16-1 Genes and Variation
... allele (T) occurs in a gene pool compared with the number of times other alleles (t) occur. ...
... allele (T) occurs in a gene pool compared with the number of times other alleles (t) occur. ...
Chapter 12 SWBAT`s and Standards
... organism that specify the sequence of amino acids in proteins characteristic of that organism. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. ...
... organism that specify the sequence of amino acids in proteins characteristic of that organism. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. ...
chapter15_Sections 5
... • A gene may be altered and reinserted into an individual of the same species • A gene from one species may be transferred to another to produce an organism that is transgenic ...
... • A gene may be altered and reinserted into an individual of the same species • A gene from one species may be transferred to another to produce an organism that is transgenic ...
Review - Jeopardy PowerPoint
... This process occurs when the cell’s nucleus divides into two new nuclei, each with an exact copy of DNA ...
... This process occurs when the cell’s nucleus divides into two new nuclei, each with an exact copy of DNA ...
Principles_of_Genetic_engineering
... To describe the main stages in genetic engineering Genetic engineering: recombinant DNA technology, – altering the genes in a living organism to produce a Genetically Modified Organism (GMO) with a new genotype. • inserting a foreign gene from one species into another, forming a transgenic organism ...
... To describe the main stages in genetic engineering Genetic engineering: recombinant DNA technology, – altering the genes in a living organism to produce a Genetically Modified Organism (GMO) with a new genotype. • inserting a foreign gene from one species into another, forming a transgenic organism ...
PCR - share1
... genetic engineering Genes can be transferred from one organism to another, and the gene products produced even if the organisms are very different, because of the universality of the genetic code. (Prokaryotes have the same genetic language as do you.) We will discuss some of what can be done, and ...
... genetic engineering Genes can be transferred from one organism to another, and the gene products produced even if the organisms are very different, because of the universality of the genetic code. (Prokaryotes have the same genetic language as do you.) We will discuss some of what can be done, and ...
Chapter 20 PowerPoint
... haploid set of human chromosomes contains approximately 3 billion nucleotide pairs Genbank ...
... haploid set of human chromosomes contains approximately 3 billion nucleotide pairs Genbank ...
Chapter on Biotechnology
... haploid set of human chromosomes contains approximately 3 billion nucleotide pairs Genbank ...
... haploid set of human chromosomes contains approximately 3 billion nucleotide pairs Genbank ...
Chapter 15 Study Guide
... Complete each statement by underlining the correct term or phrase in the brackets. 1. Cohen and Boyer revolutionized genetics by producing recombinant [DNA / RNA]. 2. In Cohen and Boyer’s 1973 experiment, genetically engineered [bacterial / human] cells produced frog rRNA. 3. Moving genes from one o ...
... Complete each statement by underlining the correct term or phrase in the brackets. 1. Cohen and Boyer revolutionized genetics by producing recombinant [DNA / RNA]. 2. In Cohen and Boyer’s 1973 experiment, genetically engineered [bacterial / human] cells produced frog rRNA. 3. Moving genes from one o ...
Increasing Food Supply and Sustainable Agriculture
... • Positive: high yielding, disease resistant “super” plants • Negative: periphery excluded by distance and cost + concerns about safety ...
... • Positive: high yielding, disease resistant “super” plants • Negative: periphery excluded by distance and cost + concerns about safety ...
Presentation
... Queen Victoria was a carrier of hemophilia. She had nine children and passed hemophilia on to several of them. All of her children married into the royal families of various countries of Europe. In this way, all of the Royal Families of Europe inherited the gene for hemophilia. ...
... Queen Victoria was a carrier of hemophilia. She had nine children and passed hemophilia on to several of them. All of her children married into the royal families of various countries of Europe. In this way, all of the Royal Families of Europe inherited the gene for hemophilia. ...
Microbial Universe Part 3
... small form of life microbes include bacteria, fungi, and protozon parasite s. They are too small to se e with the naked eye! ...
... small form of life microbes include bacteria, fungi, and protozon parasite s. They are too small to se e with the naked eye! ...
Evolution Study Guide 1. Define Evolution: Change in species ove
... 1. Define Evolution: Change in species over a long period of time Common Descent: Modern species have evolved from earlier, different species and share a common ancestor. All living things are related. 2. Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection. Define Natural Selection: Organisms with good adaptations ...
