looking for the best characteristics from the parents. ...
Biotechnology
... two copies of a mutant gene • This gene is called p53. The mutated version is linked to colon cancer. • How do you think we will go about this? – RFLPs and gel electrophoresis ...
... two copies of a mutant gene • This gene is called p53. The mutated version is linked to colon cancer. • How do you think we will go about this? – RFLPs and gel electrophoresis ...
Molecular Genetics
... - DNA mutations can be positive, negative, or neutral based on the effect or lack of effect they have on the resulting protein and the phenotypes that are conferred by the protein. - Changes in genotype may affect phenotype which, in turn, may affect natural selection and evolution. - Viral reproduc ...
... - DNA mutations can be positive, negative, or neutral based on the effect or lack of effect they have on the resulting protein and the phenotypes that are conferred by the protein. - Changes in genotype may affect phenotype which, in turn, may affect natural selection and evolution. - Viral reproduc ...
DNA Manipulation
... The Human Genome Project has the goals of 1) mapping and sequencing all of the DNA basepairs 2) identify ALL genes within the sequence. ...
... The Human Genome Project has the goals of 1) mapping and sequencing all of the DNA basepairs 2) identify ALL genes within the sequence. ...
Evolutionary forces: in small populations
... Evolutionary mechanisms 1. Mutation: the only source of new genetic information. Mutation: any heritable change in the structure or amount of genetic material. Different levels of mutation DNA: point and frame shift mutations (mistakes made during DNA replication) Arrangements of DNA +/- of single ...
... Evolutionary mechanisms 1. Mutation: the only source of new genetic information. Mutation: any heritable change in the structure or amount of genetic material. Different levels of mutation DNA: point and frame shift mutations (mistakes made during DNA replication) Arrangements of DNA +/- of single ...
Genetically Modified Organisms - Lightweight OCW University of
... • Scientists, working with farmers, have now found ways to unlock the genetic codes of many plants and animals for the sake of improving these organisms. ...
... • Scientists, working with farmers, have now found ways to unlock the genetic codes of many plants and animals for the sake of improving these organisms. ...
TOPIC: Applied Genetics AIM: What methods can be used to
... successfully removed the gene that controls the production of clotting factors and have inserted this gene into the DNA of certain bacteria. These bacteria can now produce clotting factors. This technique is known as (1.) amniocentesis (2.) genetic engineering (3.) differentiation (4.) karyotyping ...
... successfully removed the gene that controls the production of clotting factors and have inserted this gene into the DNA of certain bacteria. These bacteria can now produce clotting factors. This technique is known as (1.) amniocentesis (2.) genetic engineering (3.) differentiation (4.) karyotyping ...
Genetic Engineering
... The bacteria then infects other cells, giving them the gene (bacteria cell is called a transgenic organism) ...
... The bacteria then infects other cells, giving them the gene (bacteria cell is called a transgenic organism) ...
Bio Chp 15.2 Page 1
... 9. Any factor that affects phenotype can change allelic frequencies, thereby disrupting the genetic equilib- ...
... 9. Any factor that affects phenotype can change allelic frequencies, thereby disrupting the genetic equilib- ...
Genetic Engineering
... The bacteria then infects other cells, giving them the gene (bacteria cell is called a transgenic organism) ...
... The bacteria then infects other cells, giving them the gene (bacteria cell is called a transgenic organism) ...
Discovering the genetic material
... which is heat-resistant, could get into the R cells, providing new genetic information. The proteins were denatured int he heat-killed S cells, so proteins could not carry the genetic information. 2., The phage infection experiments (of Hershey and Chase, 1952) DNA virus ...
... which is heat-resistant, could get into the R cells, providing new genetic information. The proteins were denatured int he heat-killed S cells, so proteins could not carry the genetic information. 2., The phage infection experiments (of Hershey and Chase, 1952) DNA virus ...
Biology Vocab Words
... 9. Allele that is expressed when two different alleles are present in an organism's genotype 10. Tendency for genes located close together on the same chromosome to be inherited together 11. Characteristic of having two different alleles that appear at the same locus of sister ...
... 9. Allele that is expressed when two different alleles are present in an organism's genotype 10. Tendency for genes located close together on the same chromosome to be inherited together 11. Characteristic of having two different alleles that appear at the same locus of sister ...
Mutations
... • If a mutation happens in the sex cell the mutation might be passed onto an offspring • If a mutation happens in a body cell, like a skin cell, it will not be passed on • A mutation is harmful if it reduces the organisms chance for survival and reproduction • A mutation is helpful if it improves an ...
... • If a mutation happens in the sex cell the mutation might be passed onto an offspring • If a mutation happens in a body cell, like a skin cell, it will not be passed on • A mutation is harmful if it reduces the organisms chance for survival and reproduction • A mutation is helpful if it improves an ...
Detection of different genes heredity
... Sickle-Cell Disease is a genetic disorder that affects the blood. People with sickle-cell disease produce an abnormal form of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Sickle-shaped red blood cells cannot carry as much oxygen as normal-shaped cells. The allele for the sickle-cell ...
... Sickle-Cell Disease is a genetic disorder that affects the blood. People with sickle-cell disease produce an abnormal form of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Sickle-shaped red blood cells cannot carry as much oxygen as normal-shaped cells. The allele for the sickle-cell ...
Biotechnology and Mutation Quiz key
... 5. ______ Genetic disorders are caused by the insertion, deletion, or alteration of segments of DNA. However, in order for scientists to be able to determine which genes are faulty, they must first know the normal sequences of DNA. In 1990, an international effort began to analyze the human DNA seq ...
... 5. ______ Genetic disorders are caused by the insertion, deletion, or alteration of segments of DNA. However, in order for scientists to be able to determine which genes are faulty, they must first know the normal sequences of DNA. In 1990, an international effort began to analyze the human DNA seq ...
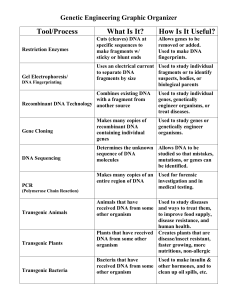
DNA Technology Tools Graphic Organizer KEY
... entire region of DNA investigation and in medical testing. Animals that have Used to study diseases received DNA from some and ways to treat them, other organism to improve food supply, disease resistance, and human health. Plants that have received Creates plants that are DNA from some other diseas ...
... entire region of DNA investigation and in medical testing. Animals that have Used to study diseases received DNA from some and ways to treat them, other organism to improve food supply, disease resistance, and human health. Plants that have received Creates plants that are DNA from some other diseas ...
Genetics Standards
... inherited from generation to generation. A dominant trait is an observable trait of an organism that masks the recessive form of the trait if it is present. A recessive trait of an organism can be masked by the dominant trait. 2 organisms can look alike but have different underlying gene combination ...
... inherited from generation to generation. A dominant trait is an observable trait of an organism that masks the recessive form of the trait if it is present. A recessive trait of an organism can be masked by the dominant trait. 2 organisms can look alike but have different underlying gene combination ...
13 Important Genetic Engineering Pros And Cons Last Updated: Oct
... In literature, there are in fact many synonyms of the term “genetic engineering”: genetic modification, genome manipulation, genetic enhancement, and many more. However, this term shall not be confused with cloning because genetic engineering involves the production of new set of genes while the lat ...
... In literature, there are in fact many synonyms of the term “genetic engineering”: genetic modification, genome manipulation, genetic enhancement, and many more. However, this term shall not be confused with cloning because genetic engineering involves the production of new set of genes while the lat ...
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct manipulation of an organism's genome using biotechnology. It is therefore a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA may be inserted in the host genome by first isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using molecular cloning methods to generate a DNA sequence, or by synthesizing the DNA, and then inserting this construct into the host organism. Genes may be removed, or ""knocked out"", using a nuclease. Gene targeting is a different technique that uses homologous recombination to change an endogenous gene, and can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene, or introduce point mutations.An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be a genetically modified organism (GMO). The first GMOs were bacteria generated in 1973 and GM mice in 1974. Insulin-producing bacteria were commercialized in 1982 and genetically modified food has been sold since 1994. Glofish, the first GMO designed as a pet, was first sold in the United States December in 2003.Genetic engineering techniques have been applied in numerous fields including research, agriculture, industrial biotechnology, and medicine. Enzymes used in laundry detergent and medicines such as insulin and human growth hormone are now manufactured in GM cells, experimental GM cell lines and GM animals such as mice or zebrafish are being used for research purposes, and genetically modified crops have been commercialized.