... 1. Define Evolution: Change in species over a long period of time Common Descent: Modern species have evolved from earlier, different species and share a common ancestor. All living things are related. 2. Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection. Define Natural Selection: Organisms with good adaptations ...
7th Grade Life Science: Genetics Unit Essential Question: How does
... How does DNA determine traits and how are traits inherited? ...
... How does DNA determine traits and how are traits inherited? ...
MT Jeopardy 2
... classification categories we use, from most diverse to most unique in classifying an organism ...
... classification categories we use, from most diverse to most unique in classifying an organism ...
Key Concepts File - Northwest ISD Moodle
... cells). Eukaryotic multicellular organisms reproduce sexually by combining two gametes containing homologous chromosomes (one set of chromosomes from each parent) during fertilization. Crossing over during meiosis allows for the reshuffling of genetic combinations between individual homologous chrom ...
... cells). Eukaryotic multicellular organisms reproduce sexually by combining two gametes containing homologous chromosomes (one set of chromosomes from each parent) during fertilization. Crossing over during meiosis allows for the reshuffling of genetic combinations between individual homologous chrom ...
Applied Genetics
... • Increasing the frequency of an allele • Cut (cleave) DNA from an organism into fragments and insert into another organism ...
... • Increasing the frequency of an allele • Cut (cleave) DNA from an organism into fragments and insert into another organism ...
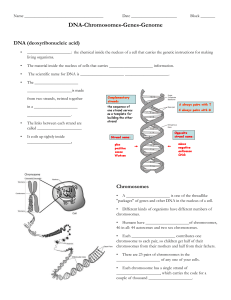
DNA-Chromosomes-Genes-Genome student notesheet
... _____________________ of any one of your cells. • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
... _____________________ of any one of your cells. • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
chapter18-20packet
... 5. a. List the multiple levels of packing in a metaphase chromosome in order of increasing complexity. ...
... 5. a. List the multiple levels of packing in a metaphase chromosome in order of increasing complexity. ...
Lecture 25 - life.illinois.edu
... 1. change in a gene, either in DNA sequence or location b. locus 3. 2. physical appearance of an organism c. allele 5. 3. location of a gene on a chromosome d. mutation 1. 4. genetic make-up of an organism e. genotype 4. 5. alternative state of a gene or trait f. phenotype 2. 6. segment of DNA on a ...
... 1. change in a gene, either in DNA sequence or location b. locus 3. 2. physical appearance of an organism c. allele 5. 3. location of a gene on a chromosome d. mutation 1. 4. genetic make-up of an organism e. genotype 4. 5. alternative state of a gene or trait f. phenotype 2. 6. segment of DNA on a ...
lecture0
... A variety of plasma membrane receptor proteins bind extracellular signaling molecules and transmit signals across the membrane to the cell interior ...
... A variety of plasma membrane receptor proteins bind extracellular signaling molecules and transmit signals across the membrane to the cell interior ...
LE 3
... Plants – naturally resistant to disease GENE MANIPULATION – using genetic engineering to produce better plants and animals (ex) Plants containing genes that make chemicals harmful to insects but are harmless to humans. Organisms like Bacteria that eat oil spills or that make insulin for diabetics. H ...
... Plants – naturally resistant to disease GENE MANIPULATION – using genetic engineering to produce better plants and animals (ex) Plants containing genes that make chemicals harmful to insects but are harmless to humans. Organisms like Bacteria that eat oil spills or that make insulin for diabetics. H ...
Genetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct manipulation of an organism's genome using biotechnology. It is therefore a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA may be inserted in the host genome by first isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using molecular cloning methods to generate a DNA sequence, or by synthesizing the DNA, and then inserting this construct into the host organism. Genes may be removed, or ""knocked out"", using a nuclease. Gene targeting is a different technique that uses homologous recombination to change an endogenous gene, and can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene, or introduce point mutations.An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be a genetically modified organism (GMO). The first GMOs were bacteria generated in 1973 and GM mice in 1974. Insulin-producing bacteria were commercialized in 1982 and genetically modified food has been sold since 1994. Glofish, the first GMO designed as a pet, was first sold in the United States December in 2003.Genetic engineering techniques have been applied in numerous fields including research, agriculture, industrial biotechnology, and medicine. Enzymes used in laundry detergent and medicines such as insulin and human growth hormone are now manufactured in GM cells, experimental GM cell lines and GM animals such as mice or zebrafish are being used for research purposes, and genetically modified crops have been commercialized.